Abstract
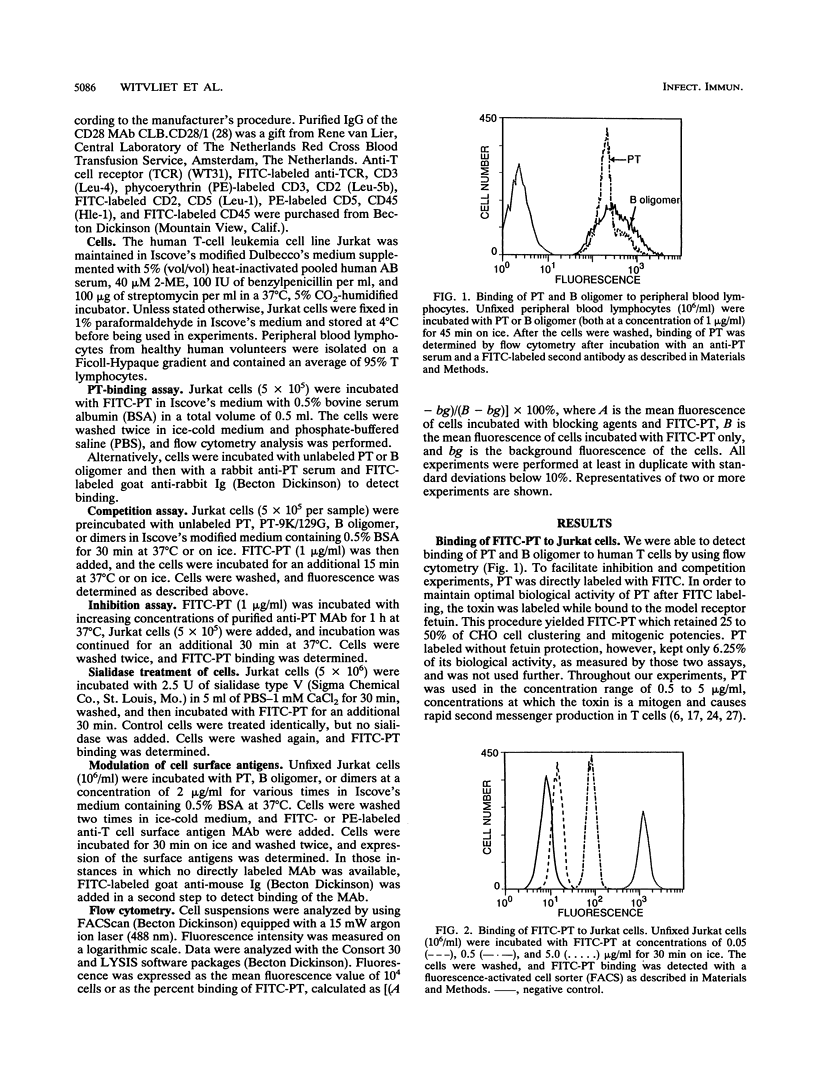
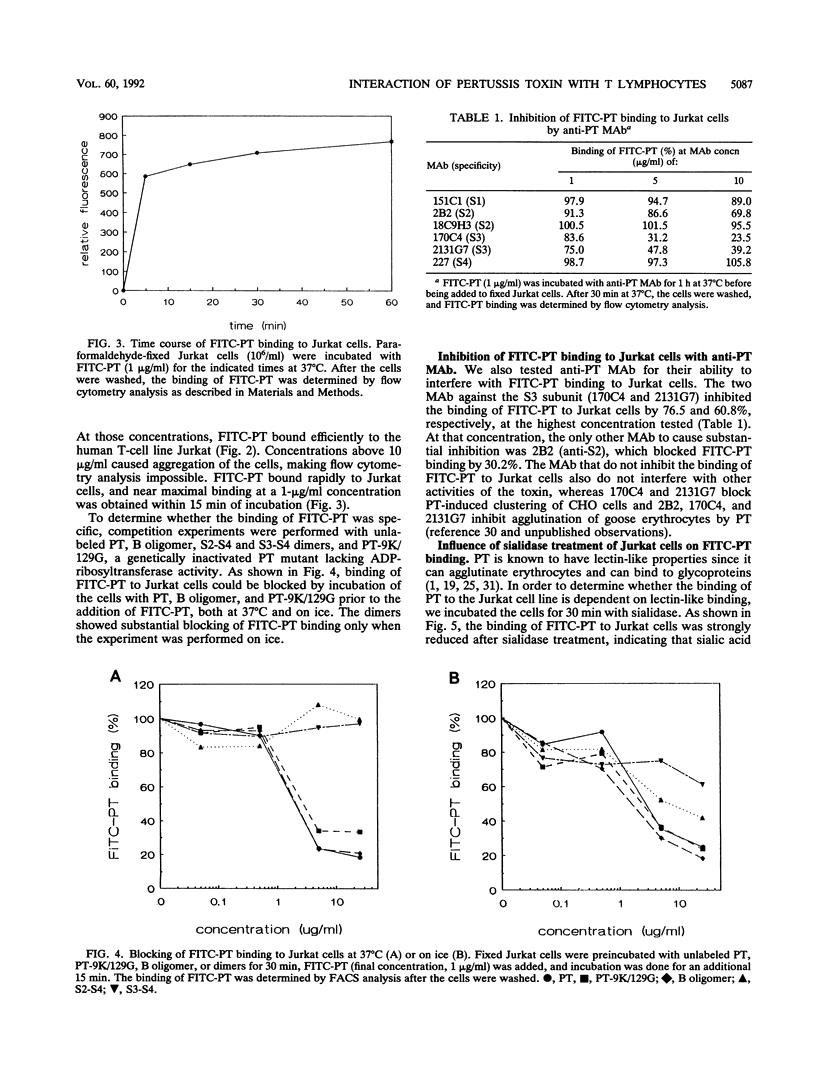
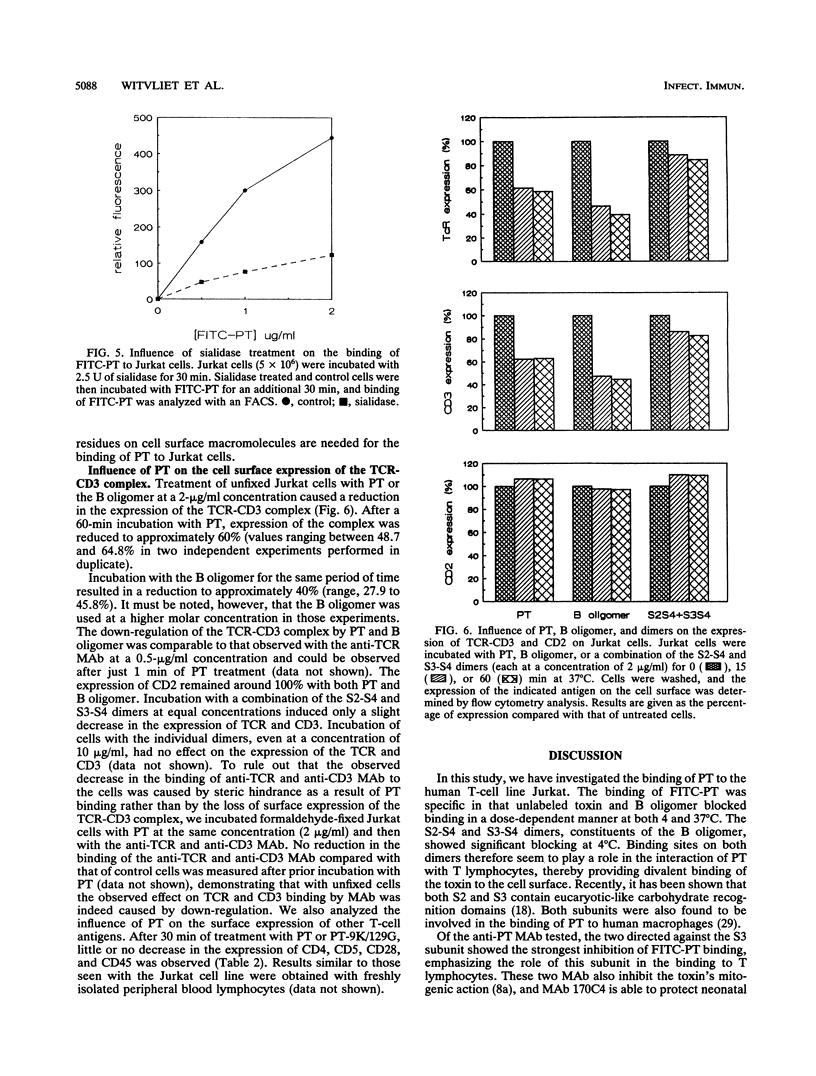
The binding of pertussis toxin (PT) to the human T-cell line Jurkat was examined by using flow cytometry. Fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-labeled PT bound rapidly to the cells in a specific manner as determined by blocking experiments with unlabeled toxin, B oligomer, and the S2-S4 and S3-S4 dimers. Monoclonal antibodies against the S3 subunit of the toxin also significantly inhibited the binding of FITC-PT. Sialidase treatment of the cells resulted in decreased binding of FITC-PT, indicating that sialic acid residues are involved in the binding process. In addition, we studied the effect of PT binding on the expression of cell surface molecules. On binding of PT to the cell surface, a rapid down-regulation of the T-cell receptor (TCR)-CD3 complex was observed. The modulation of the TCR-CD3 complex was independent of the toxin's enzymatic activity, as the B oligomer and a nonenzymatic toxin mutant induced modulation comparable to that caused by the native holotoxin. Isolated dimers did not cause down-regulation. Stimulation of the TCR-CD3 complex, leading to reduced cell surface expression of this complex, provides a possible explanation for the second messenger production associated with the interaction of PT or B oligomer with T lymphocytes. We therefore conclude that PT activates T cells by divalent binding to the TCR-CD3 complex itself or by binding a structure closely associated with it.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arai H., Sato Y. Separation and characterization of two distinct hemagglutinins contained in purified leukocytosis-promoting factor from Bordetella pertussis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 22;444(3):765–782. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90323-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arciniega J. L., Burns D. L., Garcia-Ortigoza E., Manclark C. R. Immune response to the B oligomer of pertussis toxin. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1132–1136. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1132-1136.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong G. D., Peppler M. S. Maintenance of biological activity of pertussis toxin radioiodinated while bound to fetuin-agarose. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1294–1299. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1294-1299.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark C. G., Armstrong G. D. Lymphocyte receptors for pertussis toxin. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):3840–3846. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.3840-3846.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray L. S., Huber K. S., Gray M. C., Hewlett E. L., Engelhard V. H. Pertussis toxin effects on T lymphocytes are mediated through CD3 and not by pertussis toxin catalyzed modification of a G protein. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 1;142(5):1631–1638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett E. L., Sauer K. T., Myers G. A., Cowell J. L., Guerrant R. L. Induction of a novel morphological response in Chinese hamster ovary cells by pertussis toxin. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1198–1203. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1198-1203.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. I., Barron B. A. Studies on the leukocytosis and lymphocytosis induced by Bordetella pertussis. 3. The distribution of transfused lymphocytes in pertussis-treated and normal mice. J Exp Med. 1970 Oct 1;132(4):663–672. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.4.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nencioni L., Pizza M., Bugnoli M., De Magistris T., Di Tommaso A., Giovannoni F., Manetti R., Marsili I., Matteucci G., Nucci D. Characterization of genetically inactivated pertussis toxin mutants: candidates for a new vaccine against whooping cough. Infect Immun. 1990 May;58(5):1308–1315. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.5.1308-1315.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogimori K., Tamura M., Yajima M., Hashimura N., Ishii S., Ui M. Structure-function relationship of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin: biological activities of hybrid toxins reconstituted from native and methylated subunits. Biochemistry. 1986 Mar 25;25(6):1355–1363. doi: 10.1021/bi00354a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizza M., Covacci A., Bartoloni A., Perugini M., Nencioni L., De Magistris M. T., Villa L., Nucci D., Manetti R., Bugnoli M. Mutants of pertussis toxin suitable for vaccine development. Science. 1989 Oct 27;246(4929):497–500. doi: 10.1126/science.2683073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman J. T., Kuipers B., Vogel M. L., Hamstra H. J., Nagel J. Description of a hybridoma bank towards Bordetella pertussis toxin and surface antigens. Microb Pathog. 1990 Jun;8(6):377–382. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90024-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratcliffe M. J., Coggeshall K. M., Newell M. K., Julius M. H. T cell receptor aggregation, but not dimerization, induces increased cytosolic calcium concentrations and reveals a lack of stable association between CD4 and the T cell receptor. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 15;148(6):1643–1651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers T. S., Corey S. J., Rosoff P. M. Identification of a 43-kilodalton human T lymphocyte membrane protein as a receptor for pertussis toxin. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 15;145(2):678–683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosoff P. M., Walker R., Winberry L. Pertussis toxin triggers rapid second messenger production in human T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 1;139(7):2419–2423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saukkonen K., Burnette W. N., Mar V. L., Masure H. R., Tuomanen E. I. Pertussis toxin has eukaryotic-like carbohydrate recognition domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):118–122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekura R. D., Fish F., Manclark C. R., Meade B., Zhang Y. L. Pertussis toxin. Affinity purification of a new ADP-ribosyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14647–14651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahin R. D., Witvliet M. H., Manclark C. R. Mechanism of pertussis toxin B oligomer-mediated protection against Bordetella pertussis respiratory infection. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):4063–4068. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.4063-4068.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommermeyer H., Schwinzer R., Kaever V., Resch K. Cholera toxin-mediated inhibition of signalling in Jurkat cells is followed by, but not due to a loss of T cell receptor complex. Immunobiology. 1991 Jun;182(3-4):266–276. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80662-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommermeyer H., Schwinzer R., Kaever V., Wessel K., Schmidt R. E., Behl B., Wonigeit K., Szamel M., Resch K. Cholera toxin modulates the T cell antigen receptor/CD3 complex but not the CD2 molecule and inhibits signaling via both receptor structures in the human T cell lymphoma Jurkat. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Dec;19(12):2387–2390. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830191232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spangrude G. J., Braaten B. A., Daynes R. A. Molecular mechanisms of lymphocyte extravasation. I. Studies of two selective inhibitors of lymphocyte recirculation. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):354–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strnad C. F., Carchman R. A. Human T lymphocyte mitogenesis in response to the B oligomer of pertussis toxin is associated with an early elevation in cytosolic calcium concentrations. FEBS Lett. 1987 Dec 10;225(1-2):16–20. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81123-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura M., Nogimori K., Murai S., Yajima M., Ito K., Katada T., Ui M., Ishii S. Subunit structure of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, in conformity with the A-B model. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5516–5522. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura M., Nogimori K., Yajima M., Ase K., Ui M. A role of the B-oligomer moiety of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, in development of the biological effects on intact cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6756–6761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thom R. E., Casnellie J. E. Pertussis toxin activates protein kinase C and a tyrosine protein kinase in the human T cell line Jurkat. FEBS Lett. 1989 Feb 13;244(1):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81188-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witvliet M. H., Burns D. L., Brennan M. J., Poolman J. T., Manclark C. R. Binding of pertussis toxin to eucaryotic cells and glycoproteins. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3324–3330. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3324-3330.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van't Wout J., Burnette W. N., Mar V. L., Rozdzinski E., Wright S. D., Tuomanen E. I. Role of carbohydrate recognition domains of pertussis toxin in adherence of Bordetella pertussis to human macrophages. Infect Immun. 1992 Aug;60(8):3303–3308. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.8.3303-3308.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



