Abstract
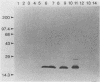
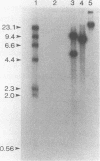
Immunization with Anaplasma marginale outer membranes induced immunity against clinical disease which correlated with antibody titer to outer membrane proteins, including a 19-kDa protein (N. Tebele, T. C. McGuire, and G. H. Palmer, Infect. Immun. 59:3199-3204, 1991). This 19-kDa protein, designated major surface protein 5 (MSP-5), was encoded by a single-copy 633-bp gene. The molecular mass of MSP-5, defined in immunoblots by binding to monoclonal antibody ANAF16C1, was conserved among all recognized species of Anaplasma: A. marginale, A. centrale, and A. ovis. Recombinant MSP-5, which absorbed the antibody reactivity of bovine immune serum to native MSP-5, was recognized by anti-A. marginale and anti-A. centrale immune sera in a competitive inhibition assay with monoclonal antibody ANAF16C1. The presence of antibody to the epitope defined by monoclonal antibody ANAF16C1 in all postinfection sera tested indicates that this epitope is a potential diagnostic antigen for use in identifying persistently infected cattle.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allred D. R., McGuire T. C., Palmer G. H., Leib S. R., Harkins T. M., McElwain T. F., Barbet A. F. Molecular basis for surface antigen size polymorphisms and conservation of a neutralization-sensitive epitope in Anaplasma marginale. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3220–3224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson B. E., Regnery R. L., Carlone G. M., Tzianabos T., McDade J. E., Fu Z. Y., Bellini W. J. Sequence analysis of the 17-kilodalton-antigen gene from Rickettsia rickettsii. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2385–2390. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2385-2390.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson B. E., Tzianabos T. Comparative sequence analysis of a genus-common rickettsial antigen gene. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):5199–5201. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.5199-5201.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. Use of monoclonal antibody in a blocking ELISA to detect group specific antibodies to bluetongue virus. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Nov 16;74(1):139–149. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90375-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbet A. F., Allred D. R. The msp1 beta multigene family of Anaplasma marginale: nucleotide sequence analysis of an expressed copy. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):971–976. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.971-976.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbet A. F., Palmer G. H., Myler P. J., McGuire T. C. Characterization of an immunoprotective protein complex of Anaplasma marginale by cloning and expression of the gene coding for polypeptide Am105L. Infect Immun. 1987 Oct;55(10):2428–2435. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.10.2428-2435.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carl M., Dobson M. E., Ching W. M., Dasch G. A. Characterization of the gene encoding the protective paracrystalline-surface-layer protein of Rickettsia prowazekii: presence of a truncated identical homolog in Rickettsia typhi. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8237–8241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frorath B., Scanarini M., Netter H. J., Abney C. C., Liedvogel B., Lakomek H. J., Northemann W. Cloning and expression of antigenic epitopes of the human 68-kDa (U1) ribonucleoprotein antigen in Escherichia coli. Biotechniques. 1991 Sep;11(3):364-6, 368-71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearney J. F., Radbruch A., Liesegang B., Rajewsky K. A new mouse myeloma cell line that has lost immunoglobulin expression but permits the construction of antibody-secreting hybrid cell lines. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1548–1550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles D. P., Jr, Perryman L. E., Kappmeyer L. S., Hennager S. G. Detection of equine antibody to Babesia equi merozoite proteins by a monoclonal antibody-based competitive inhibition enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Sep;29(9):2056–2058. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.9.2056-2058.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eucaryotes, and organelles. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):1–45. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.1-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McElwain T. F., Perryman L. E., Davis W. C., McGuire T. C. Antibodies define multiple proteins with epitopes exposed on the surface of live Babesia bigemina merozoites. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2298–2304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire T. C., Davis W. C., Brassfield A. L., McElwain T. F., Palmer G. H. Identification of Anaplasma marginale long-term carrier cattle by detection of serum antibody to isolated MSP-3. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Apr;29(4):788–793. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.4.788-793.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire T. C., Perryman L. E., Davis W. C. Analysis of serum and lymphocyte surface IgM of healthy and immunodeficient horses with monoclonal antibodies. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Jul;44(7):1284–1288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberle S. M., Palmer G. H., Barbet A. F., McGuire T. C. Molecular size variations in an immunoprotective protein complex among isolates of Anaplasma marginale. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1567–1573. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1567-1573.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer G. H., Barbet A. F., Davis W. C., McGuire T. C. Immunization with an isolate-common surface protein protects cattle against anaplasmosis. Science. 1986 Mar 14;231(4743):1299–1302. doi: 10.1126/science.3945825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer G. H., Barbet A. F., Musoke A. J., Katende J. M., Rurangirwa F., Shkap V., Pipano E., Davis W. C., McGuire T. C. Recognition of conserved surface protein epitopes on Anaplasma centrale and Anaplasma marginale isolates from Israel, Kenya and the United States. Int J Parasitol. 1988 Feb;18(1):33–38. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(88)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer G. H., McGuire T. C. Immune serum against Anaplasma marginale initial bodies neutralizes infectivity for cattle. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):1010–1015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer G. H., Oberle S. M., Barbet A. F., Goff W. L., Davis W. C., McGuire T. C. Immunization of cattle with a 36-kilodalton surface protein induces protection against homologous and heterologous Anaplasma marginale challenge. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1526–1531. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1526-1531.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipano E., Krigel Y., Frank M., Markovics A., Mayer E. Frozen Anaplasma centrale vaccine against anaplasmosis in cattle. Br Vet J. 1986 Nov-Dec;142(6):553–556. doi: 10.1016/0007-1935(86)90113-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stover C. K., Marana D. P., Carter J. M., Roe B. A., Mardis E., Oaks E. V. The 56-kilodalton major protein antigen of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi: molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the sta56 gene and precise identification of a strain-specific epitope. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2076–2084. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2076-2084.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swift B. L., Thomas G. M. Bovine anaplasmosis: elimination of the carrier state with injectable long-acting oxytetracycline. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1983 Jul 1;183(1):63–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tebele N., McGuire T. C., Palmer G. H. Induction of protective immunity by using Anaplasma marginale initial body membranes. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3199–3204. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3199-3204.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Gordon J. Immunoblotting and dot immunobinding--current status and outlook. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Sep 4;72(2):313–340. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson M. E. Compilation of published signal sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5145–5164. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]