Abstract
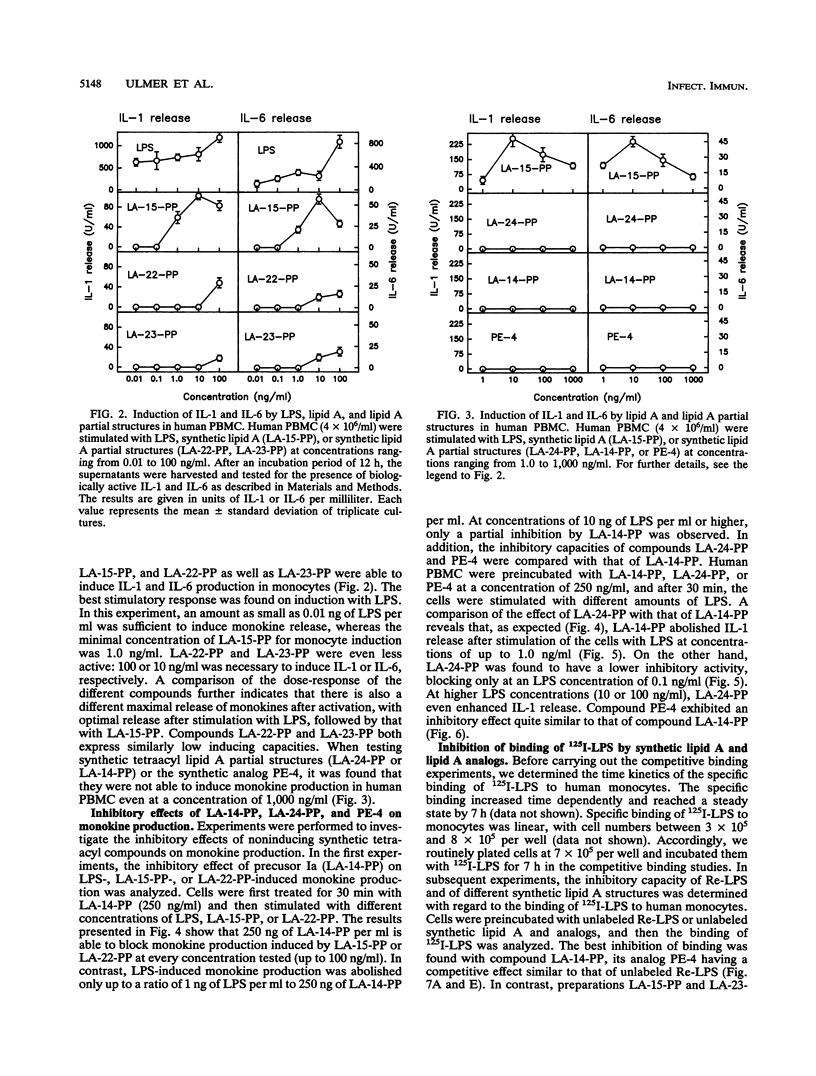
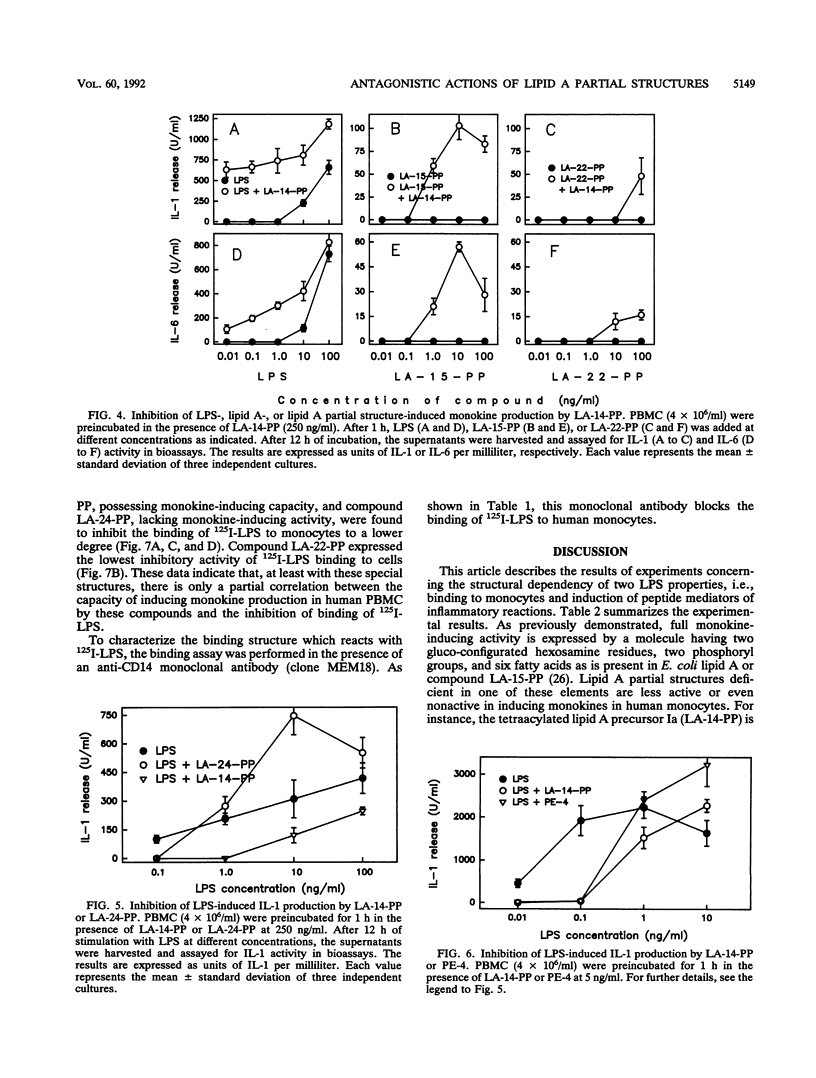
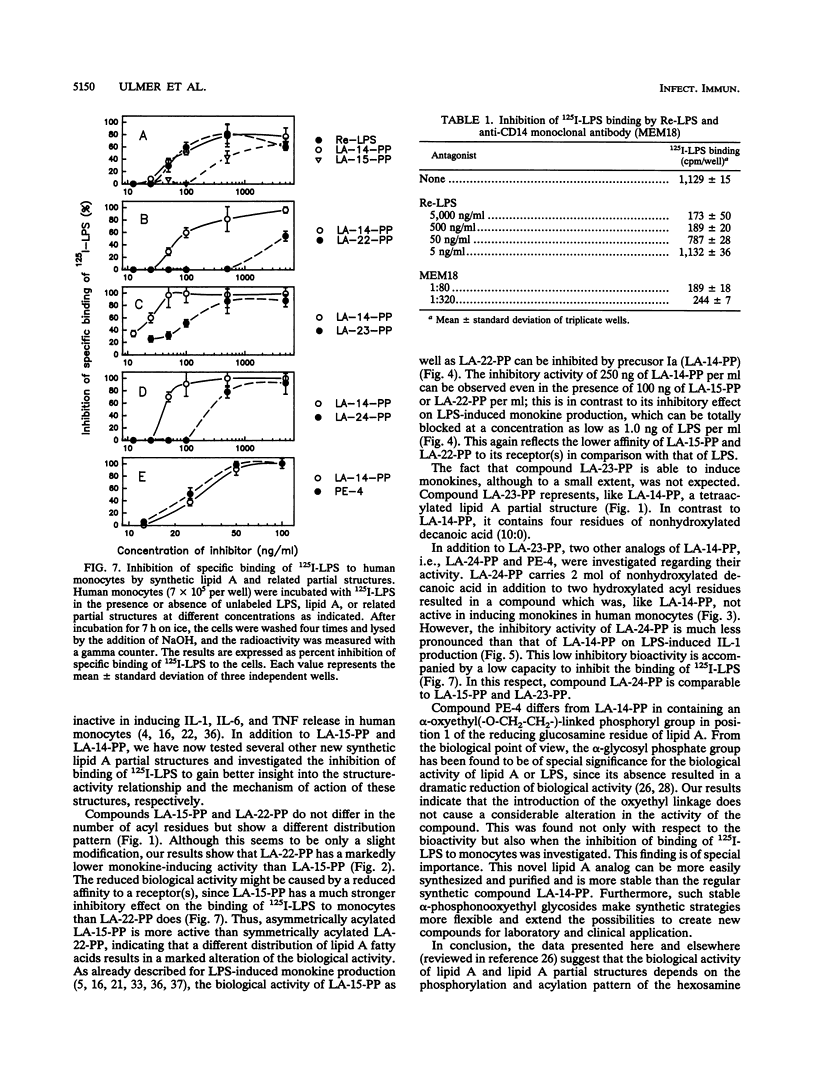
We have previously shown that the synthetic tetraacyl precursor Ia (compound 406, LA-14-PP, or lipid IVa) was not able to induce the production of tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-1, and interleukin-6 in human monocytes but strongly antagonized lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced formation of these monokines. This inhibition was detectable at the level of mRNA production. To achieve a better understanding of molecular basis of this inhibition, we investigated whether lipid A precursor Ia (LA-14-PP), Escherichia coli-type lipid A (LA-15-PP), Chromobacterium violaceum-type lipid A (LA-22-PP), and synthetic lipid A partial structures and analogs (LA-23-PP, LA-24-PP, and PE-4) were able to influence the binding of 125I-LPS to human monocytes and compared this inhibitory activity with the agonistic and antagonistic action in the induction of monokines in human monocytes. 125I-LPS (20 ng per well) was added to human monocytes in the presence or absence of unlabeled rough Re mutant-derived LPS (Re-LPS) or lipid A compounds, and specific LPS binding was determined after 7 h. This binding was found to be dependent on CD14 as shown by the use of an anti-CD14 monoclonal antibody. Compound LA-14-PP was found to inhibit the binding of 125I-LPS to the cells in a similar dose-response to that of unlabeled LPS. This shows that the inhibitory capacity on LPS binding does not correlate with the monokine-inducing capacity because Re-LPS is active in inducing tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-1, and interleukin-6, while LA-14-PP is not. The strong capacity of LA-14-PP to inhibit 125I-LPS binding, however, correlates with the strong inhibitory capacity of this compound on LPS-induced monokine production. Compounds LA-15-PP, LA-23-PP, and LA-24-PP were active in the inhibition of 125I-LPS binding but were 5- to 10-fold weaker than Re-LPS and LA-14-PP. Of all lipid A structures tested, compound LA-22-PP expressed the weakest inhibitory capacity on LPS binding. These compounds showed again that the activity of binding inhibition does not correlate with the monokine-inducing capacity. We assume that the inhibitory effects of lipid A partial structures on LPS-induced monokine production have their origin in a competitive inhibition between LPS and the lipid A partial structures for the same binding site on the cell membrane.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aarden L. A., De Groot E. R., Schaap O. L., Lansdorp P. M. Production of hybridoma growth factor by human monocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Oct;17(10):1411–1416. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brade H., Brade L., Rietschel E. T. Structure-activity relationships of bacterial lipopolysaccharides (endotoxins). Current and future aspects. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1988 Apr;268(2):151–179. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(88)80001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brade L., Brade H., Fischer W. A 28 kDa protein of normal mouse serum binds lipopolysaccharides of gram-negative and lipoteichoic acids of gram-positive bacteria. Microb Pathog. 1990 Nov;9(5):355–362. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90069-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feist W., Ulmer A. J., Musehold J., Brade H., Kusumoto S., Flad H. D. Induction of tumor necrosis factor-alpha release by lipopolysaccharide and defined lipopolysaccharide partial structures. Immunobiology. 1989 Oct;179(4-5):293–307. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(89)80036-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feist W., Ulmer A. J., Wang M. H., Musehold J., Schlüter C., Gerdes J., Herzbeck H., Brade H., Kusumoto S., Diamantstein T. Modulation of lipopolysaccharide-induced production of tumor necrosis factor, interleukin 1, and interleukin 6 by synthetic precursor Ia of lipid A. FEMS Microbiol Immunol. 1992 Jan;4(2):73–89. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1992.tb04973.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O. Electrodialysis of lipopolysaccharides and their conversion to uniform salt forms. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun;54(2):603–610. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04172.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Rietschel E. T., Westphal O., Brade H., Brade L., Freudenberg M., Schade U., Imoto M., Yoshimura H. Synthetic and natural Escherichia coli free lipid A express identical endotoxic activities. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Apr 1;148(1):1–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golenbock D. T., Hampton R. Y., Qureshi N., Takayama K., Raetz C. R. Lipid A-like molecules that antagonize the effects of endotoxins on human monocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19490–19498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirikae T., Kirikae F., Schade F. U., Yoshida M., Kondo S., Hisatsune K., Nishikawa S., Rietschel E. T. Detection of lipopolysaccharide-binding proteins on membranes of murine lymphocyte and macrophage-like cell lines. FEMS Microbiol Immunol. 1991 Nov;3(6):327–336. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1991.tb04257.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovach N. L., Yee E., Munford R. S., Raetz C. R., Harlan J. M. Lipid IVA inhibits synthesis and release of tumor necrosis factor induced by lipopolysaccharide in human whole blood ex vivo. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):77–84. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusama T., Soga T., Ono Y., Kumazawa E., Shioya E., Osada Y., Kusumoto S., Shiba T. Synthesis and biological activities of analogs of a lipid A biosynthetic precursor: 1-O-phosphonooxyethyl-4'-O-phosphono-disaccharides with (R)-3-hydroxytetradecanoyl or tetradecanoyl groups at positions 2, 3, 2' and 3'. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1991 Aug;39(8):1994–1999. doi: 10.1248/cpb.39.1994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusama T., Soga T., Shioya E., Nakayama K., Nakajima H., Osada Y., Ono Y., Kusumoto S., Shiba T. Synthesis and antitumor activity of lipid A analogs having a phosphonooxyethyl group with alpha- or beta-configuration at position 1. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1990 Dec;38(12):3366–3372. doi: 10.1248/cpb.38.3366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesslauer W., Tabuchi H., Gentz R., Brockhaus M., Schlaeger E. J., Grau G., Piguet P. F., Pointaire P., Vassalli P., Loetscher H. Recombinant soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor proteins protect mice from lipopolysaccharide-induced lethality. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Nov;21(11):2883–2886. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830211134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loppnow H., Brade H., Dürrbaum I., Dinarello C. A., Kusumoto S., Rietschel E. T., Flad H. D. IL-1 induction-capacity of defined lipopolysaccharide partial structures. J Immunol. 1989 May 1;142(9):3229–3238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loppnow H., Brade L., Brade H., Rietschel E. T., Kusumoto S., Shiba T., Flad H. D. Induction of human interleukin 1 by bacterial and synthetic lipid A. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Oct;16(10):1263–1267. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830161013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loppnow H., Flad H. D., Dürrbaum I., Musehold J., Fetting R., Ulmer A. J., Herzbeck H., Brandt E. Detection of interleukin 1 with human dermal fibroblasts. Immunobiology. 1989 Jun;179(2-3):283–291. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(89)80023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietschel E. T., Schade U., Jensen M., Wollenweber H. W., Lüderitz O., Greisman S. G. Bacterial endotoxins: chemical structure, biological activity and role in septicaemia. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1982;31:8–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumann R. R., Leong S. R., Flaggs G. W., Gray P. W., Wright S. D., Mathison J. C., Tobias P. S., Ulevitch R. J. Structure and function of lipopolysaccharide binding protein. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1429–1431. doi: 10.1126/science.2402637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütt C., Ringel B., Nausch M., Bazil V., Horejsí V., Neels P., Walzel H., Jonas L., Siegl E., Friemel H. Human monocyte activation induced by an anti-CD14 monoclonal antibody. Immunol Lett. 1988 Dec;19(4):321–327. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(88)90162-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütt C., Schilling T., Grunwald U., Schönfeld W., Krüger C. Endotoxin-neutralizing capacity of soluble CD14. Res Immunol. 1992 Jan;143(1):71–78. doi: 10.1016/0923-2494(92)80082-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama K., Qureshi N., Beutler B., Kirkland T. N. Diphosphoryl lipid A from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides ATCC 17023 blocks induction of cachectin in macrophages by lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1336–1338. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1336-1338.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulevitch R. J. The preparation and characterization of a radioiodinated bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Immunochemistry. 1978 Mar;15(3):157–164. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulmer A. J., Scholz W., Ernst M., Brandt E., Flad H. D. Isolation and subfractionation of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) by density gradient centrifugation on Percoll. Immunobiology. 1984 May;166(3):238–250. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(84)80042-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang M. H., Flad H. D., Feist W., Brade H., Kusumoto S., Rietschel E. T., Ulmer A. J. Inhibition of endotoxin-induced interleukin-6 production by synthetic lipid A partial structures in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4655–4664. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4655-4664.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang M. H., Flad H. D., Feist W., Musehold J., Kusumoto S., Brade H., Gerdes J., Rietschel H. T., Ulmer A. J. Inhibition of endotoxin or lipid A-induced tumor necrosis factor production by synthetic lipid A partial structures in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Lymphokine Cytokine Res. 1992 Feb;11(1):23–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D. Multiple receptors for endotoxin. Curr Opin Immunol. 1991 Feb;3(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(91)90082-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



