Abstract
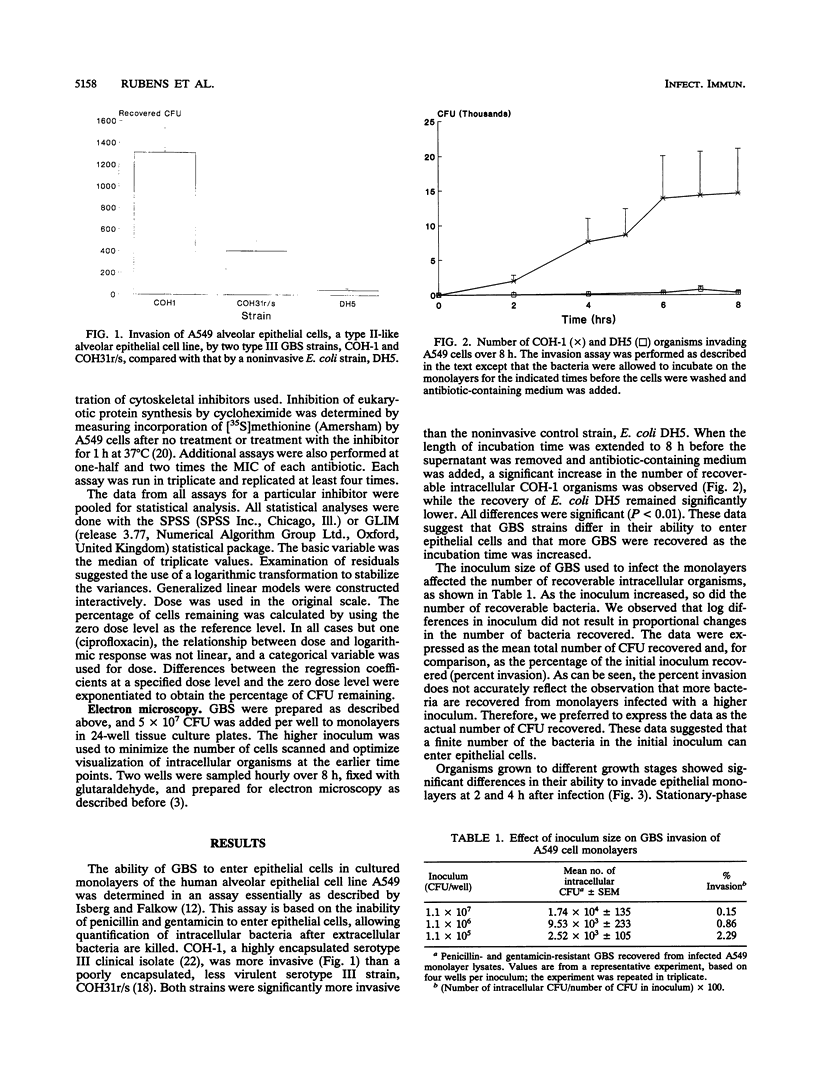
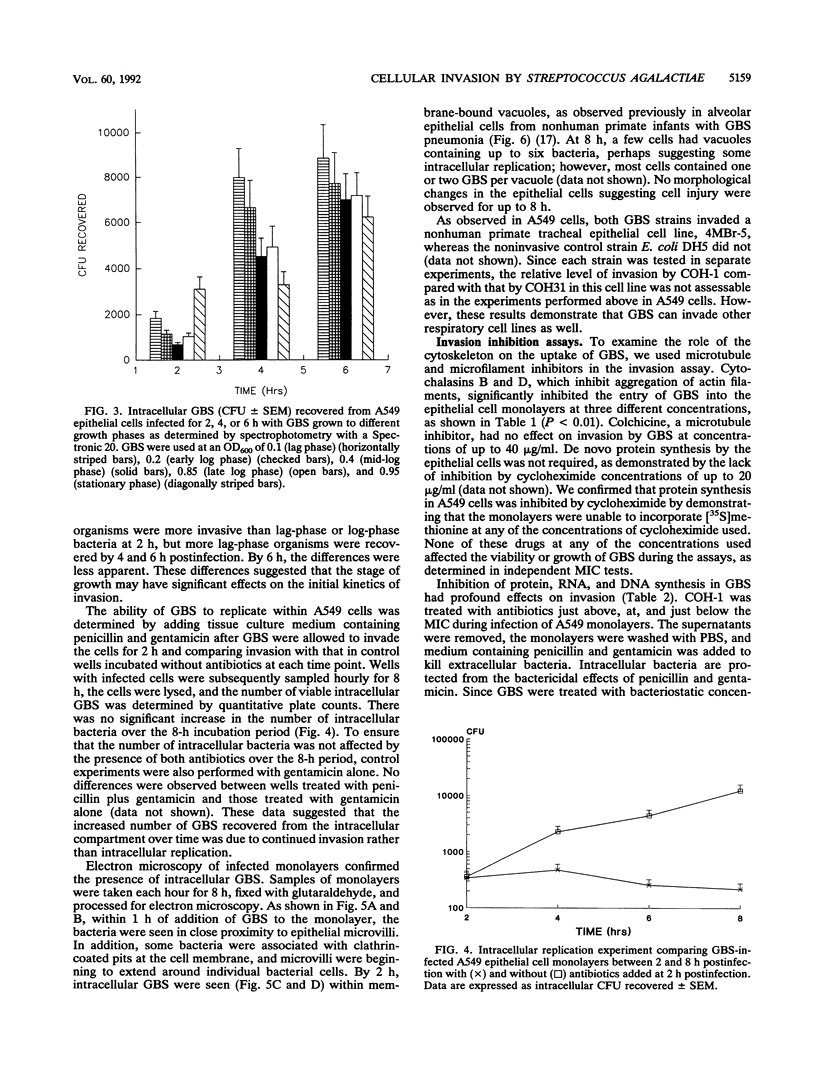
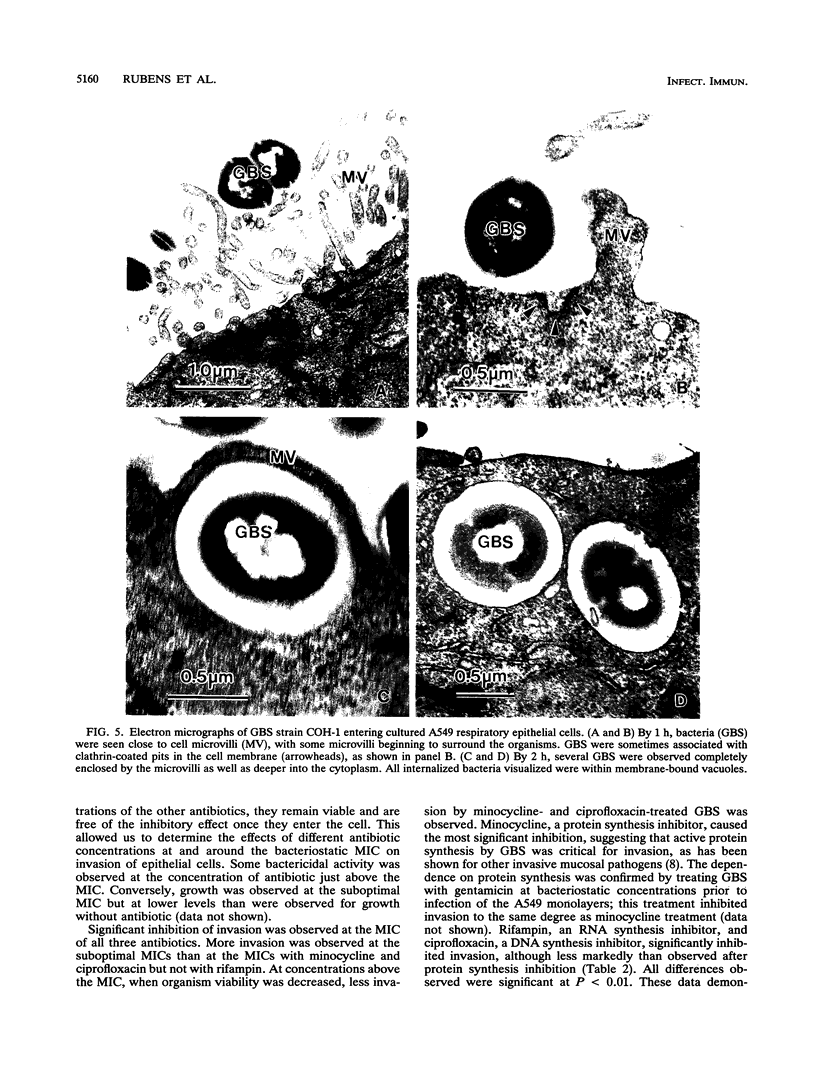
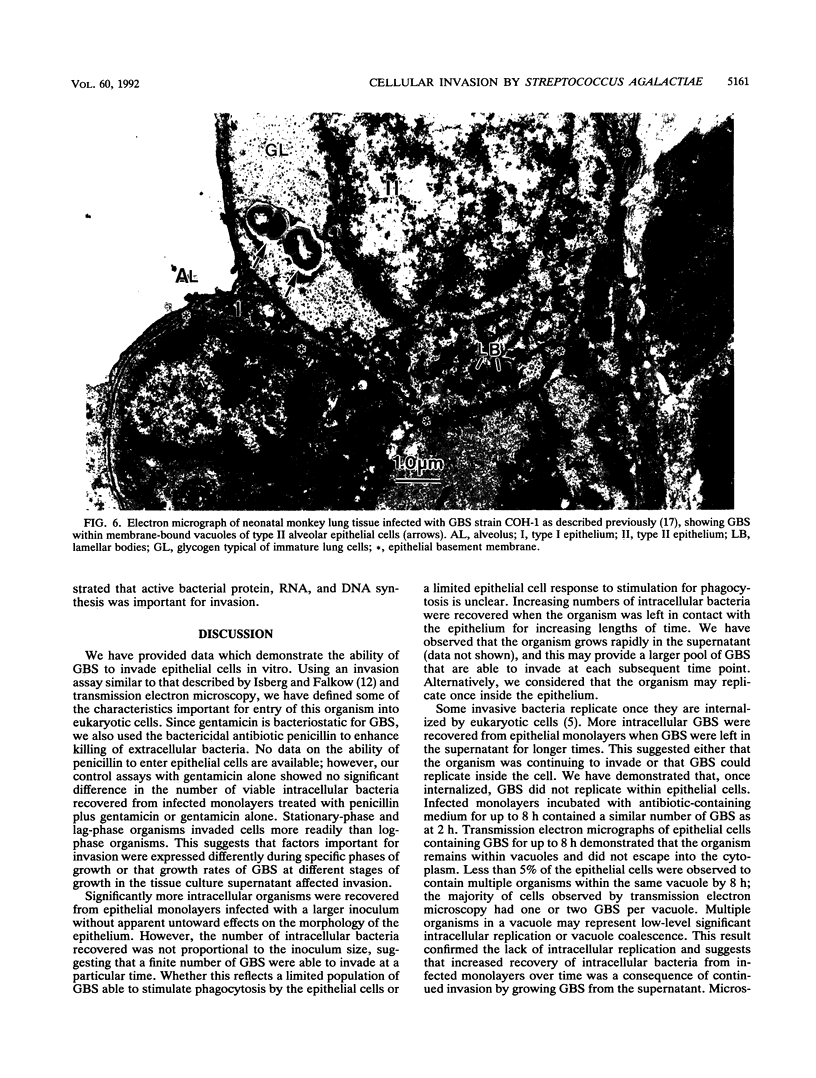
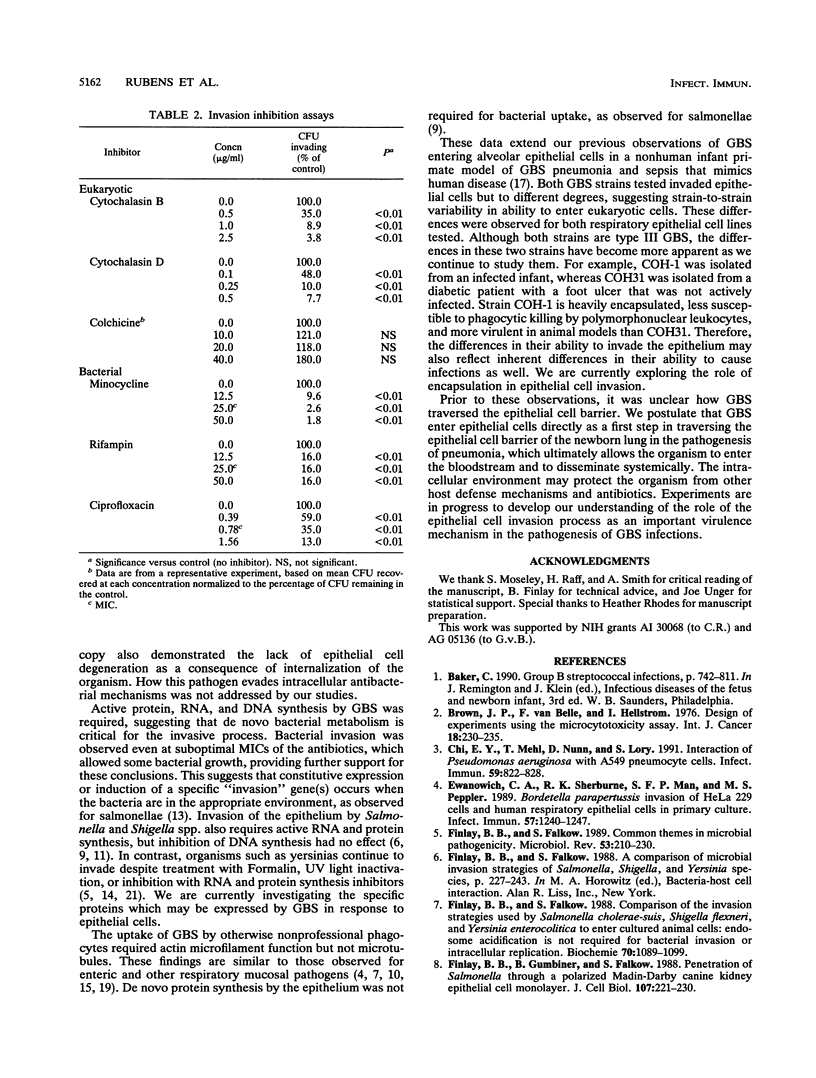
Group B streptococci (GBS) are the most common cause of pneumonia and sepsis during the neonatal period; however, the pathogenesis of this infection is poorly understood. We investigated the ability of GBS to enter epithelial cells in culture. Two strains of GBS were capable of invading immortalized respiratory epithelial cell lines in vitro at different levels, suggesting strain differences in invasiveness. Intracellular replication was not observed. Invasion required actin microfilaments but not microtubular cytoskeletal elements. Active bacterial protein, DNA, and RNA syntheses were required for invasion. These findings are consistent with our previous observation of intracellular GBS in the lungs of infected primates. We hypothesize that this organism may access the bloodstream by direct invasion of the epithelial cell barrier.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown J. P., van Belle G., Hellström I. Design of experiments using the microcytotoxicity assay. Int J Cancer. 1976 Aug 15;18(2):230–235. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910180213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chi E., Mehl T., Nunn D., Lory S. Interaction of Pseudomonas aeruginosa with A549 pneumocyte cells. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):822–828. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.822-828.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewanowich C. A., Sherburne R. K., Man S. F., Peppler M. S. Bordetella parapertussis invasion of HeLa 229 cells and human respiratory epithelial cells in primary culture. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1240–1247. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1240-1247.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Common themes in microbial pathogenicity. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;53(2):210–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.2.210-230.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Comparison of the invasion strategies used by Salmonella cholerae-suis, Shigella flexneri and Yersinia enterocolitica to enter cultured animal cells: endosome acidification is not required for bacterial invasion or intracellular replication. Biochimie. 1988 Aug;70(8):1089–1099. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90271-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Gumbiner B., Falkow S. Penetration of Salmonella through a polarized Madin-Darby canine kidney epithelial cell monolayer. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):221–230. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Heffron F., Falkow S. Epithelial cell surfaces induce Salmonella proteins required for bacterial adherence and invasion. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):940–943. doi: 10.1126/science.2919285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Mounier J., Richard S., Sansonetti P. In vitro model of penetration and intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes in the human enterocyte-like cell line Caco-2. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2822–2829. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2822-2829.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L., Bonventre P. F. Shigella infection of Henle intestinal epithelial cells: role of the bacterium. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):879–886. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.879-886.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Falkow S. A single genetic locus encoded by Yersinia pseudotuberculosis permits invasion of cultured animal cells by Escherichia coli K-12. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):262–264. doi: 10.1038/317262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. A., Falkow S. The ability of Salmonella to enter mammalian cells is affected by bacterial growth state. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4304–4308. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen K. B., Winblad S., Bitsch V. Studies on the interaction between different O-serotypes of Yersinia enterocolitica and HeLa cells. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1979 Apr;87B(2):141–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1979.tb02417.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Jacks P. S., Hinrichs D. J. Role of hemolysin for the intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1459–1471. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubens C. E., McNeill W. F., Farrar W. E., Jr Transposable plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid sequence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa which mediates resistance to gentamicin and four other antimicrobial agents. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):877–882. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.877-882.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubens C. E., Raff H. V., Jackson J. C., Chi E. Y., Bielitzki J. T., Hillier S. L. Pathophysiology and histopathology of group B streptococcal sepsis in Macaca nemestrina primates induced after intraamniotic inoculation: evidence for bacterial cellular invasion. J Infect Dis. 1991 Aug;164(2):320–330. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.2.320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubens C. E., Wessels M. R., Heggen L. M., Kasper D. L. Transposon mutagenesis of type III group B Streptococcus: correlation of capsule expression with virulence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7208–7212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Geme J. W., 3rd, Falkow S. Haemophilus influenzae adheres to and enters cultured human epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):4036–4044. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.4036-4044.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura G. S., Dailey M. O., Gallatin W. M., McGrath M. S., Weissman I. L., Pillemer E. A. Isolation of molecules recognized by monoclonal antibodies and antisera: the solid phase immunoisolation technique. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;136(2):458–464. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90244-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesikari T., Sundqvist C., Mäki M. Adherence and toxicity of Yersinia enterocolitica 0:3 and 0:9 containing virulence-associated plasmids for various cultured cells. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1983 Apr;91(2):121–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1983.tb00020.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. B., Jacobs R. F., Smith A. L. Cellular antibiotic pharmacology. Semin Perinatol. 1982 Apr;6(2):205–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]