Abstract
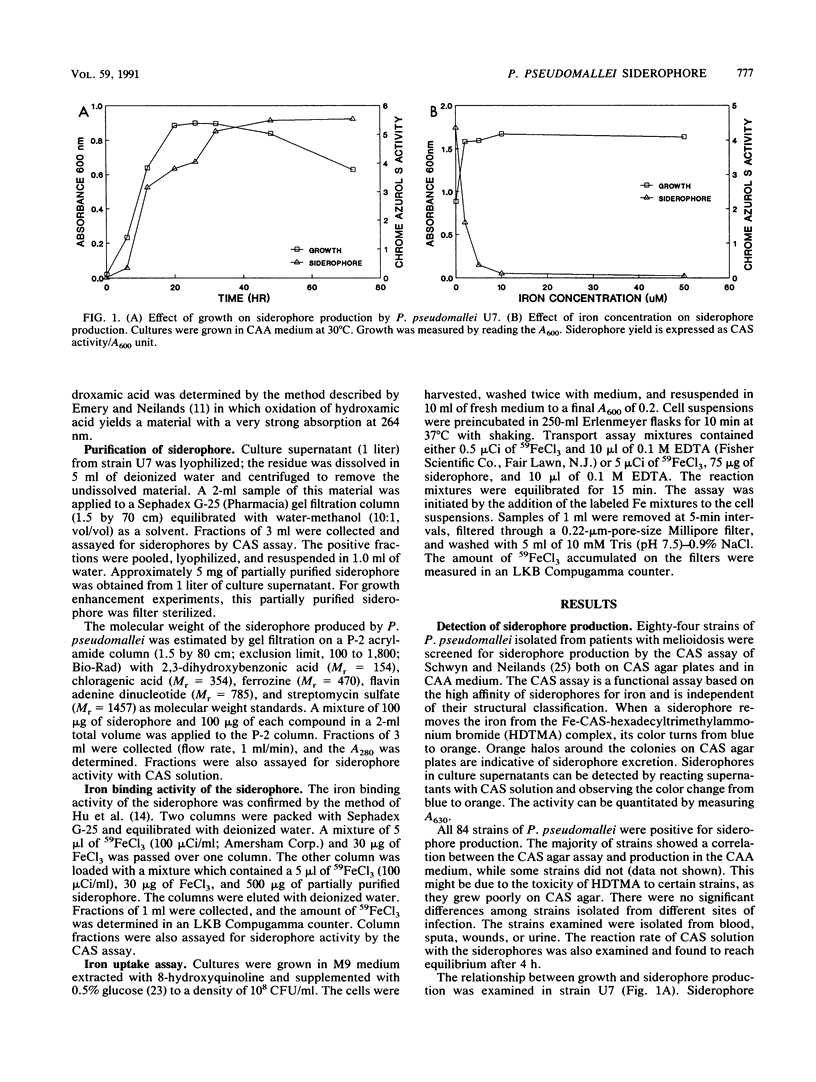
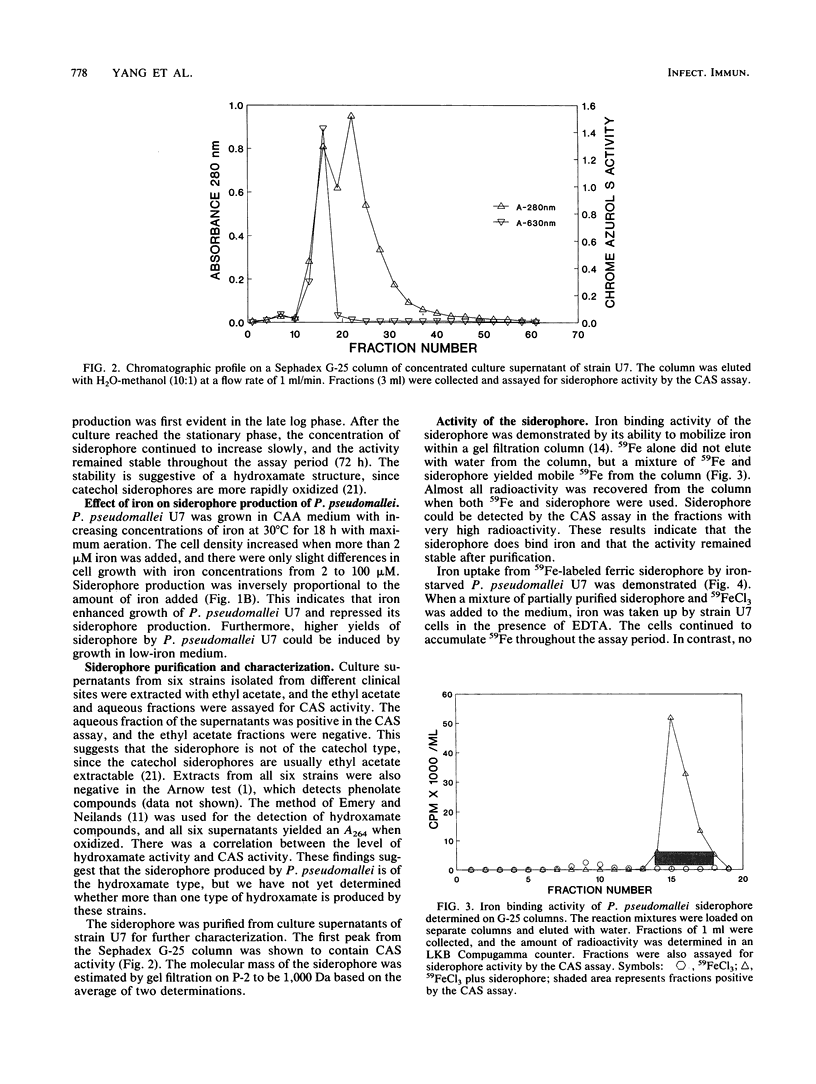
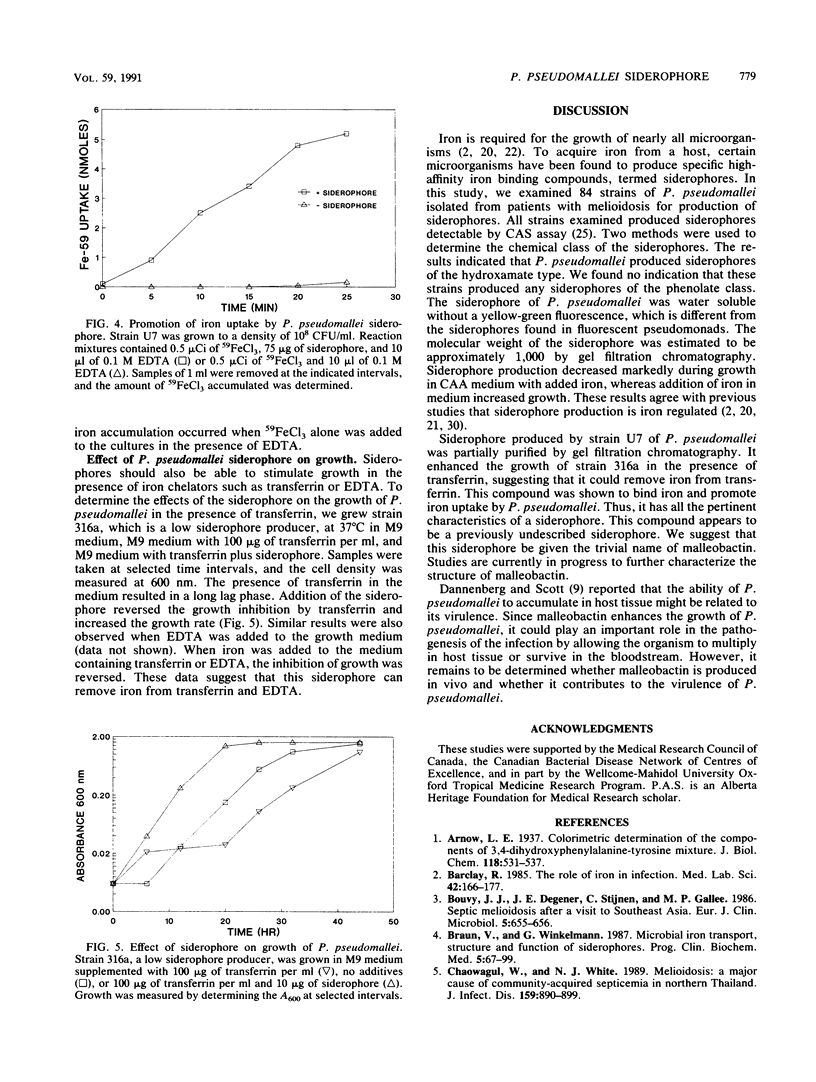
Eighty-four strains of Pseudomonas pseudomallei isolated from patients with melioidosis were examined for siderophore production. All the strains were shown to produce siderophore both on chrome azurol S agar plates and in liquid medium under iron-deficient conditions. Chemical assays indicated that the siderophore belongs to the hydroxamate class. Addition of iron to the culture medium resulted in increased culture growth with markedly decreased yield of siderophore. Siderophore produced by strain U7 was purified by gel filtration chromatography, and the molecular weight was estimated to be 1,000. When this partially purified siderophore was added to culture medium, it promoted iron uptake by P. pseudomallei in the presence of EDTA and enhanced growth of the organism in the presence of transferrin. We have given this siderophore the trivial name malleobactin.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barclay R. The role of iron in infection. Med Lab Sci. 1985 Apr;42(2):166–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvy J. J., Degener J. E., Stijnen C., Gallee M. P., van der Berg B. Septic melioidosis after a visit to Southeast Asia. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Dec;5(6):655–656. doi: 10.1007/BF02013291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLING M., NIGG C., HECKLY R. J. Toxins of Pseudomonas pseudomallei. I. Production in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1958 Oct;76(4):422–426. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.4.422-426.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaowagul W., White N. J., Dance D. A., Wattanagoon Y., Naigowit P., Davis T. M., Looareesuwan S., Pitakwatchara N. Melioidosis: a major cause of community-acquired septicemia in northeastern Thailand. J Infect Dis. 1989 May;159(5):890–899. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.5.890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox C. D. Effect of pyochelin on the virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):17–23. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.17-23.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosa J. H. The relationship of plasmid-mediated iron transport and bacterial virulence. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984;38:69–89. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.38.100184.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANNENBERG A. M., Jr, SCOTT E. M. Melioidosis: pathogenesis and immunity in mice and hamsters. II. Studies with avirulent strains of Malleomyces pseudomallei. Am J Pathol. 1958 Nov-Dec;34(6):1099–1121. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison D. W., Baker H. J., Mariappan M. Melioidosis in Malaysia. I. A method for isolation of Pseudomonas pseudomallei from soil and surface water. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1969 Sep;18(5):694–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HECKLY R. J., NIGG C. Toxins of Pseudomonas pseudomallei. II. Characterization. J Bacteriol. 1958 Oct;76(4):427–436. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.4.427-436.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe C., Sampath A., Spotnitz M. The pseudomallei group: a review. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124(6):598–606. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.6.598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. P., Felice L. J., Sivanandan V., Maheswaran S. K. Siderophore production by Pasteurella multocida. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):804–810. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.804-810.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismail G., Razak N., Mohamed R., Embi N., Omar O. Resistance of Pseudomonas pseudomallei to normal human serum bactericidal action. Microbiol Immunol. 1988;32(7):645–652. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1988.tb01426.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai K., Dejsirilert S. Pseudomonas pseudomallei and melioidosis, with special reference to the status in Thailand. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1988 Aug;41(4):123–157. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.41.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE H. B., LIEN O. G., MAURER R. L. Mortality-enhancing polypeptide constituents from Pseudomonas pseudomallei. J Immunol. 1959 Nov;83:468–477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leelarasamee A., Bovornkitti S. Melioidosis: review and update. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 May-Jun;11(3):413–425. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.3.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilands J. B. Iron absorption and transport in microorganisms. Annu Rev Nutr. 1981;1:27–46. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.01.070181.000331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. M., Finkelstein R. A. The critical role of iron in host-bacterial interactions. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jun;61(6):1428–1440. doi: 10.1172/JCI109062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P., Reeves P. Iron uptake in colicin B-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1052–1062. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1052-1062.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rode J. W., Webling D. D. Melioidosis in the Northern Territory of Australia. Med J Aust. 1981 Feb 21;1(4):181–184. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1981.tb135443.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwyn B., Neilands J. B. Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal Biochem. 1987 Jan;160(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90612-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokol P. A. Production and utilization of pyochelin by clinical isolates of Pseudomonas cepacia. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Mar;23(3):560–562. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.3.560-562.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokol P. A., Woods D. E. Effect of pyochelin on Pseudomonas cepacia respiratory infections. Microb Pathog. 1988 Sep;5(3):197–205. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanphaichitra D. Tropical disease in the immunocompromised host: melioidosis and pythiosis. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Nov-Dec;11 (Suppl 7):S1629–S1643. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_7.s1629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber D. R., Douglass L. E., Brundage W. G., Stallkamp T. C. Acute varieties of melioidosis occurring in U. S. soldiers in Vietnam. Am J Med. 1969 Feb;46(2):234–244. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(69)90008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron and infection. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):45–66. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.45-66.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


