Abstract
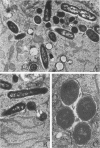
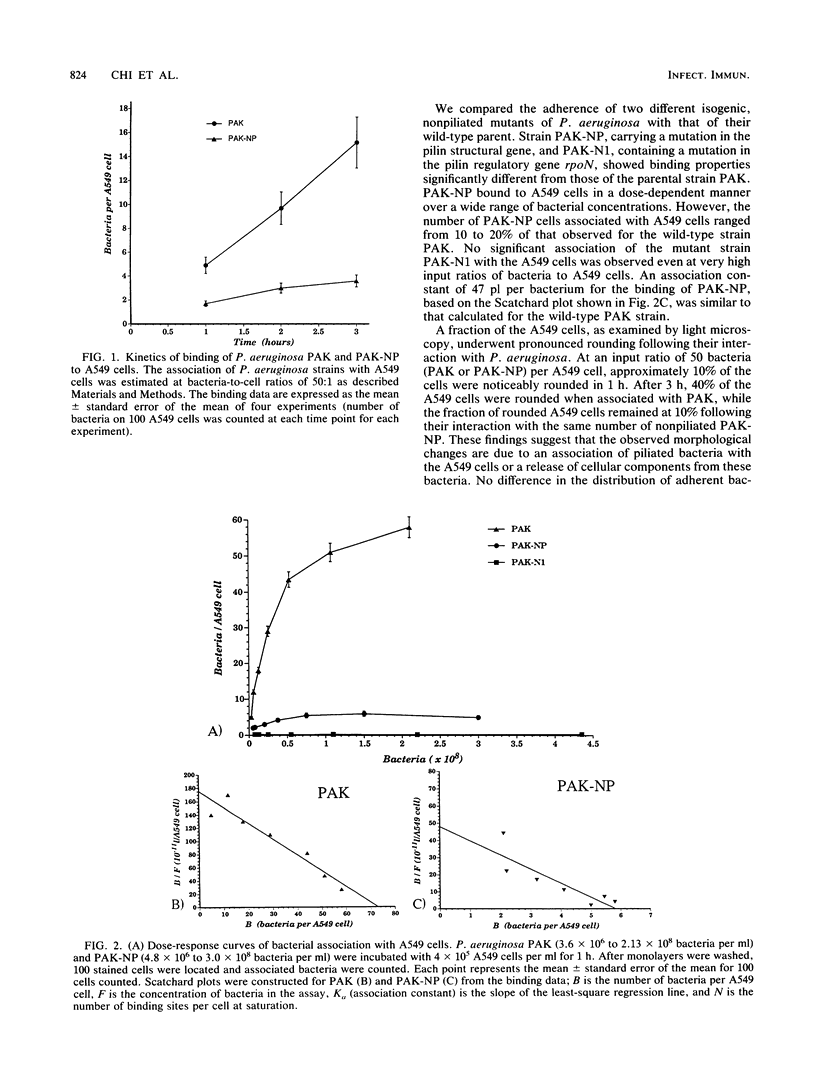
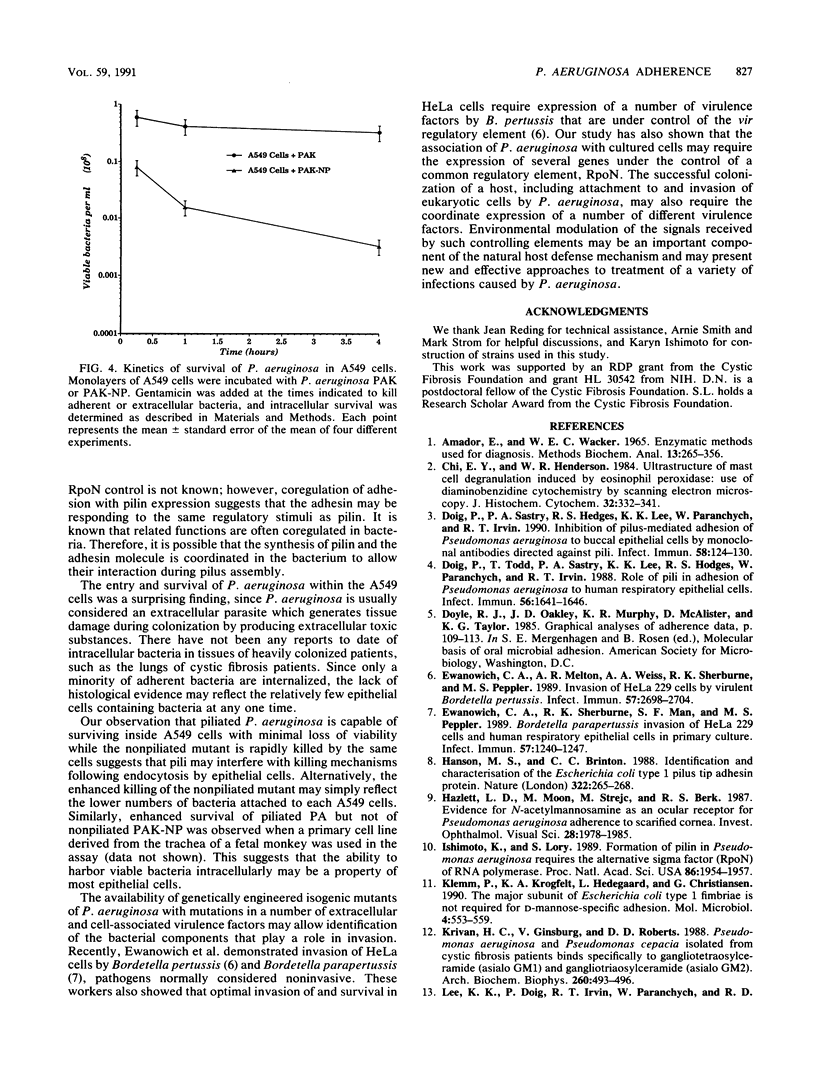
The interaction of Pseudomonas aeruginosa with a human lung pneumocyte cell line (A549) was studied. Wild-type strain PAK adhered efficiently to the A549 cells, while an isogenic mutant, carrying a mutation in the pilin structural gene, adhered at 10 to 20% of the wild-type levels. Another nonpiliated mutant of P. aeruginosa PAK, defective in the pleiotropic regulatory gene rpoN, did not adhere to A549 cells, suggesting the presence of a second, RpoN-controlled adhesin on the bacterial surface. Endocytosis of wild-type P. aeruginosa PAK by A549 cells was also demonstrated. A significant fraction of the internalized bacteria were recovered in a viable form after several hours of residence within the A549 cells. When examined by electron microscopy, intracellular bacteria were located in membranous vesicles, and no evidence of killing by lysosomal mechanisms was observed. These studies raise the possibility that during chronic respiratory tract infections in immunocompromised patients, P. aeruginosa may persist in intracellular compartments and therefore be protected from the defense mechanisms of the host.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amador E., Wacker W. E. Enzymatic methods used for diagnosis. Methods Biochem Anal. 1965;13:265–356. doi: 10.1002/9780470110317.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chi E. Y., Henderson W. R. Ultrastructure of mast cell degranulation induced by eosinophil peroxidase: Use of diaminobenzidine cytochemistry by scanning electron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Mar;32(3):337–341. doi: 10.1177/32.3.6420461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doig P., Sastry P. A., Hodges R. S., Lee K. K., Paranchych W., Irvin R. T. Inhibition of pilus-mediated adhesion of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to human buccal epithelial cells by monoclonal antibodies directed against pili. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):124–130. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.124-130.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doig P., Todd T., Sastry P. A., Lee K. K., Hodges R. S., Paranchych W., Irvin R. T. Role of pili in adhesion of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to human respiratory epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1641–1646. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1641-1646.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewanowich C. A., Melton A. R., Weiss A. A., Sherburne R. K., Peppler M. S. Invasion of HeLa 229 cells by virulent Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2698–2704. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2698-2704.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewanowich C. A., Sherburne R. K., Man S. F., Peppler M. S. Bordetella parapertussis invasion of HeLa 229 cells and human respiratory epithelial cells in primary culture. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1240–1247. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1240-1247.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson M. S., Brinton C. C., Jr Identification and characterization of E. coli type-1 pilus tip adhesion protein. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):265–268. doi: 10.1038/332265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazlett L. D., Moon M. M., Strejc M., Berk R. S. Evidence for N-acetylmannosamine as an ocular receptor for P. aeruginosa adherence to scarified cornea. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1987 Dec;28(12):1978–1985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishimoto K. S., Lory S. Formation of pilin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa requires the alternative sigma factor (RpoN) of RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1954–1957. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemm P., Krogfelt K. A., Hedegaard L., Christiansen G. The major subunit of Escherichia coli type 1 fimbriae is not required for D-mannose-specific adhesion. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Apr;4(4):553–559. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00623.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krivan H. C., Ginsburg V., Roberts D. D. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas cepacia isolated from cystic fibrosis patients bind specifically to gangliotetraosylceramide (asialo GM1) and gangliotriaosylceramide (asialo GM2). Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Jan;260(1):493–496. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90473-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. K., Doig P., Irvin R. T., Paranchych W., Hodges R. S. Mapping the surface regions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAK pilin: the importance of the C-terminal region for adherence to human buccal epithelial cells. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Nov;3(11):1493–1499. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00135.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber M., Smith B., Szakal A., Nelson-Rees W., Todaro G. A continuous tumor-cell line from a human lung carcinoma with properties of type II alveolar epithelial cells. Int J Cancer. 1976 Jan 15;17(1):62–70. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund B., Lindberg F., Marklund B. I., Normark S. The PapG protein is the alpha-D-galactopyranosyl-(1----4)-beta-D-galactopyranose-binding adhesin of uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5898–5902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus H., Austria A., Baker N. R. Adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to tracheal epithelium. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1050–1053. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1050-1053.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paruchuri D. K., Seifert H. S., Ajioka R. S., Karlsson K. A., So M. Identification and characterization of a Neisseria gonorrhoeae gene encoding a glycolipid-binding adhesin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):333–337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B. Pulmonary disease associated with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis: current status of the host-bacterium interaction. J Infect Dis. 1985 Apr;151(4):575–580. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.4.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramphal R., Guay C., Pier G. B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa adhesins for tracheobronchial mucin. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):600–603. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.600-603.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramphal R., Sadoff J. C., Pyle M., Silipigni J. D. Role of pili in the adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to injured tracheal epithelium. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):38–40. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.38-40.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiman L., Ishimoto K., Lory S., Prince A. The effect of piliation and exoproduct expression on the adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to respiratory epithelial monolayers. J Infect Dis. 1990 Mar;161(3):541–548. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.3.541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiman L., Sadoff J., Prince A. Cross-reactivity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa antipilin monoclonal antibodies with heterogeneous strains of P. aeruginosa and Pseudomonas cepacia. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2764–2770. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2764-2770.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Okinaga K. Role of pili in the adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to mouse epidermal cells. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1774–1778. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1774-1778.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlin B. E., Norgren M., Båga M., Normark S. Adhesion to human cells by Escherichia coli lacking the major subunit of a digalactoside-specific pilus-adhesin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1800–1804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Straus D. C., Johanson W. G., Jr, Berry V. K., Bass J. A. Role of pili in adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to mammalian buccal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):1146–1151. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.1146-1151.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]