Abstract
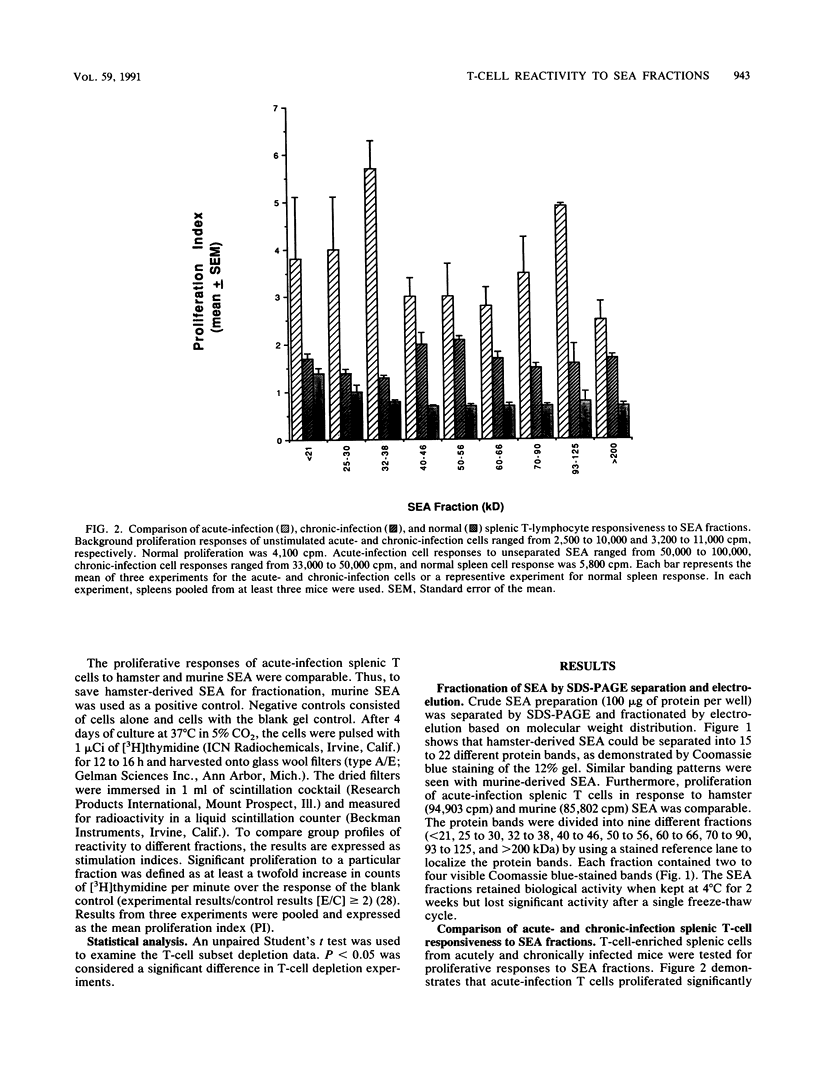
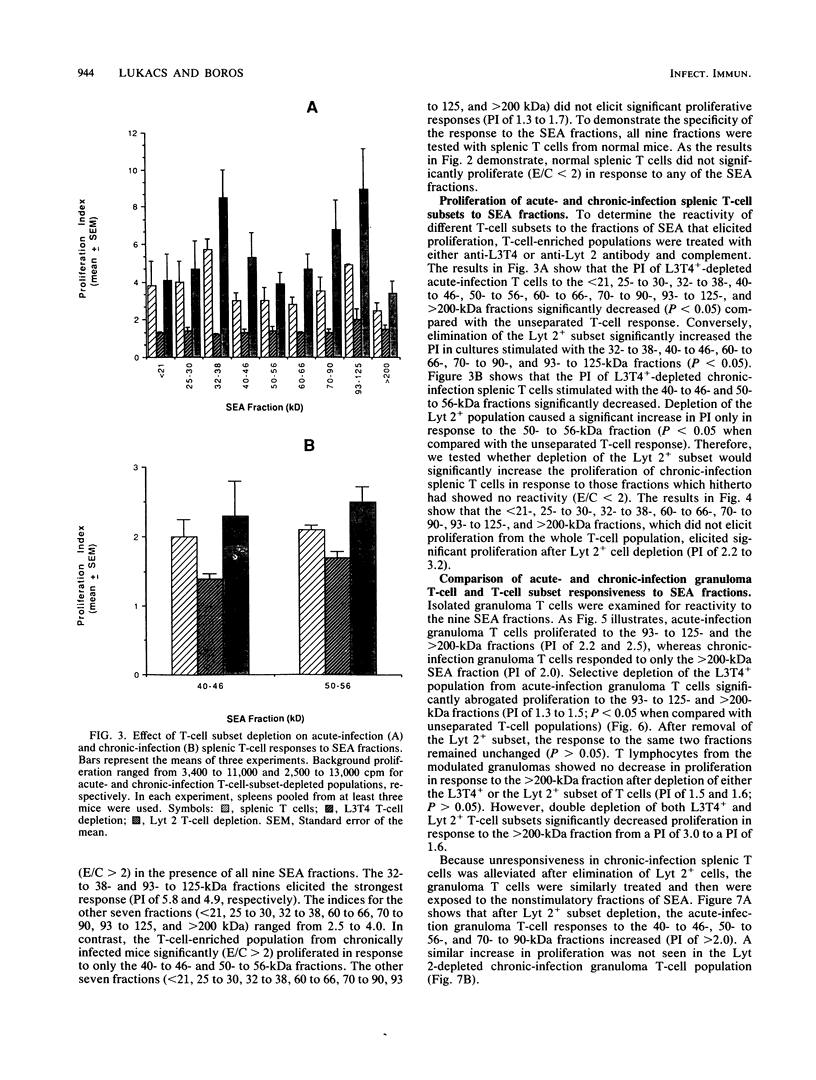
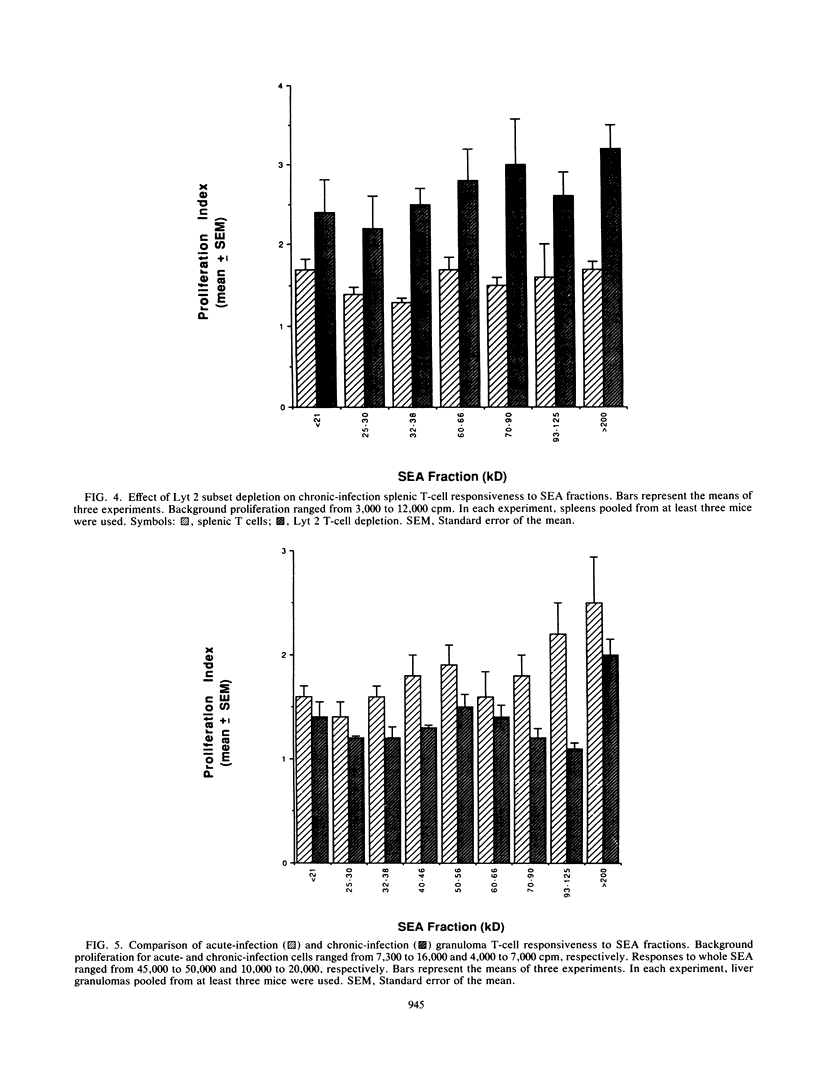
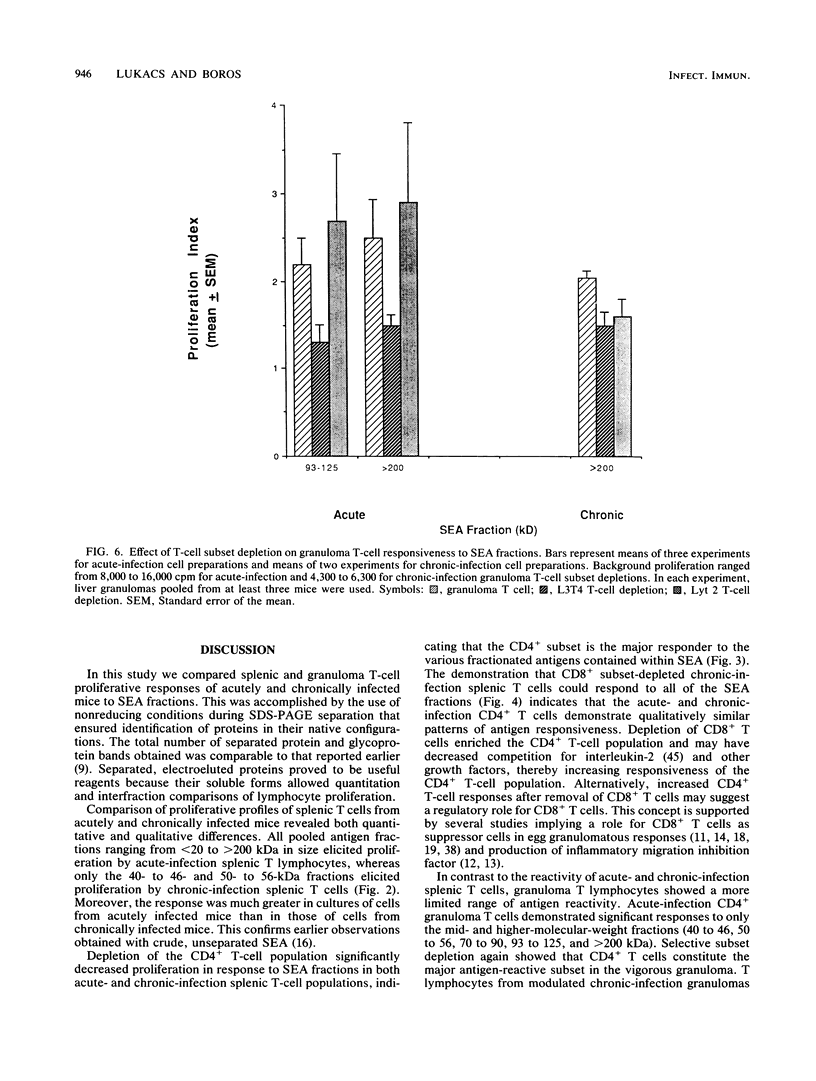
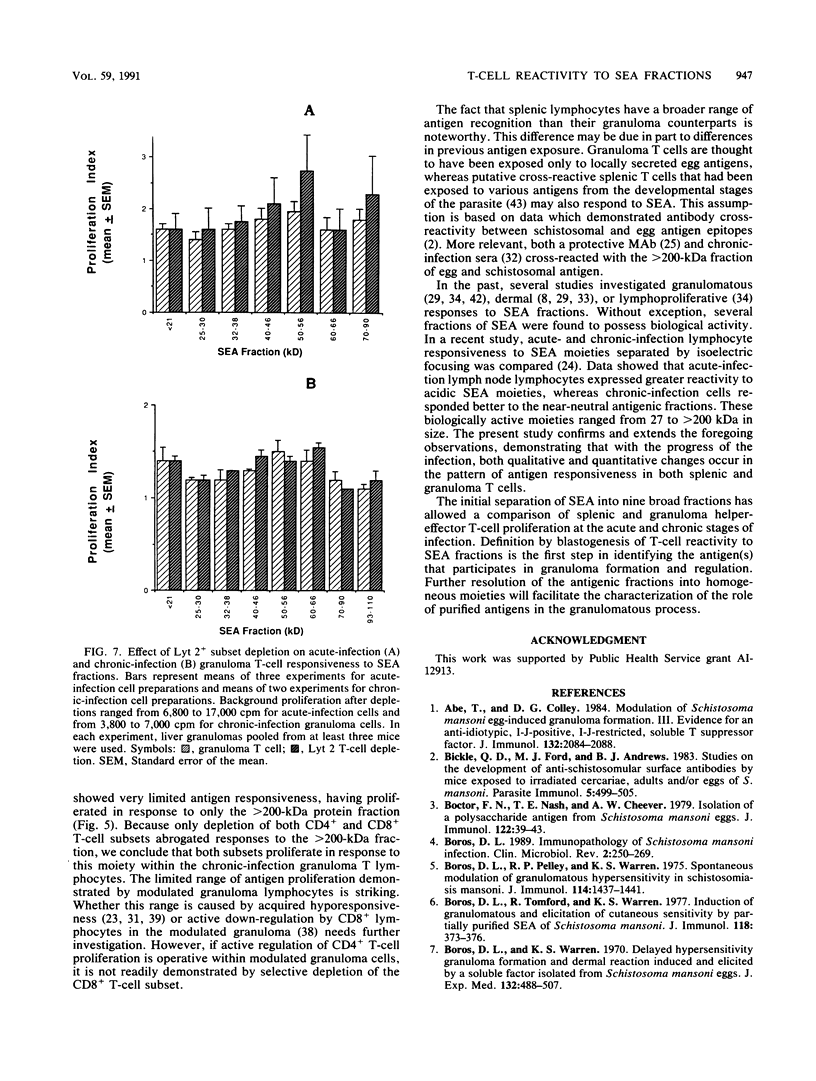
Soluble egg antigens (SEA) secreted by the eggs of Schistosoma mansoni worms induce a T-cell-mediated granulomatous response that is principally responsible for the pathology of the disease. In the present study sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis-separated SEA proteins were divided into nine fractions (less than 21, 25 to 30, 32 to 38, 40 to 46, 50 to 56, 60 to 66, 70 to 90, 93 to 125, and greater than 200 kDa), electroeluted, and utilized in in vitro lymphoproliferation assays. T-cell-enriched spleen cells from acutely infected mice responded to all nine fractions, while those from chronically infected mice responded to only the 50- to 56- and the 60- to 66-kDa fractions. Depletion of the CD4+ T-cell subset among acute and chronic-infection spleen cells abrogated the response. Depletion of the CD8+ T-cell population resulted in increased proliferation in response to fractions by acute-infection T cells and facilitated responsiveness to hitherto-inactive SEA fractions in chronic-infection T cells. Acute-infection CD4+ granuloma T cells responded to the 40- to 46-, 50- to 56-, 70- to 90-, 93- to 125-, and greater than 200-kDa fractions, while the chronic-infection granuloma T cells responded only to the greater than 200-kDa fraction of SEA. Selective depletion of the CD4+ T-cell subset when acute-infection granuloma lymphocytes were tested abrogated proliferation, whereas subset depletions when chronic-infection granuloma cells were tested indicated that both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells respond to the greater than 200-kDa fraction. The present study reveals differences between acute- and chronic-infection splenic and granuloma T cells in the pattern of T-cell blastogenic responses to fractionated SEA.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe T., Colley D. G. Modulation of Schistosoma mansoni egg-induced granuloma formation. III. Evidence for an anti-idiotypic, I-J-positive, I-J-restricted, soluble T suppressor factor. J Immunol. 1984 Apr;132(4):2084–2088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bickle Q. D., Ford M. J., Andrews B. J. Studies on the development of anti-schistosomular surface antibodies by mice exposed to irradiated cercariae, adults and/or eggs of S. mansoni. Parasite Immunol. 1983 Sep;5(5):499–511. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1983.tb00764.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boctor F. N., Nash T. E., Cheever A. W. Isolation of a polysaccharide antigen from Schistosoma mansoni eggs. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):39–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boros D. L. Immunopathology of Schistosoma mansoni infection. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jul;2(3):250–269. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.3.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boros D. L., Pelley R. P., Warren K. S. Spontaneous modulation of granulomatous hypersensitivity in schistosomiasis mansoni. J Immunol. 1975 May;114(5):1437–1441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boros D. L., Tomford R., Warren K. S. Induction of granulomatous and elicitation of cutaneous sensitivity by partially purified SEA of Schistosoma mansoni. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):373–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boros D. L., Warren K. S. Delayed hypersensitivity-type granuloma formation and dermal reaction induced and elicited by a soluble factor isolated from Schistosoma mansoni eggs. J Exp Med. 1970 Sep 1;132(3):488–507. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.3.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. P., Remold H. G., Warren K. S., David J. R. Partial purification of antigens from eggs of Schistosoma mansoni that elicit delayed hypersensitivity. J Immunol. 1977 Oct;119(4):1275–1278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COKER C. M., LICHTENBERG F. A revised method for isolation of Schistosoma mansoni eggs for biological experimentation. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Aug-Sep;92(4):780–782. doi: 10.3181/00379727-92-22612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter C. E., Colley D. G. Partial purification and characterization of Schistosoma mansoni soluble egg antigen with Con A-Sepharose chromatography. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2204–2209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chensue S. W., Boros D. L., David C. S. Regulation of granulomatous inflammation in murine schistosomiasis. II. T suppressor cell-derived, I-C subregion-encoded soluble suppressor factor mediates regulation of lymphokine production. J Exp Med. 1983 Jan 1;157(1):219–230. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.1.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chensue S. W., Boros D. L., David C. S. Regulation of granulomatous inflammation in murine schistosomiasis. In vitro characterization of T lymphocyte subsets involved in the production and suppression of migration inhibition factor. J Exp Med. 1980 Jun 1;151(6):1398–1412. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.6.1398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chensue S. W., Boros D. L. Modulation of granulomatous hypersensitivity. I. Characterization of T lymphocytes involved in the adoptive suppression of granuloma formation in Schistosoma mansoni-infected mice. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1409–1414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chensue S. W., Wellhausen S. R., Boros D. L. Modulation of granulomatous hypersensitivity. II. Participation of Ly 1+ and Ly 2+ T lymphocytes in the suppression of granuloma formation and lymphokine production in Schistosoma mansoni-infected mice. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):363–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colley D. G. Immune responses to a soluble schistosomal egg antigen preparation during chronic primary infection with Schistosoma mansoni. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):150–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colley D. G., Lewis F. A., Todd C. W. Adoptive suppression of granuloma formation by T lymphocytes and by lymphoid cells sensitive to cyclophosphamide. Cell Immunol. 1979 Aug;46(1):192–200. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90258-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doughty B. L., Phillips S. M. Delayed hypersensitivity granuloma formation and modulation around Schistosoma mansoni eggs in vitro. II. Regulatory T cell subsets. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):37–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doughty B. L., Phillips S. M. Delayed hypersensitivity granuloma formation around Schistosoma mansoni eggs in vitro. I. Definition of the model. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):30–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne D. W., Lucas S., Bickle Q., Pearson S., Madgwick L., Bain J., Doenhoff M. J. Identification and partial purification of an antigen (omega 1) from Schistosoma mansoni eggs which is putatively hepatotoxic in T-cell deprived mice. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1981;75(1):54–71. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(81)90013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green W. F., Colley D. G. Modulation of Schistosoma mansoni egg-induced granuloma formation: I-J restriction of T cell-mediated suppression in a chronic parasitic infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1152–1156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
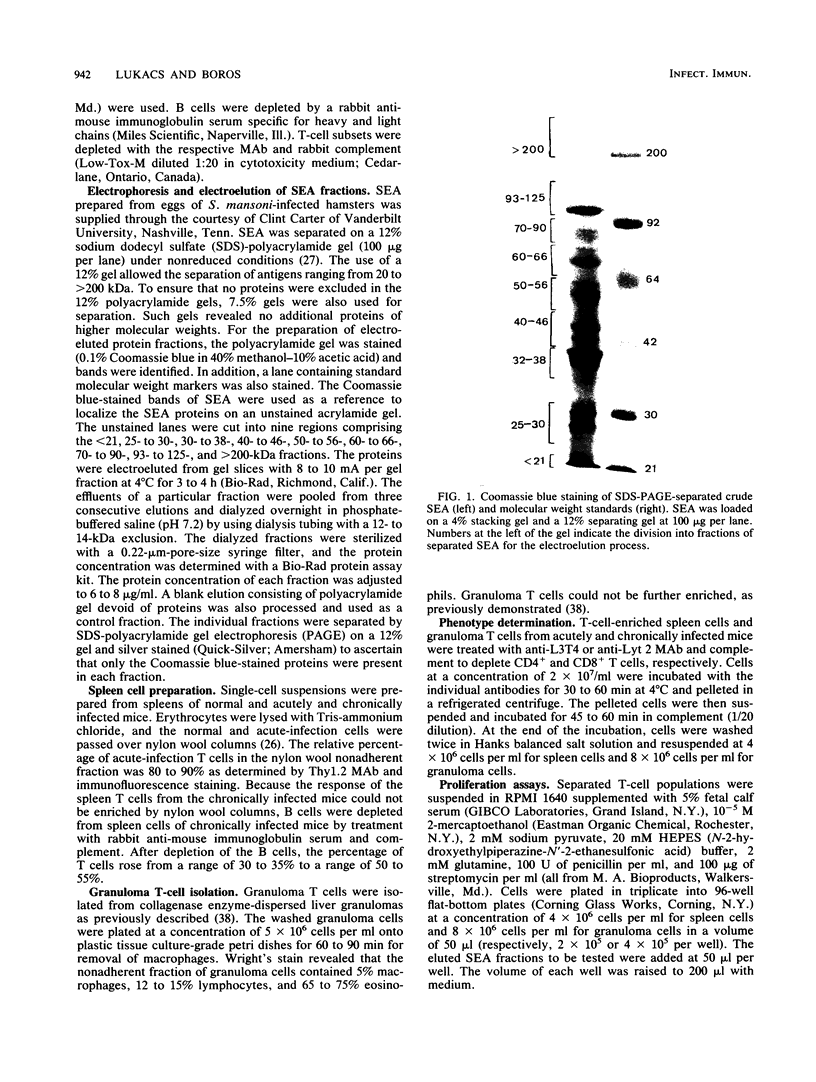
- Hamburger J., Lustigman S., Siongok T. K., Ouma J. H., Mahmoud A. A. Characterization of a purified glycoprotein from Schistosoma mansoni eggs: specificity, stability, and the involvement of carbohydrate and peptide moieties in its serologic activity. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1864–1869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hang L. M., Boros D. L., Warren K. S. Induction of immunological hyporesponsiveness to granulomatous hypersensitivity in Schistosoma mansoni infection. J Infect Dis. 1974 Nov;130(5):515–522. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.5.515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harn D. A., Danko K., Quinn J. J., Stadecker M. J. Schistosoma mansoni: the host immune response to egg antigens. I. Partial characterization of cellular and humoral responses to pI fractions of soluble egg antigens. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 15;142(6):2061–2066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harn D. A., Mitsuyama M., David J. R. Schistosoma mansoni. Anti-egg monoclonal antibodies protect against cercarial challenge in vivo. J Exp Med. 1984 May 1;159(5):1371–1387. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.5.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. P., Stoker N. G., Grant K. A., Handzel Z. T., Hussain R., McAdam K. P., Dockrell H. M. Cellular immune responses of leprosy contacts to fractionated Mycobacterium leprae antigens. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2475–2480. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2475-2480.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustigman S., Mahmoud A. A., Hamburger J. Glycopeptides in soluble egg antigen of Schistosoma mansoni: isolation, characterization, and elucidation of their immunochemical and immunopathological relation to the major egg glycoprotein (MEG). J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1961–1967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew R. C., Boros D. L. Regulation of granulomatous inflammation in murine schistosomiasis. III. Recruitment of antigen-specific I-J+ T suppressor cells of the granulomatous response by I-J+ soluble suppressor factor. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):1093–1099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J. Immunologic tolerance: collaboration between antigen and lymphokines. Science. 1989 Jul 14;245(4914):147–153. doi: 10.1126/science.2526369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omer Ali P., Smithers S. R., Bickle Q., Phillips S. M., Harn D., Simpson A. J. Analysis of the anti-Schistosoma mansoni surface antibody response during murine infection and its potential contribution to protective immunity. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):3273–3279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owhashi M., Horii Y., Imai J., Ishii A., Nawa Y. Purification and physicochemical characterization of Schistosoma mansoni egg allergen recognized by mouse sera obtained at an acute stage of infection. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1986;81(2):129–135. doi: 10.1159/000234121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelley R. P., Pelley R. J., Hamburger J., Peters P. A., Warren K. S. Schistosoma mansoni soluble egg antigens. I. Identification and purification of three major antigens, and the employment of radioimmunoassay for their further characterization. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 Pt 1):1553–1560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin P. J., Phillips S. M. The molecular basis of granuloma formation in schistosomiasis. I. A T cell-derived suppressor effector factor. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1714–1719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin P. J., Prystowsky M. B., Phillips S. M. The molecular basis of granuloma formation in schistosomiasis. II. Analogies of a T cell-derived suppressor effector factor to the T cell receptor. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 1;142(3):985–991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips S. M., Lammie P. J. Immunopathology of granuloma formation and fibrosis in schistosomiasis. Parasitol Today. 1986 Nov;2(11):296–302. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(86)90123-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragheb S., Boros D. L. Characterization of granuloma T lymphocyte function from Schistosoma mansoni-infected mice. J Immunol. 1989 May 1;142(9):3239–3246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sercarz E., Oki A., Gammon G. Central versus peripheral tolerance: clonal inactivation versus suppressor T cells, the second half of the 'Thirty Years War'. Immunol Suppl. 1989;2:9–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. S., Domingo E. O., Cowan R. B. Granuloma formation around schistosome eggs as a manifestation of delayed hypersensitivity. Am J Pathol. 1967 Nov;51(5):735–756. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. S. The secret of the immunopathogenesis of schistosomiasis: in vivo models. Immunol Rev. 1982;61:189–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J. B., Aronstein W. S., Strand M. Schistosoma mansoni: stimulation of artificial granuloma formation in vivo by carbohydrate determinants. Exp Parasitol. 1987 Oct;64(2):228–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(87)90147-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J. B., Magnani J. L., Strand M. Identification of Schistosoma mansoni glycolipids that share immunogenic carbohydrate epitopes with glycoproteins. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 1;136(11):4275–4282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J. B., Strand M. Characterization of developmentally regulated epitopes of Schistosoma mansoni egg glycoprotein antigens. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):1421–1429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita T., Boros D. L. Changing patterns of lymphocyte proliferation, IL-2 production and utilization, and IL-2 receptor expression in mice infected with Schistosoma mansoni. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 15;145(2):724–731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]