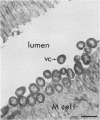
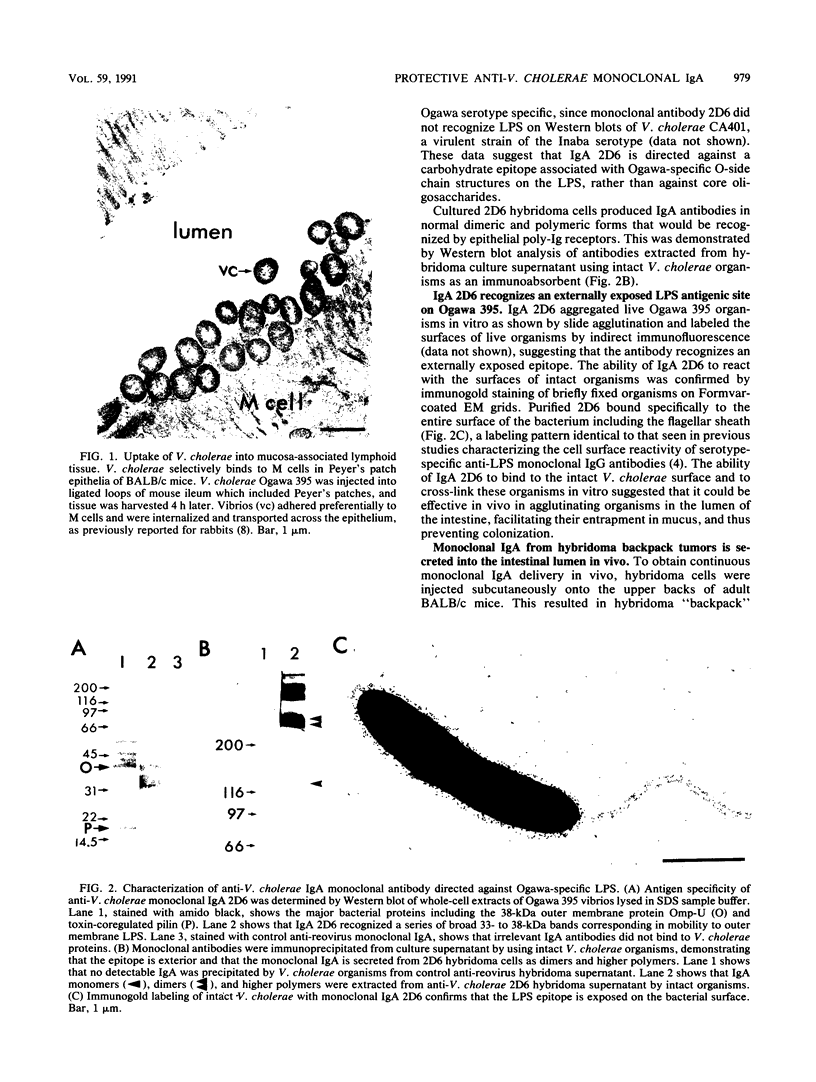
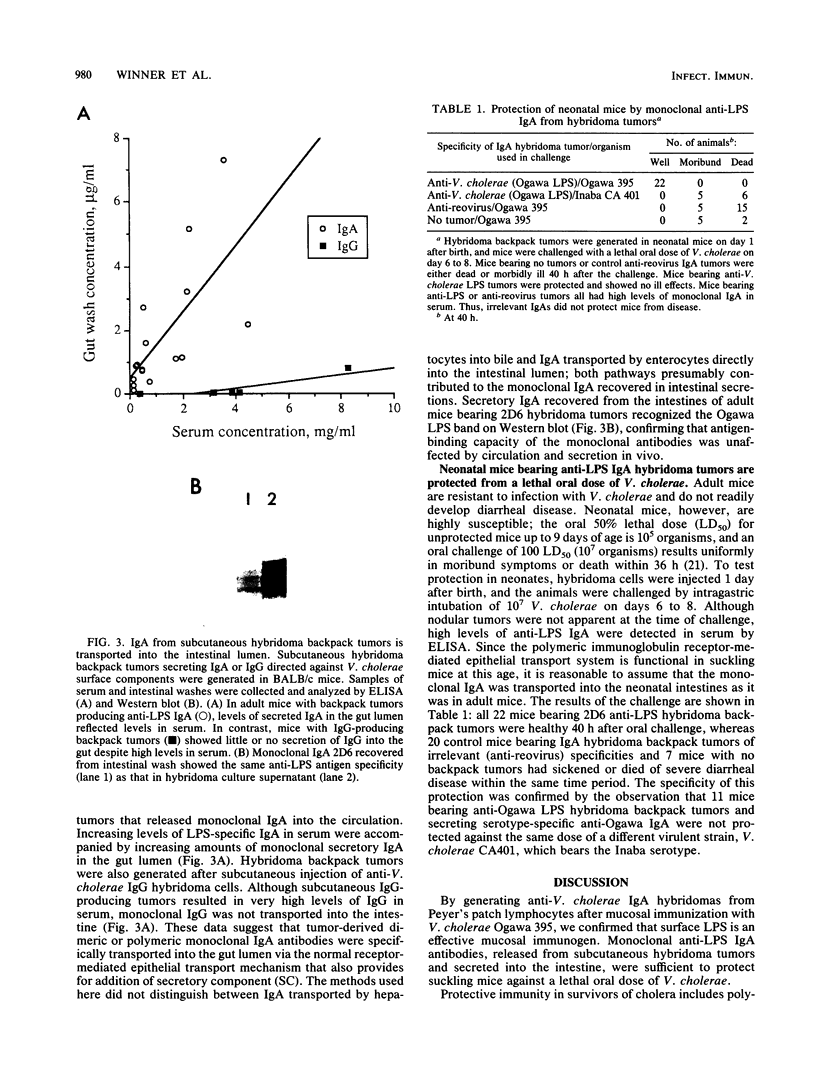
Abstract
Secretory immunoglobulin A (sIgA) plays a role in defense against Vibrio cholerae and other microorganisms that infect mucosal surfaces, but it is not established whether sIgA alone can prevent disease. We report here a strategy for identifying the antigen specificities of monoclonal sIgA antibodies that are capable of providing such protection. IgA hybridomas were generated from Peyer's patch lymphocytes after oral immunization with V. cholerae Ogawa 395. A clone was selected that produced dimeric monoclonal IgA antibodies directed against an Ogawa-specific lipopolysaccharide carbohydrate antigen exposed on the bacterial surface. Hybridoma cells were used to produce subcutaneous "backpack" tumors in syngeneic mice, resulting in secretion of monoclonal sIgA onto mucosal surfaces. Neonatal mice bearing anti-lipopolysaccharide hybridoma backpack tumors were specifically protected against oral challenge with 100 50% lethal doses of virulent Ogawa 395 organisms. Thus, the IgA hybridoma backpack tumor method identifies protective epitopes in the mucosal system and demonstrates that a single monoclonal sIgA can be sufficient to protect against intestinal disease.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold R. R., Brewer M., Gauthier J. J. Bactericidal activity of human lactoferrin: sensitivity of a variety of microorganisms. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):893–898. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.893-898.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. R., Newcomb R. W., Ishizaka K. Proteolytic degradation of exocrine and serum immunoglobulins. J Clin Invest. 1970 Jul;49(7):1374–1380. doi: 10.1172/JCI106354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cash R. A., Music S. I., Libonati J. P., Craig J. P., Pierce N. F., Hornick R. B. Response of man to infection with Vibrio cholerae. II. Protection from illness afforded by previous disease and vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1974 Oct;130(4):325–333. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.4.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst J. A., Perry J. W. Demonstration of lipopolysaccharide on sheathed flagella of Vibrio cholerae O:1 by protein A-gold immunoelectron microscopy. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1488–1494. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1488-1494.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris M. C., Douglas S. D., Kolski G. B., Polin R. A. Functional properties of anti-group B streptococcal monoclonal antibodies. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 Sep;24(3):342–350. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(82)90005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J. Actions of cholera toxin and the prevention and treatment of cholera. Nature. 1981 Jul 30;292(5822):413–417. doi: 10.1038/292413a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jertborn M., Svennerholm A. M., Holmgren J. Saliva, breast milk, and serum antibody responses as indirect measures of intestinal immunity after oral cholera vaccination or natural disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Aug;24(2):203–209. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.2.203-209.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Black R. E., Clements M. L., Cisneros L., Nalin D. R., Young C. R. Duration of infection-derived immunity to cholera. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jun;143(6):818–820. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.6.818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Kaper J. B., Black R. E., Clements M. L. New knowledge on pathogenesis of bacterial enteric infections as applied to vaccine development. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Dec;47(4):510–550. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.4.510-550.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar A. S., Dutta P., Dutta D., Ghose A. C. Antibacterial and antitoxin responses in the serum and milk of cholera patients. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.1-8.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazanec M. B., Nedrud J. G., Lamm M. E. Immunoglobulin A monoclonal antibodies protect against Sendai virus. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2624–2626. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2624-2626.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestecky J. The common mucosal immune system and current strategies for induction of immune responses in external secretions. J Clin Immunol. 1987 Jul;7(4):265–276. doi: 10.1007/BF00915547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Mekalanos J. J., Falkow S. Coordinate regulation and sensory transduction in the control of bacterial virulence. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):916–922. doi: 10.1126/science.2537530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mostov K. E., Kraehenbuhl J. P., Blobel G. Receptor-mediated transcellular transport of immunoglobulin: synthesis of secretory component as multiple and larger transmembrane forms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7257–7261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neutra M. R., Phillips T. L., Mayer E. L., Fishkind D. J. Transport of membrane-bound macromolecules by M cells in follicle-associated epithelium of rabbit Peyer's patch. Cell Tissue Res. 1987 Mar;247(3):537–546. doi: 10.1007/BF00215747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. L., Pierce N. F., Apple R. T., Cray W. C., Jr M cell transport of Vibrio cholerae from the intestinal lumen into Peyer's patches: a mechanism for antigen sampling and for microbial transepithelial migration. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jun;153(6):1108–1118. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.6.1108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm A. M., Jertborn M., Gothefors L., Karim A. M., Sack D. A., Holmgren J. Mucosal antitoxic and antibacterial immunity after cholera disease and after immunization with a combined B subunit-whole cell vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jun;149(6):884–893. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.6.884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagliabue A., Nencioni L., Villa L., Keren D. F., Lowell G. H., Boraschi D. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated antibacterial activity of intestinal lymphocytes with secretory IgA. Nature. 1983 Nov 10;306(5939):184–186. doi: 10.1038/306184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagliabue A., Villa L., Boraschi D., Peri G., de Gori V., Nencioni L. Natural anti-bacterial activity against Salmonella typhi by human T4+ lymphocytes armed with IgA antibodies. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):4178–4182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. K., Miller V. L., Furlong D. B., Mekalanos J. J. Use of phoA gene fusions to identify a pilus colonization factor coordinately regulated with cholera toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2833–2837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenovuo J., Moldoveanu Z., Mestecky J., Pruitt K. M., Rahemtulla B. M. Interaction of specific and innate factors of immunity: IgA enhances the antimicrobial effect of the lactoperoxidase system against Streptococcus mutans. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):726–731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasi T. B., Jr Mechanisms of immune regulation at mucosal surfaces. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5 (Suppl 4):S784–S792. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_4.s784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underdown B. J., Dorrington K. J. Studies on the structural and conformational basis for the relative resistance of serum and secretory immunoglobulin A to proteolysis. J Immunol. 1974 Mar;112(3):949–959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weltzin R., Lucia-Jandris P., Michetti P., Fields B. N., Kraehenbuhl J. P., Neutra M. R. Binding and transepithelial transport of immunoglobulins by intestinal M cells: demonstration using monoclonal IgA antibodies against enteric viral proteins. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1673–1685. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood G. M., Trejdosiewicz L. K., Losowsky M. S. ELISA for measurement of secretory IgA distinct from monomeric IgA. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Mar 12;97(2):269–274. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward M. P., Young W. W., Jr, Bloodgood R. A. Detection of monoclonal antibodies specific for carbohydrate epitopes using periodate oxidation. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Apr 8;78(1):143–153. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90337-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]