Abstract
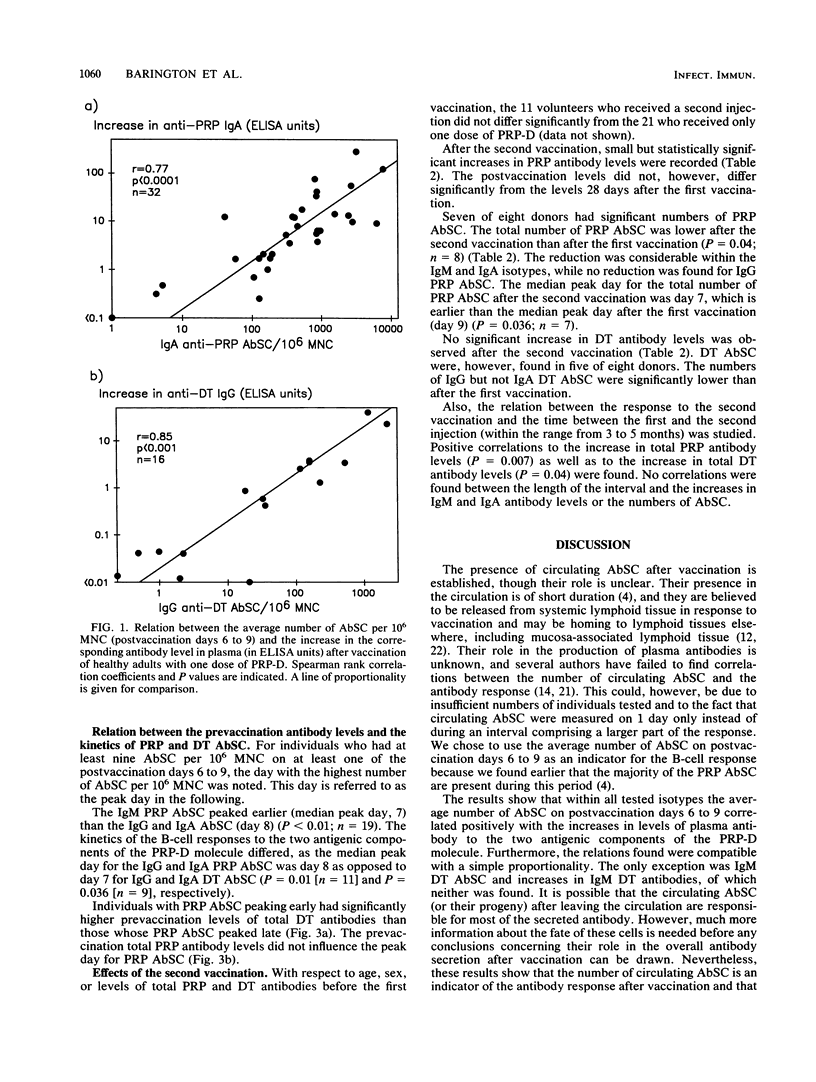
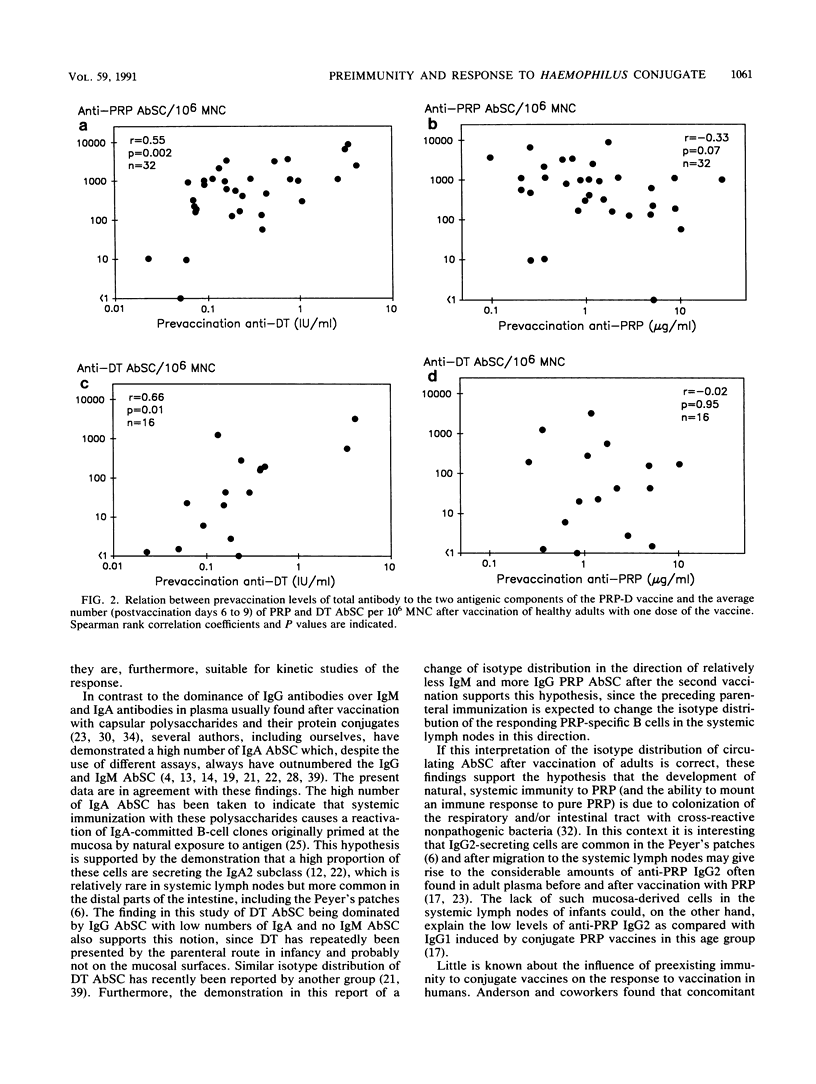
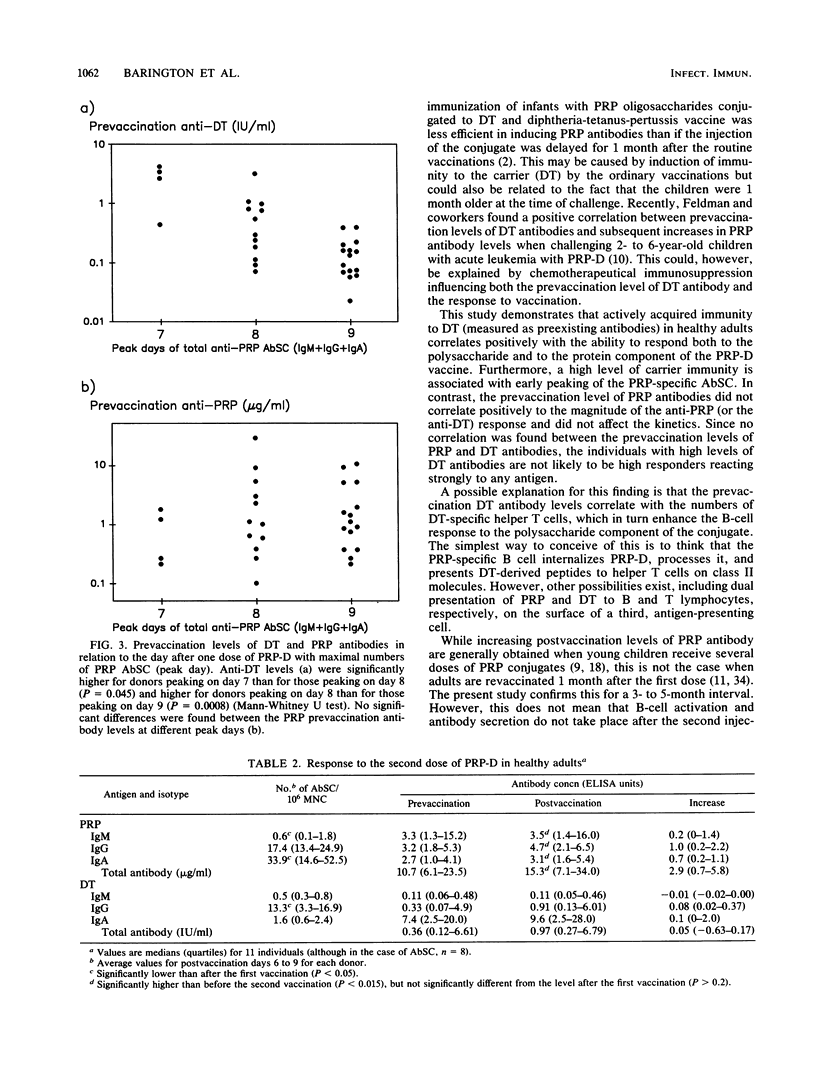
The purpose of this study was to investigate whether preexisting immunity to components of a polysaccharide-protein conjugate influences the B-lymphocyte response to vaccination with the conjugate. Thirty-two healthy adults were vaccinated once or twice with a conjugate (PRP-D) consisting of Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular polysaccharide (PRP) and diphtheria toxoid (DT), and the response was related to the prevaccination levels of PRP and DT antibodies. Positive correlations were found between increases in plasma PRP (median, 32.0 micrograms/ml) and DT (1.14 IU/ml) antibodies and numbers of circulating PRP and DT antibody-secreting cells (AbSC) (postvaccination days 6 to 9). The B-cell responses (antibody response and AbSC) to both PRP and DT correlated positively with prevaccination levels of anti-DT. DT AbSC appeared earlier (peak, day 7) than PRP AbSC (peak, day 8). Individuals whose PRP AbSC peaked early (day 7) had higher prevaccination anti-DT levels than those who peaked later (P less than 0.05). In contrast, the prevaccination levels of anti-PRP did not correlate significantly with the magnitude of the antibody or AbSC response and did not affect the kinetics of the AbSC. Following revaccination with PRP-D, small increases in the level of PRP antibodies (median, 2.9 micrograms/ml; n = 11) were found; no significant increase in the level of DT antibodies was seen. The numbers of PRP AbSC were lower (P = 0.04) and peaked earlier (day 7) than after the first vaccination. The isotype pattern of PRP AbSC, which was dominated by immunoglobulin A (IgA) after the first vaccination, now showed a more equal distribution between IgG and IgA AbSC. It is concluded that after immunization with PRP-D both the magnitude and the kinetics of the antipolysaccharide B-cell response are influenced by prevaccination immunity to the carrier molecule.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson P. Antibody responses to Haemophilus influenzae type b and diphtheria toxin induced by conjugates of oligosaccharides of the type b capsule with the nontoxic protein CRM197. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):233–238. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.233-238.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P., Pichichero M., Edwards K., Porch C. R., Insel R. Priming and induction of Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular antibodies in early infancy by Dpo20, an oligosaccharide-protein conjugate vaccine. J Pediatr. 1987 Nov;111(5):644–650. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80237-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avery O. T., Goebel W. F. CHEMO-IMMUNOLOGICAL STUDIES ON CONJUGATED CARBOHYDRATE-PROTEINS : II. IMMUNOLOGICAL SPECIFICITY OF SYNTHETIC SUGAR-PROTEIN ANTIGENS. J Exp Med. 1929 Sep 30;50(4):533–550. doi: 10.1084/jem.50.4.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barington T., Heilmann C., Andersen V. Quantitation of antibody-secreting cells in the blood after vaccination with Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine. Scand J Immunol. 1990 Apr;31(4):515–522. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1990.tb02799.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz C. D., Ward J. I., Meier K., Hendley J. O., Brunell P. A., Barkin R. A., Zahradnik J. M., Samuelson J., Gordon L. Safety and immunogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide and polysaccharide diphtheria toxoid conjugate vaccines in children 15 to 24 months of age. J Pediatr. 1987 Apr;110(4):509–514. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80540-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjerke K., Brandtzaeg P. Terminally differentiated human intestinal B cells. IgA and IgG subclass-producing immunocytes in the distal ileum, including Peyer's patches, compared with lymph nodes and palatine tonsils. Scand J Immunol. 1990 Aug;32(2):61–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1990.tb02894.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claesson B. A., Schneerson R., Robbins J. B., Johansson J., Lagergard T., Taranger J., Bryla D., Levi L., Cramton T., Trollfors B. Protective levels of serum antibodies stimulated in infants by two injections of Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular polysaccharide-tetanus toxoid conjugate. J Pediatr. 1989 Jan;114(1):97–100. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(89)80611-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einhorn M. S., Weinberg G. A., Anderson E. L., Granoff P. D., Granoff D. M. Immunogenicity in infants of Haemophilus influenzae type B polysaccharide in a conjugate vaccine with Neisseria meningitidis outer-membrane protein. Lancet. 1986 Aug 9;2(8502):299–302. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eskola J., Käyhty H., Peltola H., Karanko V., Mäkelä P. H., Samuelson J., Gordon L. K. Antibody levels achieved in infants by course of Haemophilus influenzae type B polysaccharide/diphtheria toxoid conjugate vaccine. Lancet. 1985 May 25;1(8439):1184–1186. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92863-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman S., Gigliotti F., Shenep J. L., Roberson P. K., Lott L. Risk of Haemophilus influenzae type b disease in children with cancer and response of immunocompromised leukemic children to a conjugate vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1990 May;161(5):926–931. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.5.926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granoff D. M., Boies E. G., Munson R. S., Jr Immunogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide--diphtheria toxoid conjugate vaccine in adults. J Pediatr. 1984 Jul;105(1):22–27. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80350-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilmann C., Barington T., Sigsgaard T. Subclass of individual IgA-secreting human lymphocytes. Investigation of in vivo pneumococcal polysaccharide-induced and in vitro mitogen-induced blood B cells by monolayer plaque-forming cell assays. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1496–1499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilmann C., Henrichsen J., Pedersen F. K. Vaccination-induced circulation of human B cells secreting type-specific antibodies against pneumococcal polysaccharides. Scand J Immunol. 1987 Jan;25(1):61–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1987.tb01047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilmann C., Pedersen F. K. Quantitation of blood lymphocytes secreting antibodies to pneumococcal polysaccharides after in vivo antigenic stimulation. Scand J Immunol. 1986 Feb;23(2):189–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1986.tb01957.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzenberg L. A., Tokuhisa T., Herzenberg L. A. Carrier-priming leads to hapten-specific suppression. Nature. 1980 Jun 26;285(5767):664–667. doi: 10.1038/285664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insel R. A., Anderson P. W. IgG subclass distribution of antibody induced by immunization with the isolated and protein-conjugated polysaccharide of H. influenzae b and G2m(n) distribution of serum IgG2 in man. Monogr Allergy. 1988;23:128–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehrl J. H., Fauci A. S. Activation of human B lymphocytes after immunization with pneumococcal polysaccharides. J Clin Invest. 1983 Apr;71(4):1032–1040. doi: 10.1172/JCI110830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käyhty H., Peltola H., Eskola J., Rönnberg P. R., Kela E., Karanko V., Mäkelä P. H. Immunogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae oligosaccharide-protein and polysaccharide-protein conjugate vaccination of children at 4, 6, and 14 months of age. Pediatrics. 1989 Dec;84(6):995–999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lise L. D., Mazier D., Jolivet M., Audibert F., Chedid L., Schlesinger D. Enhanced epitopic response to a synthetic human malarial peptide by preimmunization with tetanus toxoid carrier. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2658–2661. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2658-2661.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lue C., Prince S. J., Fattom A., Schneerson R., Robbins J. B., Mestecky J. Antibody-secreting peripheral blood lymphocytes induced by immunization with a conjugate consisting of Streptococcus pneumoniae type 12F polysaccharide and diphtheria toxoid. Infect Immun. 1990 Aug;58(8):2547–2554. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.8.2547-2554.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lue C., Tarkowski A., Mestecky J. Systemic immunization with pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine induces a predominant IgA2 response of peripheral blood lymphocytes and increases of both serum and secretory anti-pneumococcal antibodies. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 1;140(11):3793–3800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestecky J. The common mucosal immune system and current strategies for induction of immune responses in external secretions. J Clin Immunol. 1987 Jul;7(4):265–276. doi: 10.1007/BF00915547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuwissen J. H., Tauber I., Leeuwenberg A. D., Beckers P. J., Sieben M. Parasitologic and serologic observations of infection with Pneumocystis in humans. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jul;136(1):43–49. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munoz J. L., Insel R. A. In vitro human antibody production to the Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular polysaccharide. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):2026–2031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä O., Mattila P., Rautonen N., Seppälä I., Eskola J., Käyhty H. Isotype concentrations of human antibodies to Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide (Hib) in young adults immunized with the polysaccharide as such or conjugated to a protein (diphtheria toxoid). J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):1999–2004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltola H., Käyhty H., Sivonen A., Mäkelä H. Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular polysaccharide vaccine in children: a double-blind field study of 100,000 vaccinees 3 months to 5 years of age in Finland. Pediatrics. 1977 Nov;60(5):730–737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarvas H., Rautonen N., Sipinen S., Mäkelä O. IgG subclasses of pneumococcal antibodies--effect of allotype G2m(n). Scand J Immunol. 1989 Feb;29(2):229–237. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb01120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneerson R., Barrera O., Sutton A., Robbins J. B. Preparation, characterization, and immunogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide-protein conjugates. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):361–376. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneerson R., Bradshaw M., Whisnant J. K., Myerowitz R. L., Parke J. C., Jr, Robbins J. B. An Escherichia coli antigen cross-reactive with the capsular polysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae type b: occurrence among known serotypes, and immunochemical and biologic properties of E. coli antisera toward H. influenzae type b. J Immunol. 1972 Jun;108(6):1551–1562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneerson R., Robbins J. B., Chu C., Sutton A., Vann W., Vickers J. C., London W. T., Curfman B., Hardegree M. C., Shiloach J. Serum antibody responses of juvenile and infant rhesus monkeys injected with Haemophilus influenzae type b and pneumococcus type 6A capsular polysaccharide-protein conjugates. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):582–591. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.582-591.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneerson R., Robbins J. B., Parke J. C., Jr, Bell C., Schlesselman J. J., Sutton A., Wang Z., Schiffman G., Karpas A., Shiloach J. Quantitative and qualitative analyses of serum antibodies elicited in adults by Haemophilus influenzae type b and pneumococcus type 6A capsular polysaccharide-tetanus toxoid conjugates. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):519–528. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.519-528.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutze M. P., Deriaud E., Przewlocki G., LeClerc C. Carrier-induced epitopic suppression is initiated through clonal dominance. J Immunol. 1989 Apr 15;142(8):2635–2640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonsen O., Schou C., Heron I. Modification of the ELISA for the estimation of tetanus antitoxin in human sera. J Biol Stand. 1987 Apr;15(2):143–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-1157(87)90037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit P., Oberholzer D., Hayden-Smith S., Koornhof H. J., Hilleman M. R. Protective efficacy of pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccines. JAMA. 1977 Dec 12;238(24):2613–2616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarkowski A., Lue C., Moldoveanu Z., Kiyono H., McGhee J. R., Mestecky J. Immunization of humans with polysaccharide vaccines induces systemic, predominantly polymeric IgA2-subclass antibody responses. J Immunol. 1990 May 15;144(10):3770–3778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



