Abstract
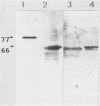
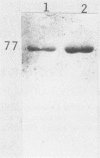
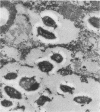
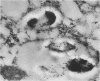
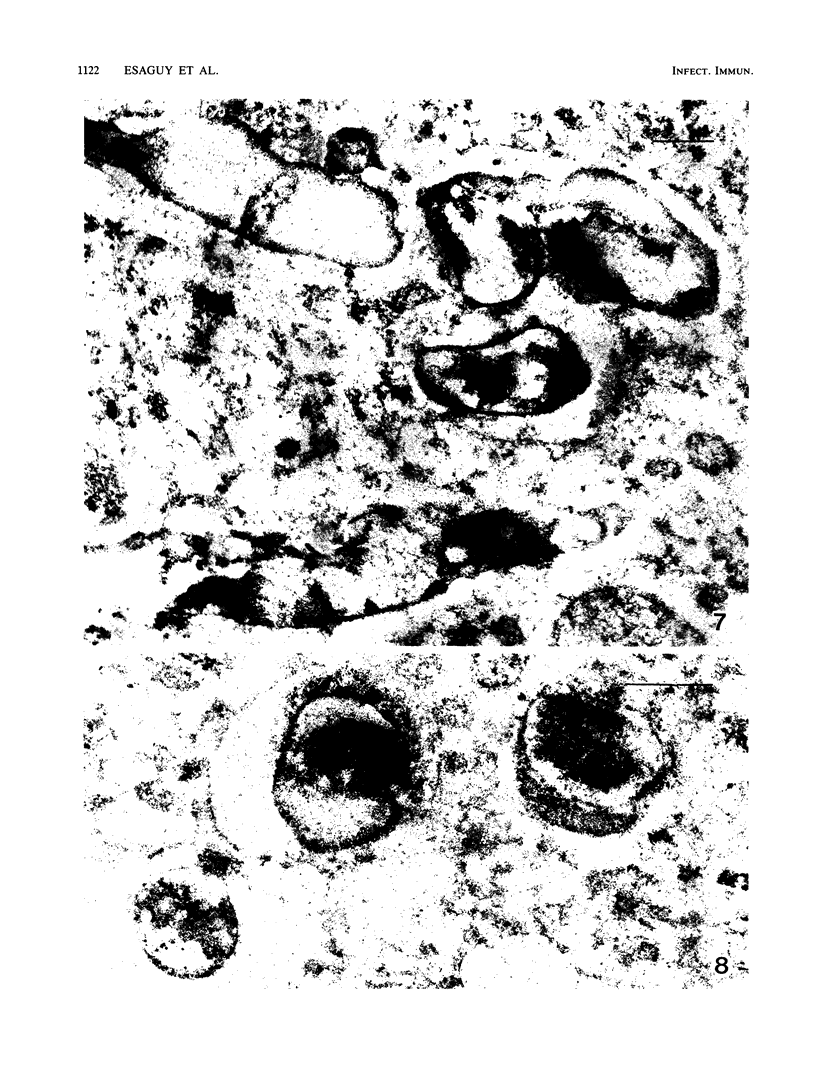
We document here by Western immunoblotting and immunogold ultracytochemistry that polyclonal antibodies against human lactoferrin (Lf) bind to tubercle and leprosy bacilli. In situ immunogold labeling of Mycobacterium leprae (present in armadillo liver and in human skin) and of Mycobacterium tuberculosis indicated that receptors for anti-Lf antibodies were present both on the cytoplasm and on the envelope of the bacilli. We found by immunoblotting that the 65-kDa heat shock protein is the major component of M. leprae and M. tuberculosis that is responsible for the binding of the anti-Lf probe. Furthermore, we show that anti-Lf immunoglobulin G eluted from the nitrocellulose-transferred mycobacterial 65-kDa protein band did bind back to Lf. Ultracytochemistry of biopsy samples of human lepromas showed that dead or severely damaged M. leprae was strongly marked by the anti-Lf antibodies; a similar pattern of immunogold marking was observed on M. leprae when antibodies against the 65-kDa mycobacterial protein were used. Our results offer direct evidence that the 65-kDa protein of leprosy and tubercle bacilli is recognized with specificity by antibodies against the human protein Lf. The Lf-65-kDa protein antigenic cross-reactivity may contribute to the formation of autoantibodies and immune complexes as well as to other autoimmune events that are frequent in tuberculosis and leprosy. Our immunocytochemical data also suggest that the cross-reactivity may persist for some time after the death of mycobacteria in infected hosts.
Full text
PDF

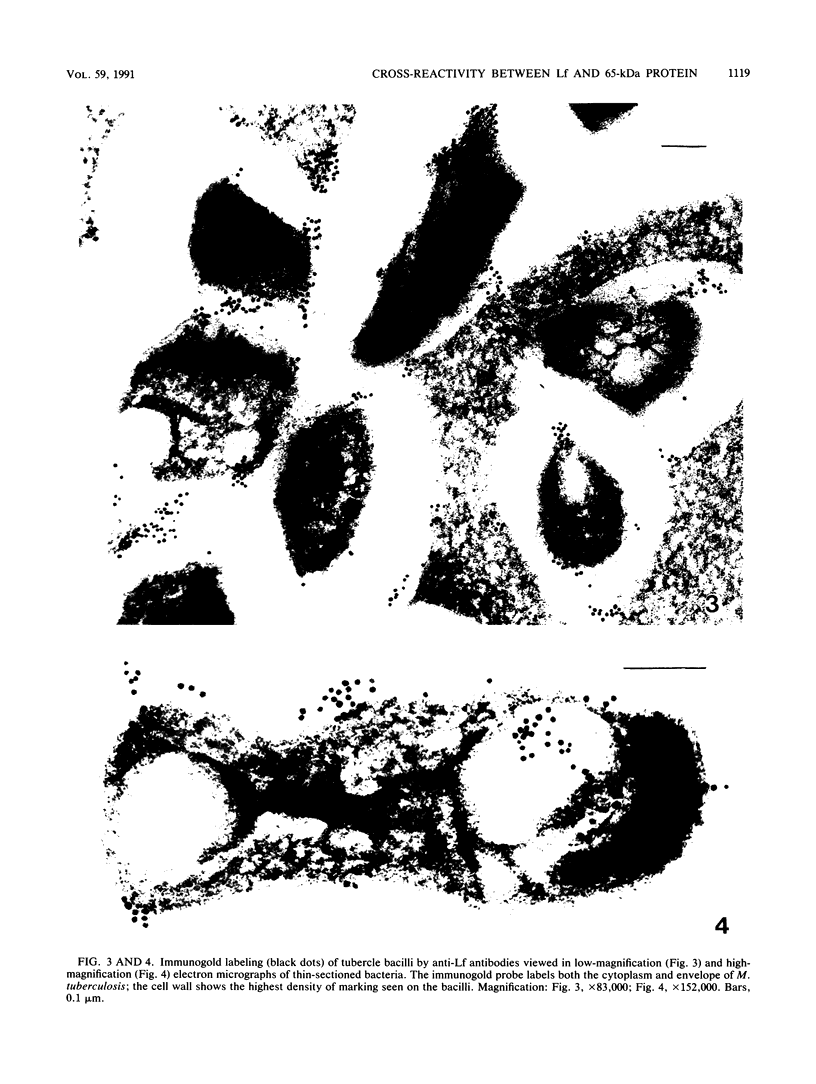
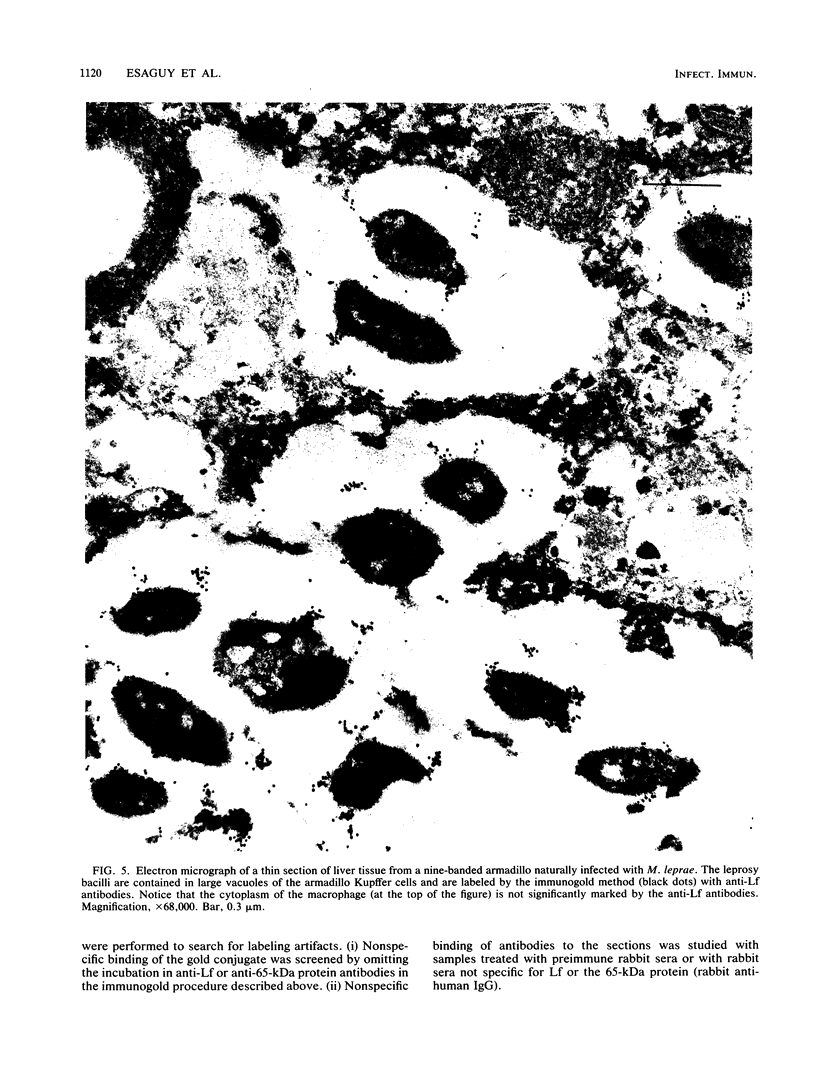
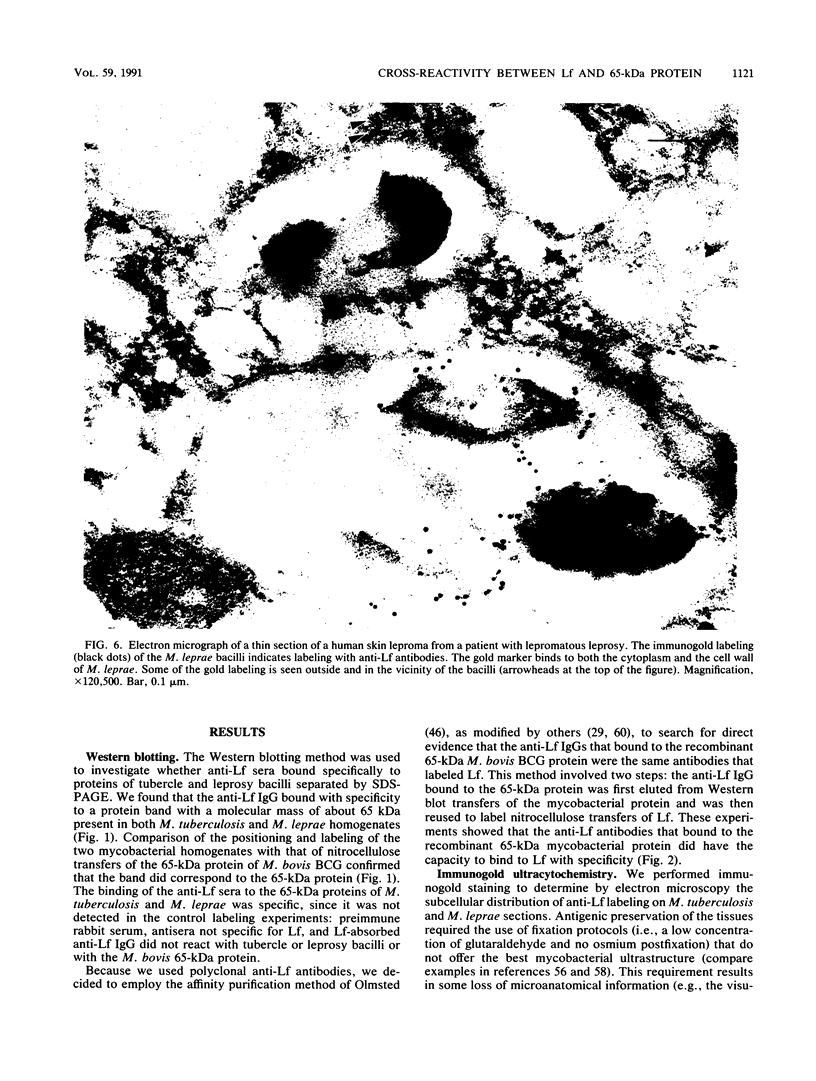



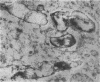
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguas A. P., Pinto da Silva P. Regionalization of transmembrane glycoproteins in the plasma membrane of boar sperm head is revealed by fracture-label. J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;97(5 Pt 1):1356–1364. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.5.1356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aguas A. P., Pinto da Silva P. The acrosomal membrane of boar sperm: a Golgi-derived membrane poor in glycoconjugates. J Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;100(2):528–534. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.2.528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aguas A., Esaguy N., Sunkel C. E., Silva M. T. Cross-reactivity and sequence homology between the 65-kilodalton mycobacterial heat shock protein and human lactoferrin, transferrin, and DR beta subsets of major histocompatibility complex class II molecules. Infect Immun. 1990 May;58(5):1461–1470. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.5.1461-1470.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. C., Barry M. E., Buchanan T. M. Exact definition of species-specific and cross-reactive epitopes of the 65-kilodalton protein of Mycobacterium leprae using synthetic peptides. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 15;141(2):607–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. C., van Schooten W. C., Barry M. E., Janson A. A., Buchanan T. M., de Vries R. R. A Mycobacterium leprae-specific human T cell epitope cross-reactive with an HLA-DR2 peptide. Science. 1988 Oct 14;242(4876):259–261. doi: 10.1126/science.2459778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkin S. L., Welbury R. R., Stanfield E., Beavis D., Iwais B., Dick W. C. Clinical and laboratory studies of inflammatory polyarthritis in patients with leprosy in Papua New Guinea. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987 Sep;46(9):688–690. doi: 10.1136/ard.46.9.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahr G. M., Rook G. A., al-Saffar M., Van Embden J., Stanford J. L., Behbehani K. Antibody levels to mycobacteria in relation to HLA type: evidence for non-HLA-linked high levels of antibody to the 65 kD heat shock protein of M. bovis in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Nov;74(2):211–215. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billingham M. E., Carney S., Butler R., Colston M. J. A mycobacterial 65-kD heat shock protein induces antigen-specific suppression of adjuvant arthritis, but is not itself arthritogenic. J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):339–344. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom B. R., Mehra V. Immunological unresponsiveness in leprosy. Immunol Rev. 1984 Aug;80:5–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1984.tb00493.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxer L. A., Björkstén B., Björk J., Yang H. H., Allen J. M., Baehner R. L. Neutropenia induced by systemic infusion of lactoferrin. J Lab Clin Med. 1982 Jun;99(6):866–872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broxmeyer H. E., Gentile P., Bognacki J., Ralph P. Lactoferrin, transferrin and acidic isoferritins: regulatory molecules with potential therapeutic value in leukemia. Blood Cells. 1983;9(1):83–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broxmeyer H. E., Smithyman A., Eger R. R., Meyers P. A., de Sousa M. Identification of lactoferrin as the granulocyte-derived inhibitor of colony-stimulating activity production. J Exp Med. 1978 Oct 1;148(4):1052–1067. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.4.1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler T. W., Grossi C. E., Canessa A., Pistoia V., Barton J. C. Immunoreactive lactoferrin in resting, activated, and neoplastic lymphocytes. Leuk Res. 1990;14(5):441–447. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(90)90030-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I. R., Holoshitz J., van Eden W., Frenkel A. T lymphocyte clones illuminate pathogenesis and affect therapy of experimental arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Aug;28(8):841–845. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I. R. Regulation of autoimmune disease physiological and therapeutic. Immunol Rev. 1986 Dec;94:5–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01161.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias D., Markovits D., Reshef T., van der Zee R., Cohen I. R. Induction and therapy of autoimmune diabetes in the non-obese diabetic (NOD/Lt) mouse by a 65-kDa heat shock protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1576–1580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmrich F., Thole J., van Embden J., Kaufmann S. H. A recombinant 64 kilodalton protein of Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guerin specifically stimulates human T4 clones reactive to mycobacterial antigens. J Exp Med. 1986 Apr 1;163(4):1024–1029. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.4.1024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esaguy N., Aguas A. P., Silva M. T. High-resolution localization of lactoferrin in human neutrophils: labeling of secondary granules and cell heterogeneity. J Leukoc Biol. 1989 Jul;46(1):51–62. doi: 10.1002/jlb.46.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaston J. S., Life P. F., Bailey L. C., Bacon P. A. In vitro responses to a 65-kilodalton mycobacterial protein by synovial T cells from inflammatory arthritis patients. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 15;143(8):2494–2500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaylord H., Brennan P. J. Leprosy and the leprosy bacillus: recent developments in characterization of antigens and immunology of the disease. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:645–675. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.003241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haregewoin A., Soman G., Hom R. C., Finberg R. W. Human gamma delta+ T cells respond to mycobacterial heat-shock protein. Nature. 1989 Jul 27;340(6231):309–312. doi: 10.1038/340309a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holoshitz J., Koning F., Coligan J. E., De Bruyn J., Strober S. Isolation of CD4- CD8- mycobacteria-reactive T lymphocyte clones from rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid. Nature. 1989 May 18;339(6221):226–229. doi: 10.1038/339226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs A. J., Sturrock R. D. Poncet's disease--fact or fiction? A re-appraisal of tuberculous rheumatism. Tubercle. 1974 Jun;55(2):135–142. doi: 10.1016/0041-3879(74)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Cohn Z. A. The immunobiology of leprosy. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1986;28:45–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H., Väth U., Thole J. E., Van Embden J. D., Emmrich F. Enumeration of T cells reactive with Mycobacterium tuberculosis organisms and specific for the recombinant mycobacterial 64-kDa protein. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Mar;17(3):351–357. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga T., Wand-Württenberger A., DeBruyn J., Munk M. E., Schoel B., Kaufmann S. H. T cells against a bacterial heat shock protein recognize stressed macrophages. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1112–1115. doi: 10.1126/science.2788923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb J. R., Bal V., Mendez-Samperio P., Mehlert A., So A., Rothbard J., Jindal S., Young R. A., Young D. B. Stress proteins may provide a link between the immune response to infection and autoimmunity. Int Immunol. 1989;1(2):191–196. doi: 10.1093/intimm/1.2.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lima M. F., Kierszenbaum F. Lactoferrin effects on phagocytic cell function. I. Increased uptake and killing of an intracellular parasite by murine macrophages and human monocytes. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):4176–4183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Maza O., Fehniger T. E., Ashman R. F. Antibody-secreting cell precursor frequencies among the sheep-erythrocyte-binding cells after immunization. Scand J Immunol. 1983 Apr;17(4):345–354. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1983.tb00799.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson P. L., Heremans J. F., Schonne E. Lactoferrin, an iron-binding protein in neutrophilic leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1969 Sep 1;130(3):643–658. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.3.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazurier J., Legrand D., Hu W. L., Montreuil J., Spik G. Expression of human lactotransferrin receptors in phytohemagglutinin-stimulated human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Isolation of the receptors by antiligand-affinity chromatography. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Feb 1;179(2):481–487. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14578.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meeker H. C., Williams D. L., Anderson D. C., Gillis T. P., Schuller-Levis G., Levis W. R. Analysis of human antibody epitopes on the 65-kilodalton protein of Mycobacterium leprae by using synthetic peptides. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3689–3694. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3689-3694.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melsom R. Serodiagnosis of leprosy: the past, the present, and some prospects for the future. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1983 Jun;51(2):235–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munk M. E., Schoel B., Modrow S., Karr R. W., Young R. A., Kaufmann S. H. T lymphocytes from healthy individuals with specificity to self-epitopes shared by the mycobacterial and human 65-kilodalton heat shock protein. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 1;143(9):2844–2849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naafs B., Kolk A. H., Chin A Lien R. A., Faber W. R., Van Dijk G., Kuijper S., Stolz E., Van Joost T. Anti-Mycobacterium leprae monoclonal antibodies cross-react with human skin: an alternative explanation for the immune responses in leprosy. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 May;94(5):685–688. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12876264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiya K., Horwitz D. A. Contrasting effects of lactoferrin on human lymphocyte and monocyte natural killer activity and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2519–2523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunes J. F., Soares J. O., Alves de Matos A. P. Micro-buffy coats of whole blood: a method for the electron microscopic study of mononuclear cells. Stain Technol. 1979 Sep;54(5):257–260. doi: 10.3109/10520297909110681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted J. B. Affinity purification of antibodies from diazotized paper blots of heterogeneous protein samples. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):11955–11957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottenhoff T. H., Ab B. K., Van Embden J. D., Thole J. E., Kiessling R. The recombinant 65-kD heat shock protein of Mycobacterium bovis Bacillus Calmette-Guerin/M. tuberculosis is a target molecule for CD4+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes that lyse human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 Nov 1;168(5):1947–1952. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.5.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley D. S., Jopling W. H. Classification of leprosy according to immunity. A five-group system. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1966 Jul-Sep;34(3):255–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rook G. A. Rheumatoid arthritis, mycobacterial antigens and agalactosyl IgG. Scand J Immunol. 1988 Oct;28(4):487–493. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb01480.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sher R., Anderson R., Glover A., Wadee A. A. Polymorphonuclear cell function in the various polar types of leprosy and erythema nodosum leprosum. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):959–965. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.959-965.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M. The 65-kilodalton antigen of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1080–1088. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1080-1088.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Vodkin M. H., Williams J. C. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis 65-kilodalton antigen is a heat shock protein which corresponds to common antigen and to the Escherichia coli GroEL protein. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):446–451. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.446-451.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoenfeld Y., Isenberg D. A. Mycobacteria and autoimmunity. Immunol Today. 1988 Jun;9(6):178–182. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91294-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva M. T., Appelberg R., Silva M. N., Macedo P. M. In vivo killing and degradation of Mycobacterium aurum within mouse peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2006–2016. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2006-2016.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva M. T., Macedo P. M., Costa M. H., Gonçalves H., Torgal J., David H. L. Ultrastructural alterations of mycobacterium leprae in skin biopsies of untreated and treated lepromatous patients. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1982 Jul-Aug;133(1):75–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva M. T., Macedo P. M. The interpretation of the ultrastructure of mycobacterial cells in transmission electron microscopy of ultrathin sections. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1983 Jun;51(2):225–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva M. T., Macedo P. M. Ultrastructure of Mycobacterium leprae and other acid-fast bacteria as influenced by fixation conditions. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1982 Jul-Aug;133(1):59–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. E., Fisher P. A. Identification, developmental regulation, and response to heat shock of two antigenically related forms of a major nuclear envelope protein in Drosophila embryos: application of an improved method for affinity purification of antibodies using polypeptides immobilized on nitrocellulose blots. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):20–28. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thole J. E., Dauwerse H. G., Das P. K., Groothuis D. G., Schouls L. M., van Embden J. D. Cloning of Mycobacterium bovis BCG DNA and expression of antigens in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):800–806. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.800-806.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thole J. E., Hindersson P., de Bruyn J., Cremers F., van der Zee J., de Cock H., Tommassen J., van Eden W., van Embden J. D. Antigenic relatedness of a strongly immunogenic 65 kDA mycobacterial protein antigen with a similarly sized ubiquitous bacterial common antigen. Microb Pathog. 1988 Jan;4(1):71–83. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thole J. E., Keulen W. J., De Bruyn J., Kolk A. H., Groothuis D. G., Berwald L. G., Tiesjema R. H., van Embden J. D. Characterization, sequence determination, and immunogenicity of a 64-kilodalton protein of Mycobacterium bovis BCG expressed in escherichia coli K-12. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1466–1475. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1466-1475.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thole J. E., van Schooten W. C., Keulen W. J., Hermans P. W., Janson A. A., de Vries R. R., Kolk A. H., van Embden J. D. Use of recombinant antigens expressed in Escherichia coli K-12 to map B-cell and T-cell epitopes on the immunodominant 65-kilodalton protein of Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1633–1640. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1633-1640.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsoulfa G., Rook G. A., Bahr G. M., Sattar M. A., Behbehani K., Young D. B., Mehlert A., Van-Embden J. D., Hay F. C., Isenberg D. A. Elevated IgG antibody levels to the mycobacterial 65-kDa heat shock protein are characteristic of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Immunol. 1989 Nov;30(5):519–527. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb02459.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Eden W. Heat-shock proteins in autoimmune arthritis: a critical contribution based on the adjuvant arthritis model. APMIS. 1990 May;98(5):383–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1990.tb01048.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schooten W. C., Elferink D. G., Van Embden J., Anderson D. C., De Vries R. R. DR3-restricted T cells from different HLA-DR3-positive individuals recognize the same peptide (amino acids 2-12) of the mycobacterial 65-kDa heat-shock protein. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Nov;19(11):2075–2079. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830191116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Goralnick S., Bullock W. E. Defective leukotaxis in patients with lepromatous leprosy. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Jun;87(6):1025–1032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D., Lathigra R., Hendrix R., Sweetser D., Young R. A. Stress proteins are immune targets in leprosy and tuberculosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4267–4270. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A. Stress proteins and immunology. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:401–420. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.002153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Eden W., Holoshitz J., Cohen I. Antigenic mimicry between mycobacteria and cartilage proteoglycans: the model of adjuvant arthritis. Concepts Immunopathol. 1987;4:144–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Eden W., Holoshitz J., Nevo Z., Frenkel A., Klajman A., Cohen I. R. Arthritis induced by a T-lymphocyte clone that responds to Mycobacterium tuberculosis and to cartilage proteoglycans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5117–5120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Eden W., Thole J. E., van der Zee R., Noordzij A., van Embden J. D., Hensen E. J., Cohen I. R. Cloning of the mycobacterial epitope recognized by T lymphocytes in adjuvant arthritis. Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):171–173. doi: 10.1038/331171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]