Abstract
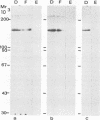
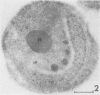
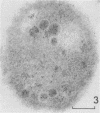
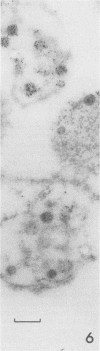
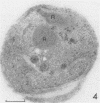
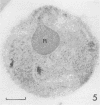
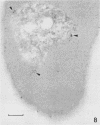
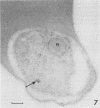
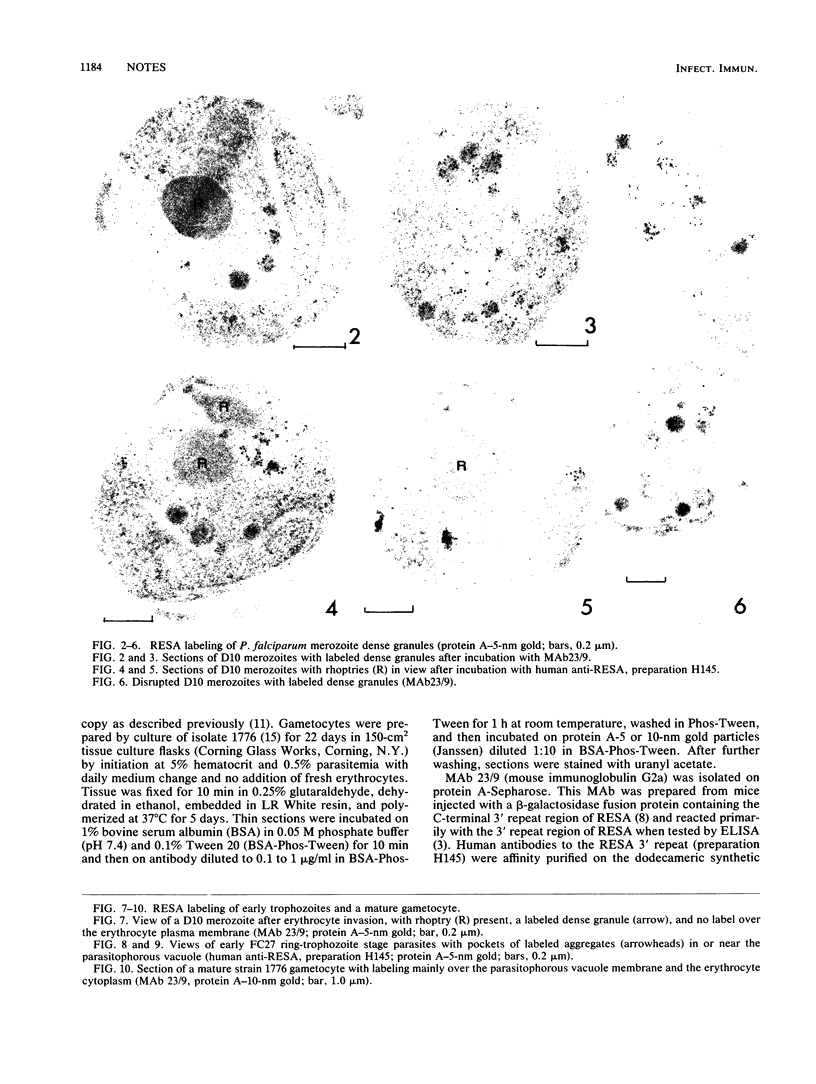
Electron microscopy was used to study the fate of Plasmodium falciparum ring-infected erythrocyte surface antigen after merozoite invasion by using postembedding immunolabeling. The antigen was localized to small dense granules located centrally or laterally in free merozoites. In newly invaded erythrocytes, labeling was found in pockets of the parasitophorous vacuole space or in aggregates closely associated with the parasitophorous vacuole. These patterns indicate that ring-infected erythrocyte surface antigen is contained in merozoite dense granules that are released after merozoite invasion and not via apical rhoptry ducts at the time of merozoite attachment.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aikawa M., Uni Y., Andrutis A. T., Howard R. J. Membrane-associated electron-dense material of the asexual stages of Plasmodium falciparum: evidence for movement from the intracellular parasite to the erythrocyte membrane. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1986 Jan;35(1):30–36. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1986.35.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anders R. F. Multiple cross-reactivities amongst antigens of Plasmodium falciparum impair the development of protective immunity against malaria. Parasite Immunol. 1986 Nov;8(6):529–539. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1986.tb00867.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannister L. H., Butcher G. A., Dennis E. D., Mitchell G. H. Structure and invasive behaviour of Plasmodium knowlesi merozoites in vitro. Parasitology. 1975 Dec;71(3):483–491. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000047247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannister L. H., Mitchell G. H. The fine structure of secretion by Plasmodium knowlesi merozoites during red cell invasion. J Protozool. 1989 Jul-Aug;36(4):362–367. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1989.tb05527.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. V., Culvenor J. G., Crewther P. E., Bianco A. E., Coppel R. L., Saint R. B., Stahl H. D., Kemp D. J., Anders R. F. Localization of the ring-infected erythrocyte surface antigen (RESA) of Plasmodium falciparum in merozoites and ring-infected erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1985 Aug 1;162(2):774–779. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.2.774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins W. E., Pappaioanou M., Anders R. F., Campbell G. H., Brown G. V., Kemp D. J., Broderson J. R., Coppel R. L., Skinner J. C., Procell P. M. Immunization trials with the ring-infected erythrocyte surface antigen of Plasmodium falciparum in owl monkeys (Aotus vociferans). Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1988 Mar;38(2):268–282. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1988.38.268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppel R. L., Cowman A. F., Anders R. F., Bianco A. E., Saint R. B., Lingelbach K. R., Kemp D. J., Brown G. V. Immune sera recognize on erythrocytes Plasmodium falciparum antigen composed of repeated amino acid sequences. 1984 Aug 30-Sep 5Nature. 310(5980):789–792. doi: 10.1038/310789a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowman A. F., Coppel R. L., Saint R. B., Favaloro J., Crewther P. E., Stahl H. D., Bianco A. E., Brown G. V., Anders R. F., Kemp D. J. The ring-infected erythrocyte surface antigen (RESA) polypeptide of Plasmodium falciparum contains two separate blocks of tandem repeats encoding antigenic epitopes that are naturally immunogenic in man. Mol Biol Med. 1984 Jun;2(3):207–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crewther P. E., Bianco A. E., Brown G. V., Coppel R. L., Stahl H. D., Kemp D. J., Anders R. F. Affinity purification of human antibodies directed against cloned antigens of Plasmodium falciparum. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Feb 12;86(2):257–264. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90462-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culvenor J. G., Crewther P. E. S-antigen localization in the erythrocytic stages of Plasmodium falciparum. J Protozool. 1990 Jan-Feb;37(1):59–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1990.tb01117.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Entzeroth R., Dubremetz J. F., Hodick D., Ferreira E. Immunoelectron microscopic demonstration of the exocytosis of dense granule contents into the secondary parasitophorous vacuole of Sarcocystis muris (Protozoa, Apicomplexa). Eur J Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;41(2):182–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J. M., Coppel R. L., Corcoran L. M., Foote S. J., Brown G. V., Anders R. F., Kemp D. J. Structure of the RESA gene of Plasmodium falciparum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 11;14(21):8265–8277. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.21.8265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foley M., Murray L. J., Anders R. F. The ring-infected erythrocyte surface antigen protein of Plasmodium falciparum is phosphorylated upon association with the host cell membrane. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1990 Jan 1;38(1):69–75. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(90)90206-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsyth K. P., Philip G., Smith T., Kum E., Southwell B., Brown G. V. Diversity of antigens expressed on the surface of erythrocytes infected with mature Plasmodium falciparum parasites in Papua New Guinea. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1989 Sep;41(3):259–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kara U. A., Stenzel D. J., Ingram L. T., Bushell G. R., Lopez J. A., Kidson C. Inhibitory monoclonal antibody against a (myristylated) small-molecular-weight antigen from Plasmodium falciparum associated with the parasitophorous vacuole membrane. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):903–909. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.903-909.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell G. H., Bannister L. H. Malaria parasite invasion: interactions with the red cell membrane. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 1988;8(4):225–310. doi: 10.1016/s1040-8428(88)80011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann H., Berzins K., Wahlgren M., Carlsson J., Björkman A., Patarroyo M. E., Perlmann P. Antibodies in malarial sera to parasite antigens in the membrane of erythrocytes infected with early asexual stages of Plasmodium falciparum. J Exp Med. 1984 Jun 1;159(6):1686–1704. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.6.1686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quakyi I. A., Matsumoto Y., Carter R., Udomsangpetch R., Sjolander A., Berzins K., Perlmann P., Aikawa M., Miller L. H. Movement of a falciparum malaria protein through the erythrocyte cytoplasm to the erythrocyte membrane is associated with lysis of the erythrocyte and release of gametes. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):833–839. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.833-839.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torii M., Adams J. H., Miller L. H., Aikawa M. Release of merozoite dense granules during erythrocyte invasion by Plasmodium knowlesi. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):3230–3233. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.3230-3233.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uni S., Masuda A., Stewart M. J., Igarashi I., Nussenzweig R., Aikawa M. Ultrastructural localization of the 150/130 Kd antigens in sexual and asexual blood stages of Plasmodium falciparum-infected human erythrocytes. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 May;36(3):481–488. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.36.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wåhlin B., Wahlgren M., Perlmann H., Berzins K., Björkman A., Patarroyo M. E., Perlmann P. Human antibodies to a Mr 155,000 Plasmodium falciparum antigen efficiently inhibit merozoite invasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7912–7916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]