Abstract
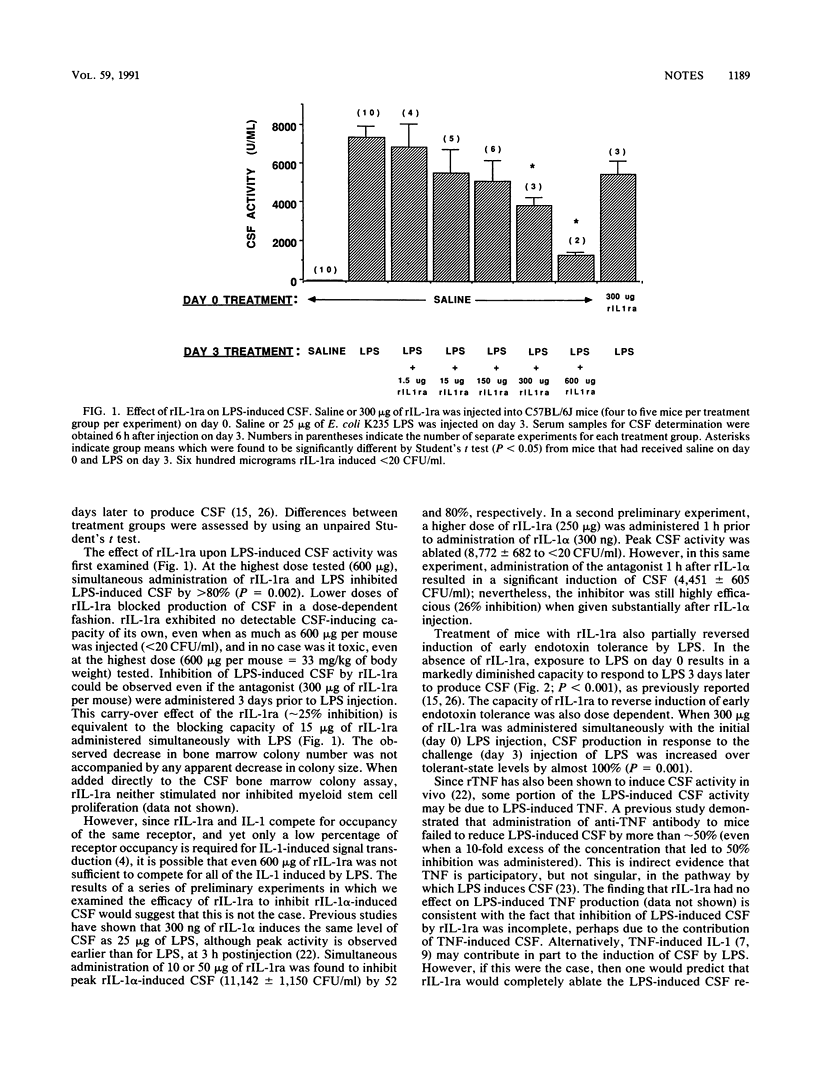
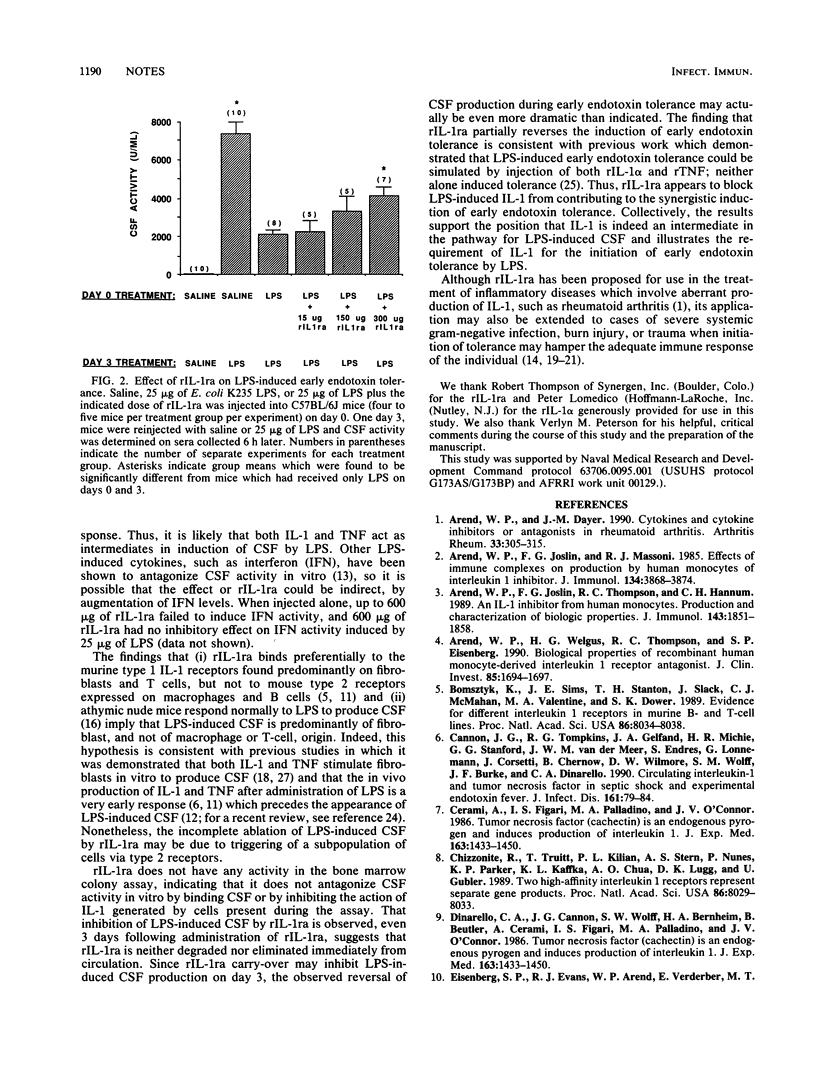
In this report, administration of a recombinant interleukin-1 receptor antagonist protein to mice was found to inhibit induction of colony-stimulating factor as well as induction of early endotoxin tolerance by lipopolysaccharide. These findings provide direct evidence that interleukin-1 is an intermediate in these two lipopolysaccharide-induced phenomena.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arend W. P., Dayer J. M. Cytokines and cytokine inhibitors or antagonists in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Mar;33(3):305–315. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arend W. P., Joslin F. G., Massoni R. J. Effects of immune complexes on production by human monocytes of interleukin 1 or an interleukin 1 inhibitor. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3868–3875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arend W. P., Joslin F. G., Thompson R. C., Hannum C. H. An IL-1 inhibitor from human monocytes. Production and characterization of biologic properties. J Immunol. 1989 Sep 15;143(6):1851–1858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arend W. P., Welgus H. G., Thompson R. C., Eisenberg S. P. Biological properties of recombinant human monocyte-derived interleukin 1 receptor antagonist. J Clin Invest. 1990 May;85(5):1694–1697. doi: 10.1172/JCI114622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bomsztyk K., Sims J. E., Stanton T. H., Slack J., McMahan C. J., Valentine M. A., Dower S. K. Evidence for different interleukin 1 receptors in murine B- and T-cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8034–8038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon J. G., Tompkins R. G., Gelfand J. A., Michie H. R., Stanford G. G., van der Meer J. W., Endres S., Lonnemann G., Corsetti J., Chernow B. Circulating interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor in septic shock and experimental endotoxin fever. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jan;161(1):79–84. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chizzonite R., Truitt T., Kilian P. L., Stern A. S., Nunes P., Parker K. P., Kaffka K. L., Chua A. O., Lugg D. K., Gubler U. Two high-affinity interleukin 1 receptors represent separate gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8029–8033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Cannon J. G., Wolff S. M., Bernheim H. A., Beutler B., Cerami A., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, O'Connor J. V. Tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is an endogenous pyrogen and induces production of interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1433–1450. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Cannon J. G., Wolff S. M., Bernheim H. A., Beutler B., Cerami A., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, O'Connor J. V. Tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is an endogenous pyrogen and induces production of interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1433–1450. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S. P., Evans R. J., Arend W. P., Verderber E., Brewer M. T., Hannum C. H., Thompson R. C. Primary structure and functional expression from complementary DNA of a human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):341–346. doi: 10.1038/343341a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannum C. H., Wilcox C. J., Arend W. P., Joslin F. G., Dripps D. J., Heimdal P. L., Armes L. G., Sommer A., Eisenberg S. P., Thompson R. C. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist activity of a human interleukin-1 inhibitor. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):336–340. doi: 10.1038/343336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henricson B. E., Benjamin W. R., Vogel S. N. Differential cytokine induction by doses of lipopolysaccharide and monophosphoryl lipid A that result in equivalent early endotoxin tolerance. Infect Immun. 1990 Aug;58(8):2429–2437. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.8.2429-2437.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimpel G. R., Fleischmann W. R., Jr, Klimpel K. D. Gamma interferon (IFN gamma) and IFN alpha/beta suppress murine myeloid colony formation (CFU-C)N: magnitude of suppression is dependent upon level of colony-stimulating factor (CSF). J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):76–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loose L. D., Turinsky J. Macrophage dysfunction after burn injury. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):157–162. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.157-162.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madonna G. S., Vogel S. N. Early endotoxin tolerance is associated with alterations in bone marrow-derived macrophage precursor pools. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):3763–3771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madonna G. S., Vogel S. N. Induction of early-phase endotoxin tolerance in athymic (nude) mice, B-cell-deficient (xid) mice, and splenectomized mice. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):707–710. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.707-710.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntire F. C., Sievert H. W., Barlow G. H., Finley R. A., Lee A. Y. Chemical, physical, biological properties of a lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli K-235. Biochemistry. 1967 Aug;6(8):2363–2372. doi: 10.1021/bi00860a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munker R., Gasson J., Ogawa M., Koeffler H. P. Recombinant human TNF induces production of granulocyte-monocyte colony-stimulating factor. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):79–82. doi: 10.1038/323079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrillo J. E., Parker M. M., Natanson C., Suffredini A. F., Danner R. L., Cunnion R. E., Ognibene F. P. Septic shock in humans. Advances in the understanding of pathogenesis, cardiovascular dysfunction, and therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Aug 1;113(3):227–242. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-113-3-227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson V. M., Robinson W. A., Wallner S. F., Rundus C., Hansbrough J. F. Granulocyte stem cells are decreased in humans with fatal burns. J Trauma. 1985 May;25(5):413–418. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198505000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson V., Hansbrough J., Buerk C., Rundus C., Wallner S., Smith H., Robinson W. A. Regulation of granulopoiesis following severe thermal injury. J Trauma. 1983 Jan;23(1):19–24. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198301000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel S. N., Douches S. D., Kaufman E. N., Neta R. Induction of colony stimulating factor in vivo by recombinant interleukin 1 alpha and recombinant tumor necrosis factor alpha 1. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2143–2148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel S. N., Havell E. A. Differential inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced phenomena by anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha antibody. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2397–2400. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2397-2400.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel S. N., Kaufman E. N., Tate M. D., Neta R. Recombinant interleukin-1 alpha and recombinant tumor necrosis factor alpha synergize in vivo to induce early endotoxin tolerance and associated hematopoietic changes. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2650–2657. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2650-2657.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams Z., Hertogs C. F., Pluznik D. H. Use of mice tolerant to lipopolysaccharide to demonstrate requirement of cooperation between macrophages and lymphocytes to generate lipopolysaccharide-induced colony-stimulating factor in vivo. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):1–5. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.1-5.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucali J. R., Dinarello C. A., Oblon D. J., Gross M. A., Anderson L., Weiner R. S. Interleukin 1 stimulates fibroblasts to produce granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating activity and prostaglandin E2. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1857–1863. doi: 10.1172/JCI112512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



