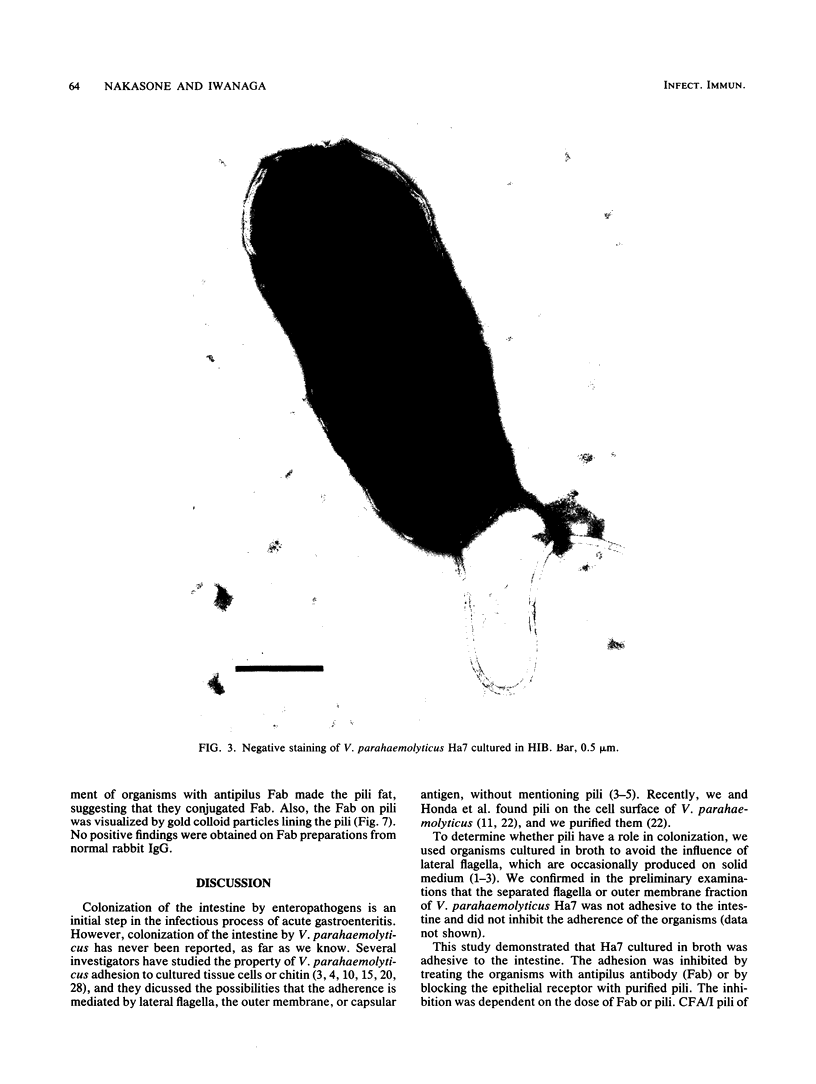
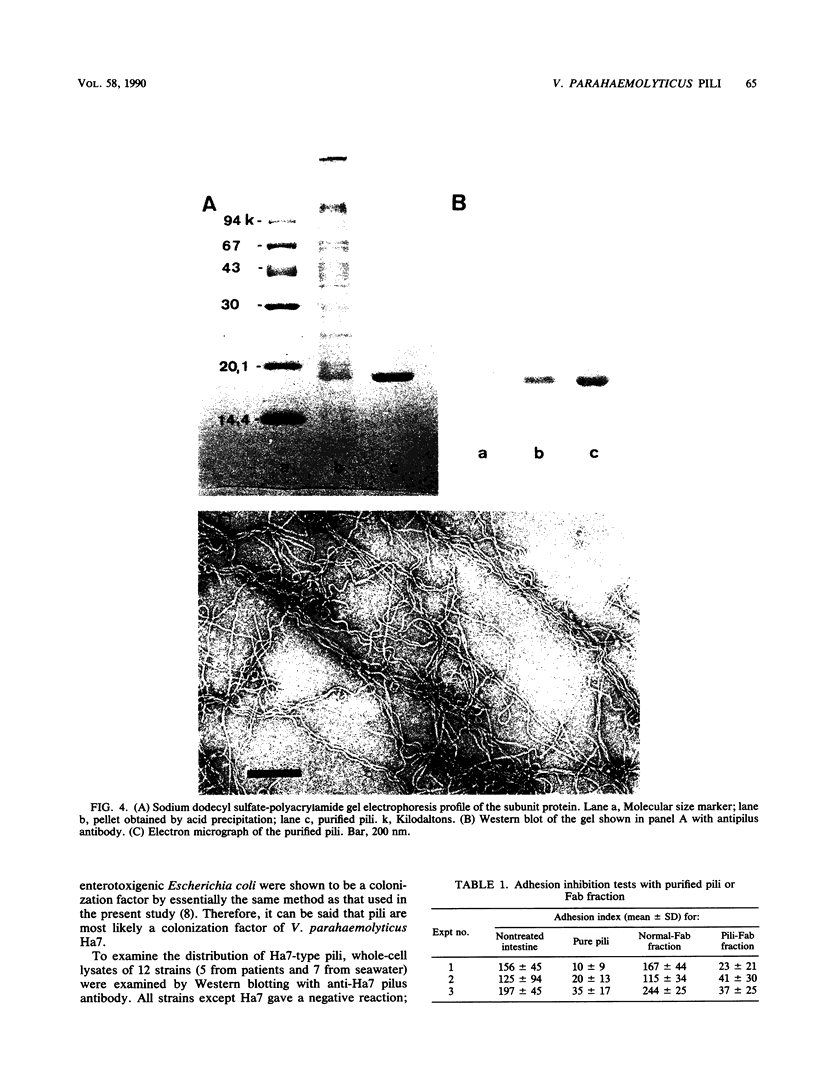
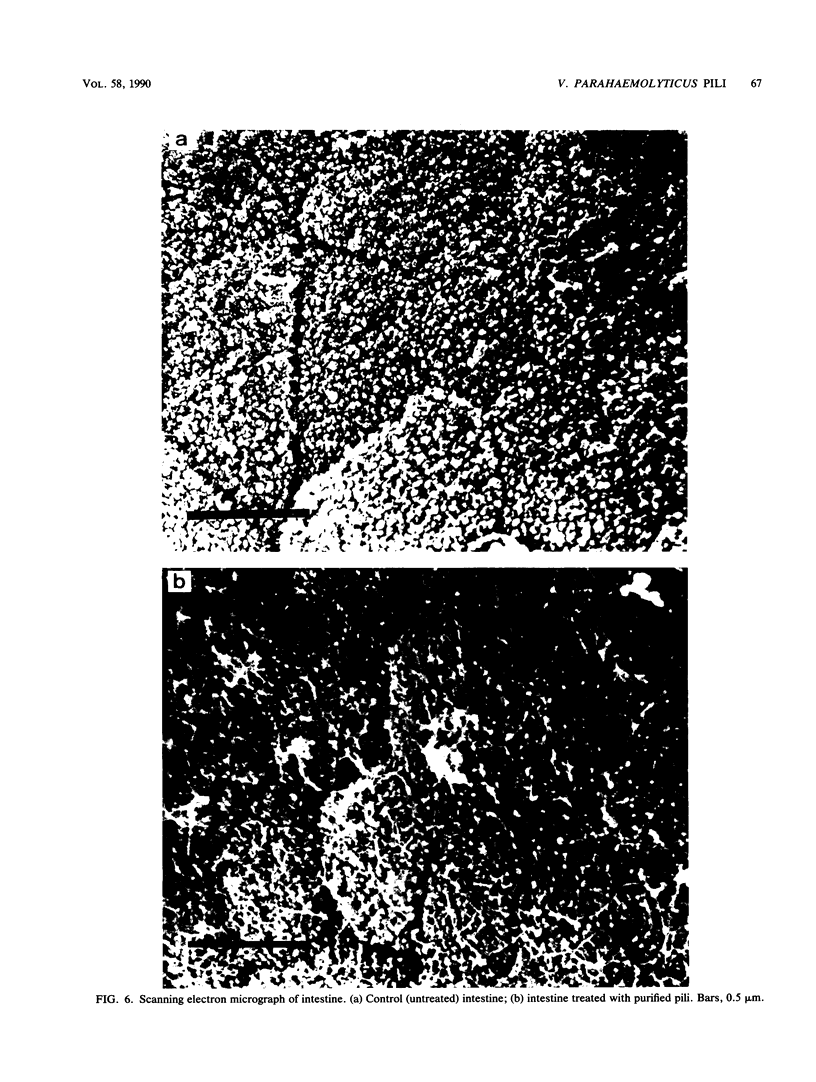
Abstract
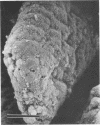
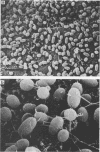
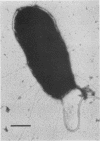
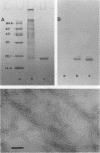
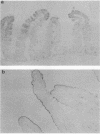
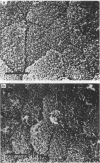
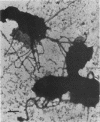
Pili of Vibrio parahaemolyticus were purified from a Kanagawa phenomenon-positive strain (Ha7) that belongs to serogroup O2:K3 and is adhesive to rabbit intestine. The organisms treated with the Fab fraction of antipilus antibody failed to adhere to the intestine. Purified pili had the ability to adhere to the intestine, but the pretreatment of the intestine with purified pili did not allow adherence of the organisms to the intestine. These results suggest that pili of this V. parahaemolyticus strain play an important role in colonization.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. D., Baumann P. Structure and arrangement of flagella in species of the genus Beneckea and Photobacterium fischeri. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jul;107(1):295–302. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.1.295-302.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann P., Baumann L., Mandel M. Taxonomy of marine bacteria: the genus Beneckea. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jul;107(1):268–294. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.1.268-294.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belas M. R., Colwell R. R. Adsorption kinetics of laterally and polarly flagellated Vibrio. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1568–1580. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1568-1580.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carruthers M. M., Anderson B. Inhibition by polyanions of adherence by Kanagawa-positive Vibrio parahaemolyticus: a physicochemical effect. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jul;140(1):119–122. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carruthers M. M. In vitro adherence of Kanagawa-positive Vibrio parahaemolyticus to epithelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1977 Oct;136(4):588–592. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.4.588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darfeuille A., Lafeuille B., Joly B., Cluzel R. A new colonization factor antigen (CFA/III) produced by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli O128:B12. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1983 Jan-Feb;134A(1):53–64. doi: 10.1016/0769-2609(83)90103-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Clegg S., Pauley J. A. Purification and characterization of the CFA/I antigen of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):738–748. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.738-748.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr New surface-associated heat-labile colonization factor antigen (CFA/II) produced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli of serogroups O6 and O8. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):638–647. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.638-647.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackney C. R., Kleeman E. G., Ray B., Speck M. L. Adherence as a method of differentiating virulent and avirulent strains of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Sep;40(3):652–658. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.3.652-658.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Arita M., Ayala E., Miwatani T. Production of pili on Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Nov;34(11):1279–1281. doi: 10.1139/m88-224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Arita M., Miwatani T. Characterization of new hydrophobic pili of human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli: a possible new colonization factor. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):959–965. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.959-965.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Ni Y. X., Miwatani T. Purification and characterization of a hemolysin produced by a clinical isolate of Kanagawa phenomenon-negative Vibrio parahaemolyticus and related to the thermostable direct hemolysin. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):961–965. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.961-965.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Taga S., Takeda T., Hasibuan M. A., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Identification of lethal toxin with the thermostable direct hemolysin produced by Vibrio parahaemolyticus, and some physicochemical properties of the purified toxin. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):133–139. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.133-139.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iijima Y., Yamada H., Shinoda S. Adherence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and its relation to pathogenicity. Can J Microbiol. 1981 Dec;27(12):1252–1259. doi: 10.1139/m81-192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwanaga M., Nakasone N., Ehara M. Pili of Vibrio cholerae O1 biotype E1 Tor: a comparative study on adhesive and non-adhesive strains. Microbiol Immunol. 1989;33(1):1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1989.tb01492.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Abrams G. D., Freter R. Adhesive properties of Vibrio cholerae: adhesion to isolated rabbit brush border membranes and hemagglutinating activity. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):232–239. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.232-239.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrell B. R., Walker R. I., Joseph S. W. In vitro and in vivo pathologic effects of Vibrio parahaemolyticus on human epithelial cells. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Mar;30(3):381–388. doi: 10.1139/m84-056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakasone N., Iwanaga M. Quantitative evaluation of colonizing ability of Vibrio cholerae O1. Microbiol Immunol. 1987;31(8):753–761. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1987.tb03137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakasone N., Iwanaga M. [Purification and characterization of Vibrio parahaemolyticus pili isolated from a patient with diarrhea: comparative studies with Vibrio cholerae O1 pili]. Nihon Saikingaku Zasshi. 1988 Nov;43(6):981–987. doi: 10.3412/jsb.43.981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibuchi M., Ishibashi M., Takeda Y., Kaper J. B. Detection of the thermostable direct hemolysin gene and related DNA sequences in Vibrio parahaemolyticus and other vibrio species by the DNA colony hybridization test. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):481–486. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.481-486.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibuchi M., Kaper J. B. Nucleotide sequence of the thermostable direct hemolysin gene of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):558–564. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.558-564.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Punsalang A. P., Jr, Sawyer W. D. Role of pili in the virulence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):255–263. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.255-263.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes A. L., Crawford R. G., Spaulding P. L., Peeler J. T., Twedt R. M. Hemagglutination and adhesiveness of epidemiologically distinct strains of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):721–725. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.721-725.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai J., Honda T., Jinguji Y., Arita M., Miwatani T. Cytotoxic effect of the thermostable direct hemolysin produced by Vibrio parahaemolyticus on FL cells. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):876–883. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.876-883.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Linggood M. A. Observations on the pathogenic properties of the K88, Hly and Ent plasmids of Escherichia coli with particular reference to porcine diarrhoea. J Med Microbiol. 1971 Nov;4(4):467–485. doi: 10.1099/00222615-4-4-467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Takeda T., Honda T., Miwatani T. Inactivation of the biological activities of the thermostable direct hemolysin of Vibrio parahaemolyticus by ganglioside Gt1. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):1–5. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.1-5.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teppema J. S., Guinée P. A., Ibrahim A. A., Pâques M., Ruitenberg E. J. In vivo adherence and colonization of Vibrio cholerae strains that differ in hemagglutinating activity and motility. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2093–2102. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2093-2102.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]