Abstract
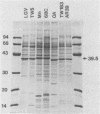
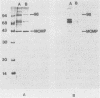
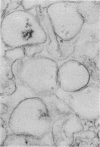
Several isolates of Chlamydia pneumoniae were compared with each other and to Chlamydia trachomatis and Chlamydia psittaci by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunoblots. Protein profiles of the C. pneumoniae isolates appeared to be the same and were distinct from the other Chlamydia species. A 39.5-kilodalton (kDa) protein, similar in molecular weight to the major outer membrane proteins (MOMP) of C. trachomatis and C. psittaci, was found in the Sarkosyl-insoluble fraction, demonstrating its association with the outer membrane complex. In the outer membrane complex, the MOMP was shown to exist in disulfide-linked protein complexes. Electron microscopy of the Sarkosyl-extracted elementary bodies showed that the structural rigidity and pear-shaped morphology remained intact. Rabbit immune sera prepared against C. pneumoniae demonstrated immunoreactive proteins of 98-, 77-, 75-, 66-, 60-, 39.5-, 28-, and 17.5-kDa proteins. Cross-reactivity experiments revealed that most of the antigenic reactivities shared between C. psittaci and C. trachomatis extend to C. pneumoniae and that the 98-kDa protein recognition appeared to be C. pneumoniae specific. In contrast to the other Chlamydia spp., the recognition of the C. pneumoniae MOMP by homologous immune sera was weak and was cross-reactive with the MOMPs of the other Chlamydia species. These results suggest that the C. pneumoniae MOMP is less immunogenic and antigenically complex than are the MOMPs of C. trachomatis and C. psittaci.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baehr W., Zhang Y. X., Joseph T., Su H., Nano F. E., Everett K. D., Caldwell H. D. Mapping antigenic domains expressed by Chlamydia trachomatis major outer membrane protein genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):4000–4004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.4000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bavoil P., Ohlin A., Schachter J. Role of disulfide bonding in outer membrane structure and permeability in Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):479–485. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.479-485.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell H. D., Kromhout J., Schachter J. Purification and partial characterization of the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1161–1176. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1161-1176.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell H. D., Kuo C. C., Kenny G. E. Antigenic analysis of Chlamydiae by two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis. I. Antigenic heterogeneity between C. trachomatis and C. psittaci. J Immunol. 1975 Oct;115(4):963–968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell L. A., Kuo C. C., Grayston J. T. Characterization of the new Chlamydia agent, TWAR, as a unique organism by restriction endonuclease analysis and DNA-DNA hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;25(10):1911–1916. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.10.1911-1916.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell L. A., Kuo C. C., Thissen R. W., Grayston J. T. Isolation of a gene encoding a Chlamydia sp. strain TWAR protein that is recognized during infection of humans. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):71–75. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.71-75.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chi E. Y., Kuo C. C., Grayston J. T. Unique ultrastructure in the elementary body of Chlamydia sp. strain TWAR. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3757–3763. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3757-3763.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke I. N., Ward M. E., Lambden P. R. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of a developmentally regulated cysteine-rich outer membrane protein from Chlamydia trachomatis. Gene. 1988 Nov 30;71(2):307–314. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90047-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlan J. W., Clarke I. N., Ward M. E. Epitope mapping with solid-phase peptides: identification of type-, subspecies-, species- and genus-reactive antibody binding domains on the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Sep;2(5):673–679. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00076.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushi H., Hirai K. Immunochemical diversity of the major outer membrane protein of avian and mammalian Chlamydia psittaci. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Apr;26(4):675–680. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.4.675-680.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grayston J. T., Kuo C. C., Wang S. P., Altman J. A new Chlamydia psittaci strain, TWAR, isolated in acute respiratory tract infections. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jul 17;315(3):161–168. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198607173150305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grayston J. T., Wang S. P., Kuo C. C., Campbell L. A. Current knowledge on Chlamydia pneumoniae, strain TWAR, an important cause of pneumonia and other acute respiratory diseases. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 Mar;8(3):191–202. doi: 10.1007/BF01965260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard L., Orenstein N. S., King N. W. Purification on renografin density gradients of Chlamydia trachomatis grown in the yolk sac of eggs. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jan;27(1):102–106. doi: 10.1128/am.27.1.102-106.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleemola M., Saikku P., Visakorpi R., Wang S. P., Grayston J. T. Epidemics of pneumonia caused by TWAR, a new Chlamydia organism, in military trainees in Finland. J Infect Dis. 1988 Feb;157(2):230–236. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.2.230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. C., Chen H. H., Wang S. P., Grayston J. T. Identification of a new group of Chlamydia psittaci strains called TWAR. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Dec;24(6):1034–1037. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.6.1034-1037.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. C., Chi E. Y., Grayston J. T. Ultrastructural study of entry of Chlamydia strain TWAR into HeLa cells. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1668–1672. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1668-1672.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maclean I. W., Peeling R. W., Brunham R. C. Characterization of Chlamydia trachomatis antigens with monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Feb;34(2):141–147. doi: 10.1139/m88-028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manire G. P., Tamura A. Preparation and chemical composition of the cell walls of mature infectious dense forms of meningopneumonitis organisms. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1178–1183. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1178-1183.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newhall W. J., Batteiger B., Jones R. B. Analysis of the human serological response to proteins of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):1181–1189. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.1181-1189.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newhall W. J., Jones R. B. Disulfide-linked oligomers of the major outer membrane protein of chlamydiae. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):998–1001. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.998-1001.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsey K. H., Newhall W. J., 5th, Rank R. G. Humoral immune response to chlamydial genital infection of mice with the agent of mouse pneumonitis. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2441–2446. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2441-2446.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salari S. H., Ward M. E. Polypeptide composition of Chlamydia trachomatis. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Apr;123(2):197–207. doi: 10.1099/00221287-123-2-197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]