Abstract
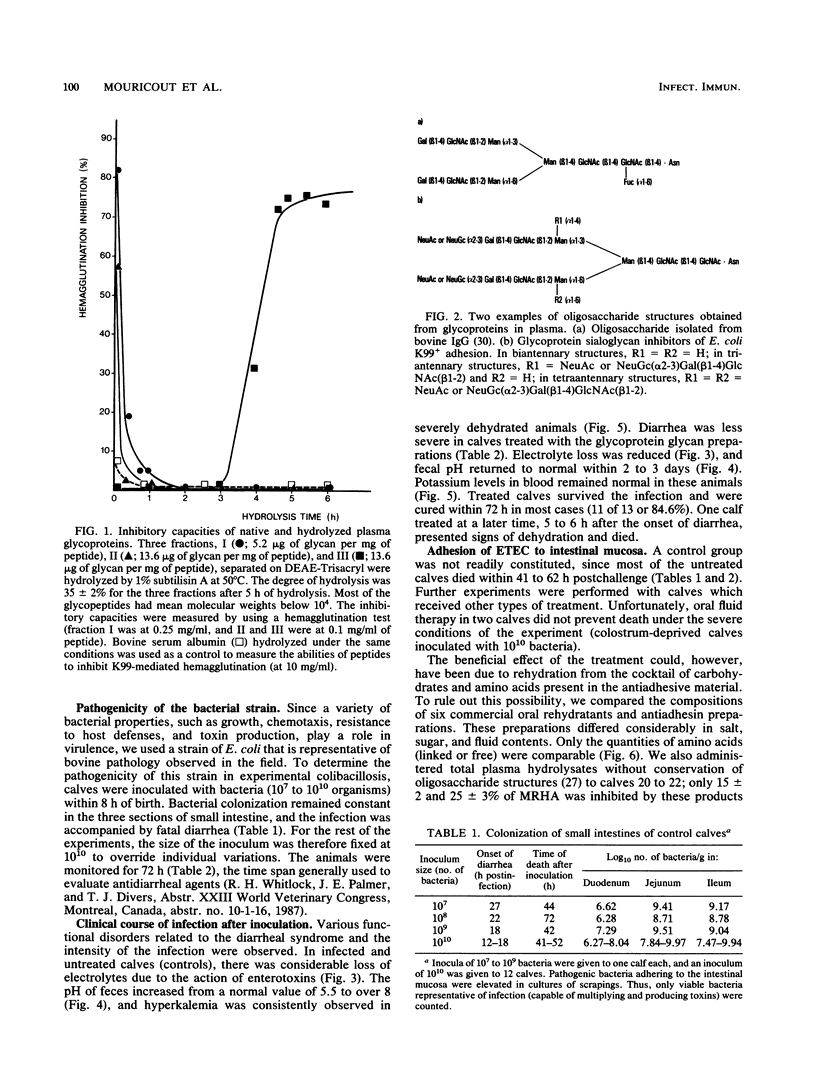
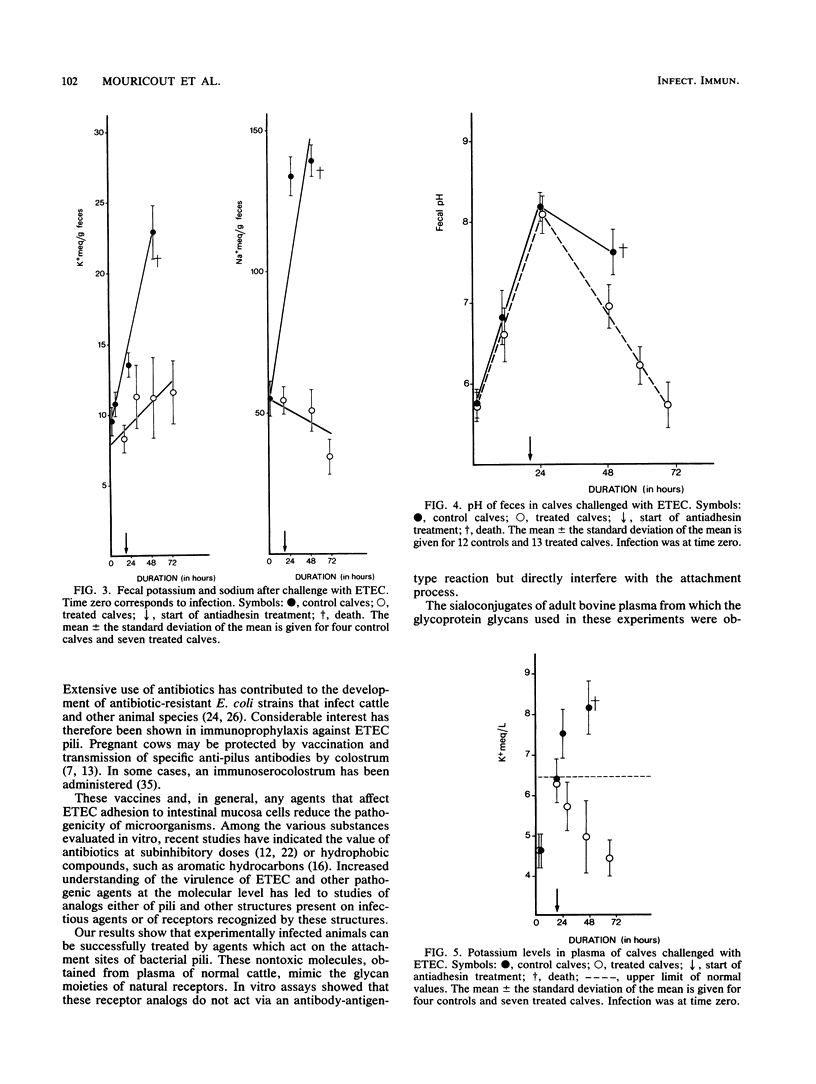
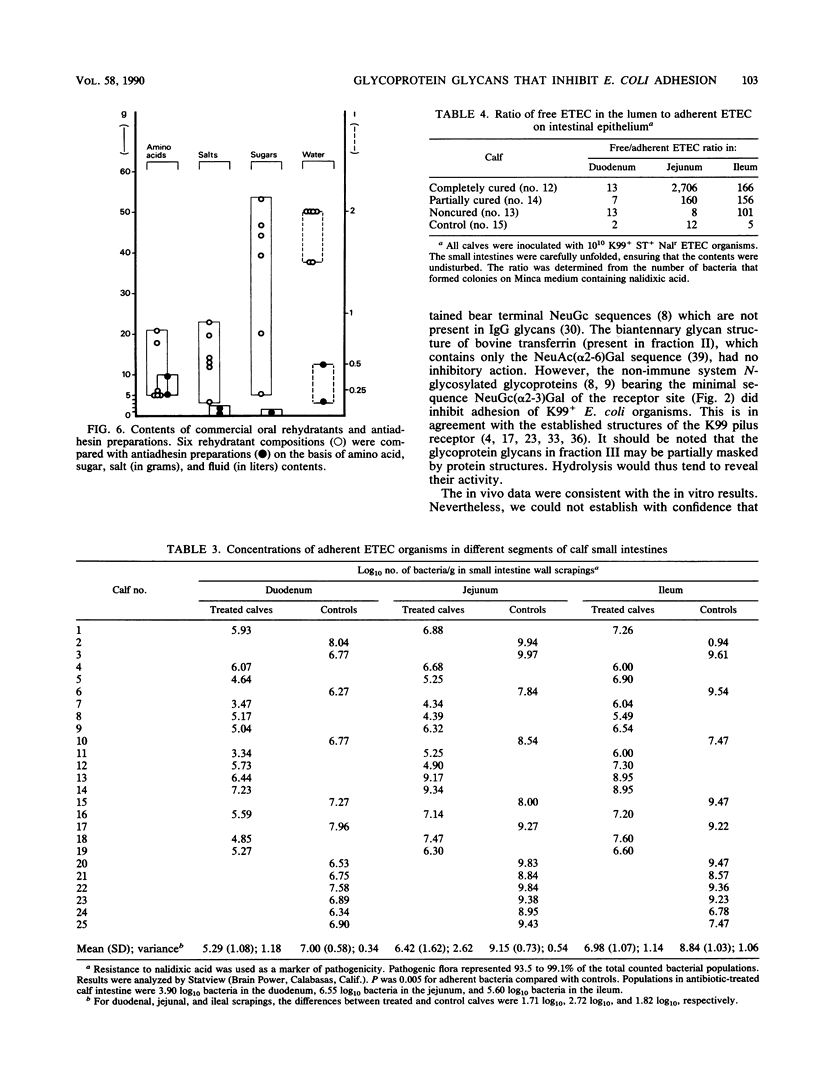
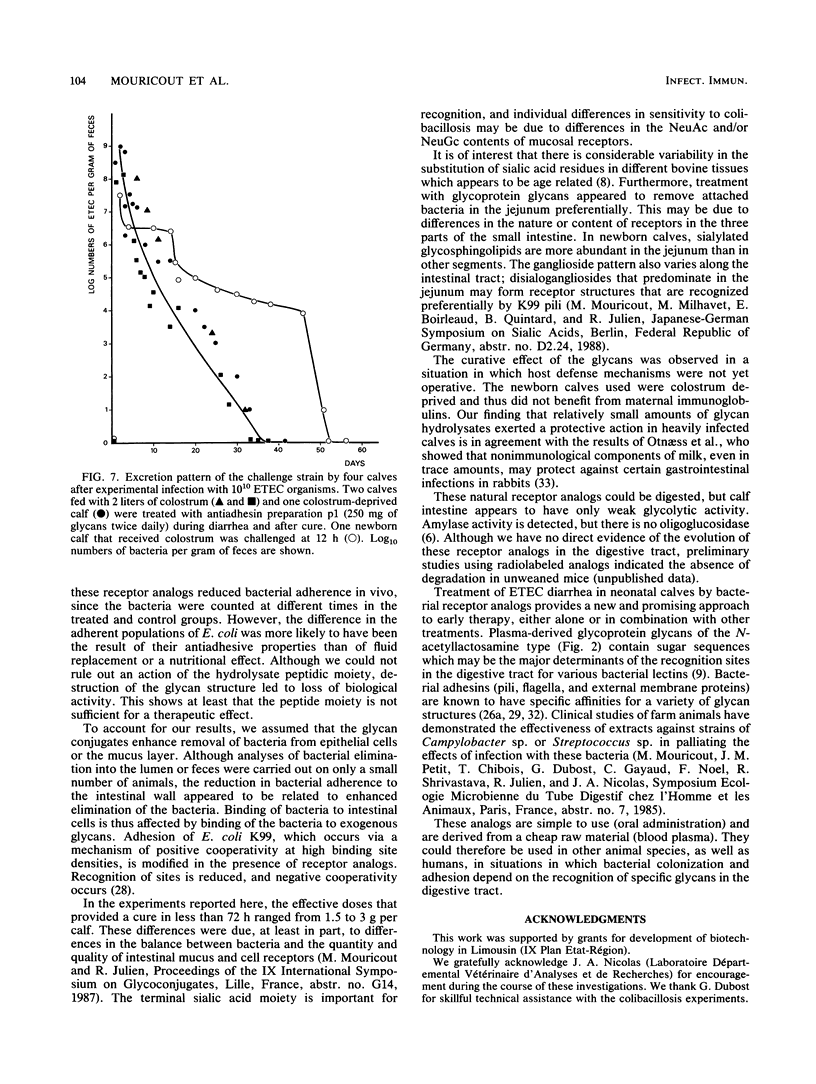
Calf diarrhea due to infection by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli was treated by administration of glycoprotein glycans derived from bovine plasma. The glycan moieties of the nonimmunoglobulin fraction of plasma mimicked the oligosaccharide moiety of intestinal receptors recognized by K99 pili. These glycoprotein glycans inhibited adhesion of E. coli K99+ ST+ to erythrocyte glycoconjugates in vitro, and they protected colostrum-deprived newborn calves against lethal doses of enterotoxigenic E. coli (10(10) bacteria). Adhesion of bacteria to the intestines (duodenum, jejunum, and ileum) was significantly reduced (by 2 orders of magnitude) in treated calves.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler-Nissen J. Enzymatic hydrolysis of proteins for increased solubility. J Agric Food Chem. 1976 Nov-Dec;24(6):1090–1093. doi: 10.1021/jf60208a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capdeville Y., Frézal J., Jos J., Rey J., Lamy M. Culture de tissu intestinal de veau. Etude de la différenciation cellulaire et des activités disaccharasiques. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1967 Jan 16;264(3):519–521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contrepois M. G., Girardeau J. P. Additive protective effects of colostral antipili antibodies in calves experimentally infected with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):947–949. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.947-949.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deneke C. F., Thorne G. M., Larson A. D., Gorbach S. L. Effect of tetracycline on the attachment of K88+ enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli to porcine small-intestinal cells. J Infect Dis. 1985 Nov;152(5):1032–1036. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.5.1032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougan G., Morrissey P. Molecular analysis of the virulence determinants of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from domestic animals: applications for vaccine development. Vet Microbiol. 1985 Apr;10(3):241–257. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(85)90050-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellens D. J., de Leeuw P. W., Straver P. J., van Balken J. A. Comparison of five diagnostic methods for the detection of rotavirus antigens in calf faeces. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1978 Nov 17;166(1-4):157–163. doi: 10.1007/BF02121145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkowski W., Edwards M., Schaeffer A. J. Inhibitory effect of substituted aromatic hydrocarbons on adherence of Escherichia coli to human epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1986 Jun;52(3):863–866. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.3.863-866.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouet P., Contrepois M., Dubourguier H. C., Riou Y., Scherrer R., Laporte J., Vautherot J. F., Cohen J., L'Haridon R. The experimental production of diarrhoea in colostrum deprived axenic and gnotoxenic calves with enteropathogenic Escherichia coli, rotavirus, coronavirus and in a combined infection of rotavirus and E. coli. Ann Rech Vet. 1978;9(3):433–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Svennerholm A. M., Ahrén C. Nonimmunoglobulin fraction of human milk inhibits bacterial adhesion (hemagglutination) and enterotoxin binding of Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):136–141. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.136-141.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Svennerholm A. M., Lindblad M. Receptor-like glycocompounds in human milk that inhibit classical and El Tor Vibrio cholerae cell adherence (hemagglutination). Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):147–154. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.147-154.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs A. A., van den Berg P. A., Bak H. J., de Graaf F. K. Localization of lysine residues in the binding domain of the K99 fibrillar subunit of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jul 25;872(1-2):92–97. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(86)90151-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein U., Pawelzik M., Opferkuch W. Influence of beta-lactam antibiotics, fosfomycin and vancomycin on the adherence (hemagglutination) of Escherichia coli-containing different adhesins. Chemotherapy. 1985;31(2):138–145. doi: 10.1159/000238326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl M., Wadström T. K99 surface haemagglutinin of enterotoxigenic E. coli recognize terminal N-acetylgalactosamine and sialic acid residues of glycophorin and other complex glycoconjugates. Vet Microbiol. 1984 Jul;9(3):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(84)90042-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linton A. H. Antibiotic resistance in veterinary practice. In Pract. 1982 Jan;4(1):11–15. doi: 10.1136/inpract.4.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan E. F., Pearson G. R., McNulty M. S. Studies on the immunity of the calf to colibacillosis--VII: the experimental reproduction of enteric colibacillosis in colostrum-fed calves. Vet Rec. 1977 Nov 26;101(22):443–446. doi: 10.1136/vr.101.22.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSweegan E., Walker R. I. Identification and characterization of two Campylobacter jejuni adhesins for cellular and mucous substrates. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):141–148. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.141-148.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouricout M. A., Julien R. A. Pilus-mediated binding of bovine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli to calf small intestinal mucins. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1216–1223. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1216-1223.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neeser J. R., Koellreutter B., Wuersch P. Oligomannoside-type glycopeptides inhibiting adhesion of Escherichia coli strains mediated by type 1 pili: preparation of potent inhibitors from plant glycoproteins. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):428–436. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.428-436.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata S., Muramatsu T., Kobata A. Fractionation of glycopeptides by affinity column chromatography on concanavalin A-sepharose. J Biochem. 1975 Oct;78(4):687–696. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono E., Abe K., Nakazawa M., Naiki M. Ganglioside epitope recognized by K99 fimbriae from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):907–911. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.907-911.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otnaess A. B., Laegreid A., Ertresvåg K. Inhibition of enterotoxin from Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae by gangliosides from human milk. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):563–569. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.563-569.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit H., Gaastra W., Kamerling J. P., Vliegenthart J. F., de Graaf F. K. Isolation and structural characterization of the equine erythrocyte receptor for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K99 fimbrial adhesin. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):578–584. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.578-584.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Halls S. Studies on Escherichia coli enterotoxin. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(2):531–543. doi: 10.1002/path.1700930212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Huggins M. B. The influence of plasmid-determined and other characteristics of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli on their ability to proliferate in the alimentary tracts of piglets, calves and lambs. J Med Microbiol. 1978 Nov;11(4):471–492. doi: 10.1099/00222615-11-4-471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll B. J., Holmgren J., Bardhan P. K., Huq I., Greenough W. B., 3rd, Fredman P., Svennerholm L. Binding of intraluminal toxin in cholera: trial of GM1 ganglioside charcoal. Lancet. 1980 Oct 25;2(8200):888–891. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Graaf F. K., Klemm P., Gaastra W. Purification, characterization, and partial covalent structure of Escherichia coli adhesive antigen K99. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):877–883. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.877-883.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Graaf F. K., Roorda I. Production, purification, and characterization of the fimbrial adhesive antigen F41 isolated from calf enteropathogenic Escherichia coli strain B41M. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):751–758. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.751-758.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


