Abstract
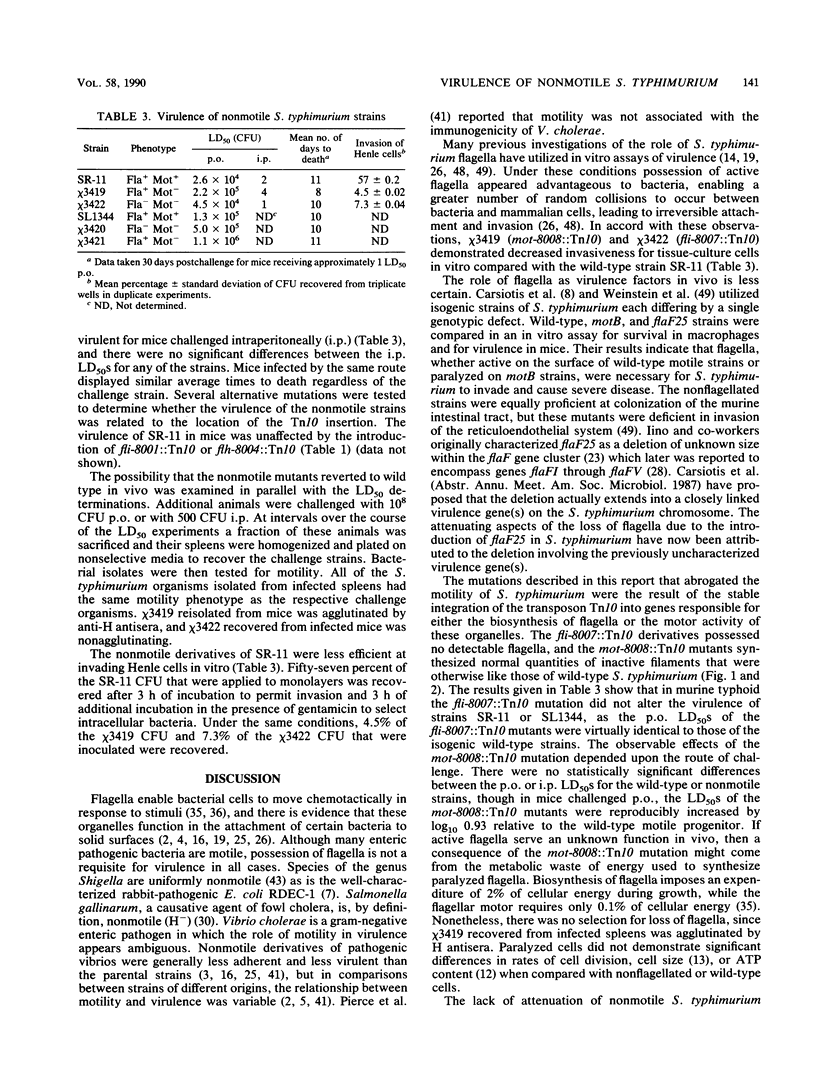
Nonmotile flagellated (mot) and nonflagellated (fla) mutants of Salmonella typhimurium LT-2 were isolated from a collection of mutants with random Tn10-insertion mutations. Both classes of mutants were resistant to infection by the flagellotropic bacteriophage chi. The nonflagellated (fla::Tn10) mutants did not react with H antigen-specific antisera and did not possess flagella when examined by electron microscopy, and sheared-cell extracts were devoid of flagellin. The nonmotile (mot::Tn10) mutants reacted with H-specific antisera and expressed paralyzed flagella that were indistinguishable from wild-type flagella. The Tn10 insertions in strain LT-2 were mapped to loci in regions II (flh and mot) and III (fli) of the flagellar genes, and the mutations were transduced into the mouse-virulent S. typhimurium strains SR-11 and SL1344. Lack of motility reduced the ability of S. typhimurium to invade Henle cells in vitro, yet the virulence in mice of the nonmotile mutants of SR-11 and SL1344 was unaffected by the inactivity or loss of flagella. Wild-type SR-11 had a 50% lethal dose (LD50) in BALB/c mice following oral (p.o.) challenge of 2.4 x 10(4) CFU. The p.o. LD50 of the SR-11 fli-8007::Tn10 mutant was 4.5 x 10(4) CFU. The mot-8008::Tn10 mutation in SR-11 conferred paralyzed flagella and increased the p.o. LD50 in mice to 2.2 x 10(5) CFU, but this was not statistically significant. A similar increase in the p.o. LD50 was observed when the SL1344 mot-8008::Tn10 mutant was tested in mice. Wild-type SR-11 and the isogenic nonflagellated and nonmotile mutants were equally virulent in mice challenged via intraperitoneal injection.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames G. F., Spudich E. N., Nikaido H. Protein composition of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium: effect of lipopolysaccharide mutations. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):406–416. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.406-416.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attridge S. R., Rowley D. The role of the flagellum in the adherence of Vibrio cholerae. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):864–872. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baselski V. S., Upchurch S., Parker C. D. Isolation and phenotypic characterization of virulence-deficient mutants of Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):181–188. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.181-188.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belas M. R., Colwell R. R. Adsorption kinetics of laterally and polarly flagellated Vibrio. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1568–1580. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1568-1580.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharjee J. W., Srivastava B. S. Adherence of wild-type and mutant strains of Vibrio cholerae to normal and immune intestinal tissue. Bull World Health Organ. 1979;57(1):123–128. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS S. R., 3rd CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATIONS ASSOCIATED WITH MUTATIONS TO BACTERIOPHAGE RESISTANCE IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jan;89:28–40. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.1.28-40.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantey J. R., Blake R. K. Diarrhea due to Escherichia coli in the rabbit: a novel mechanism. J Infect Dis. 1977 Mar;135(3):454–462. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.3.454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carsiotis M., Weinstein D. L., Karch H., Holder I. A., O'Brien A. D. Flagella of Salmonella typhimurium are a virulence factor in infected C57BL/6J mice. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):814–818. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.814-818.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENOMOTO M., IINO T. COLONIAL DIMORPHISM IN NONMOTILE SALMONELLA. J Bacteriol. 1963 Sep;86:473–477. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.3.473-477.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enomoto M. Genetic studies of paralyzed mutant in Salmonella. I. Genetic fine structure of the mot loci in Salmonella typhimurium. Genetics. 1966 Sep;54(3):715–726. doi: 10.1093/genetics/54.3.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields P. I., Swanson R. V., Haidaris C. G., Heffron F. Mutants of Salmonella typhimurium that cannot survive within the macrophage are avirulent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5189–5193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galán J. E., Curtiss R., 3rd Cloning and molecular characterization of genes whose products allow Salmonella typhimurium to penetrate tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6383–6387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guentzel M. N., Berry L. J. Motility as a virulence factor for Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1975 May;11(5):890–897. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.5.890-897.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulig P. A., Curtiss R., 3rd Plasmid-associated virulence of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):2891–2901. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.2891-2901.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett J., Attridge S., Rowley D. Oral immunization with live, avirulent fla+ strains of Salmonella protects mice against subsequent oral challenge with Salmonella typhimurium. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;157(1):78–84. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.1.78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohmann A. W., Schmidt G., Rowley D. Intestinal colonization and virulence of Salmonella in mice. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):763–770. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.763-770.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiseth S. K., Stocker B. A. Aromatic-dependent Salmonella typhimurium are non-virulent and effective as live vaccines. Nature. 1981 May 21;291(5812):238–239. doi: 10.1038/291238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., Kutsukake K., Iino T., Yamaguchi S. Hook-associated proteins essential for flagellar filament formation in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):100–108. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.100-108.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino T., Enomoto M. Genetical studies of non-flagellate mutants of Salmonella. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Jun;43(3):315–327. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-3-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino T., Komeda Y., Kutsukake K., Macnab R. M., Matsumura P., Parkinson J. S., Simon M. I., Yamaguchi S. New unified nomenclature for the flagellar genes of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Dec;52(4):533–535. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.4.533-535.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Freter R. Adhesive properties of Vibrio cholerae: nature of the interaction with isolated rabbit brush border membranes and human erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):240–245. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.240-245.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Richardson L. A., Uhlman D. The invasion of HeLa cells by Salmonella typhimurium: reversible and irreversible bacterial attachment and the role of bacterial motility. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Dec;127(2):351–360. doi: 10.1099/00221287-127-2-351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagawa H., Nishiyama T., Yamaguchi S. Motility development of Salmonella typhimurium cells with flaV mutations after addition of exogenous flagellin. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):435–437. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.435-437.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutsukake K., Iino T., Komeda Y., Yamaguchi S. Functional homology of fla genes between Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1980 Apr;178(1):59–67. doi: 10.1007/BF00267213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutsukake K., Ohya Y., Yamaguchi S., Iino T. Operon structure of flagellar genes in Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Sep;214(1):11–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00340172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENNOX E. S. Transduction of linked genetic characters of the host by bacteriophage P1. Virology. 1955 Jul;1(2):190–206. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(55)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYNELL E. W. A phage, phi chi, which attacks motile bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Jun;25:253–290. doi: 10.1099/00221287-25-2-253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., Aizawa S. Bacterial motility and the bacterial flagellar motor. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1984;13:51–83. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.13.060184.000411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayfield C. I., Inniss W. E. A rapid, simple method for staining bacterial flagella. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Sep;23(9):1311–1313. doi: 10.1139/m77-198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick B. A., Stocker B. A., Laux D. C., Cohen P. S. Roles of motility, chemotaxis, and penetration through and growth in intestinal mucus in the ability of an avirulent strain of Salmonella typhimurium to colonize the large intestine of streptomycin-treated mice. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2209–2217. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2209-2217.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. A., Sanchez D., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1529-1537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Cray W. C., Jr, Kaper J. B., Mekalanos J. J. Determinants of immunogenicity and mechanisms of protection by virulent and mutant Vibrio cholerae O1 in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):142–148. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.142-148.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHNEIDER H. A., ZINDER N. D. Nutrition of the host and natural resistance to infection. V. An improved assay employing genetic markers in the double strain inoculation test. J Exp Med. 1956 Feb 1;103(2):207–223. doi: 10.1084/jem.103.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmieger H. Phage P22-mutants with increased or decreased transduction abilities. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;119(1):75–88. doi: 10.1007/BF00270447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. I. Bacterial flagella. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:397–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita T., Kanegasaki S. Enhanced phagocytic response of macrophages to bacteria by physical impact caused by bacterial motility or centrifugation. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):865–870. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.865-870.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein D. L., Carsiotis M., Lissner C. R., O'Brien A. D. Flagella help Salmonella typhimurium survive within murine macrophages. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):819–825. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.819-825.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
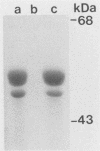
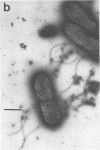
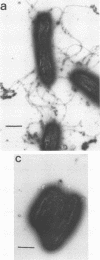
- Yamaguchi S., Fujita H., Ishihara A., Aizawa S., Macnab R. M. Subdivision of flagellar genes of Salmonella typhimurium into regions responsible for assembly, rotation, and switching. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):187–193. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.187-193.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZINDER N. D., LEDERBERG J. Genetic exchange in Salmonella. J Bacteriol. 1952 Nov;64(5):679–699. doi: 10.1128/jb.64.5.679-699.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]