Abstract
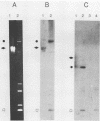
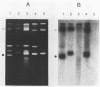
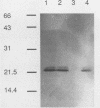
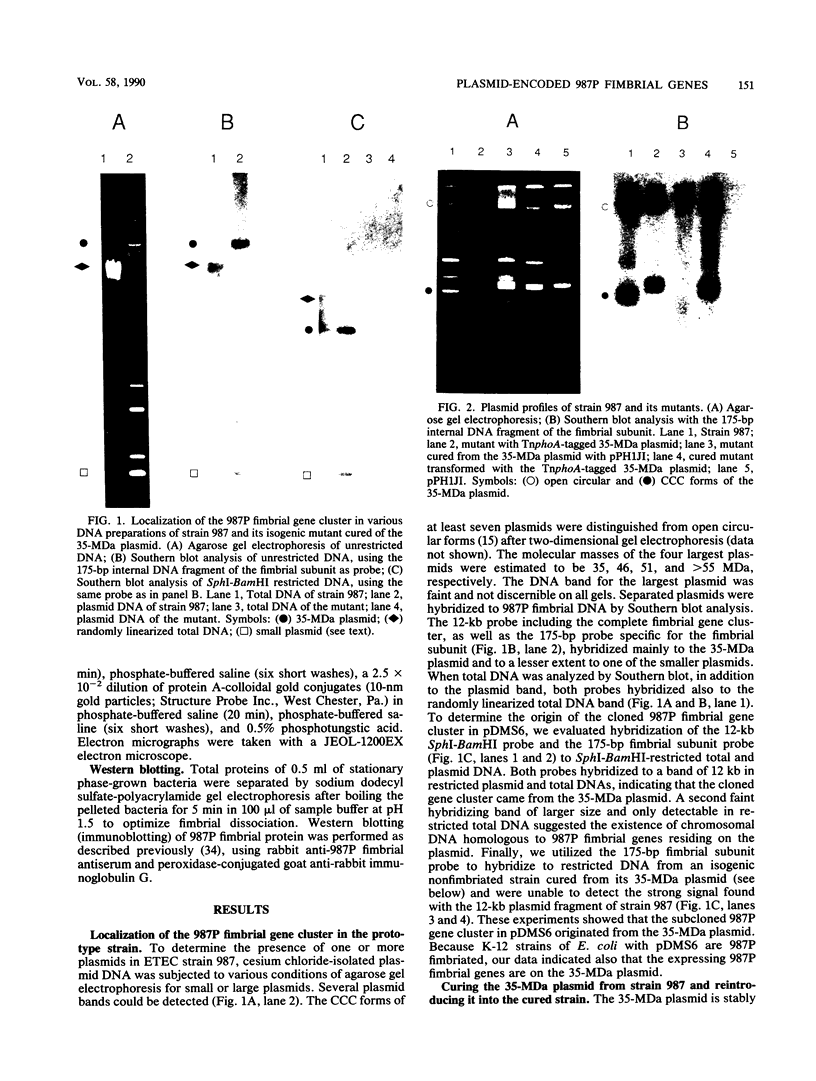
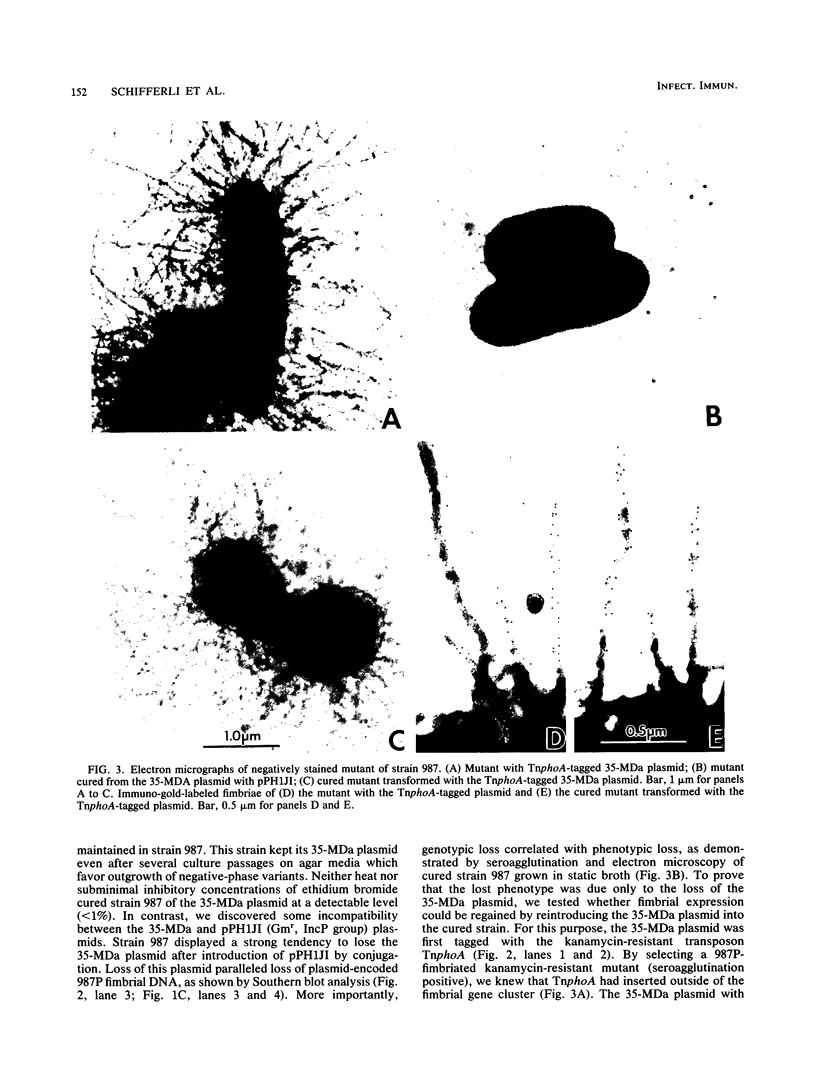
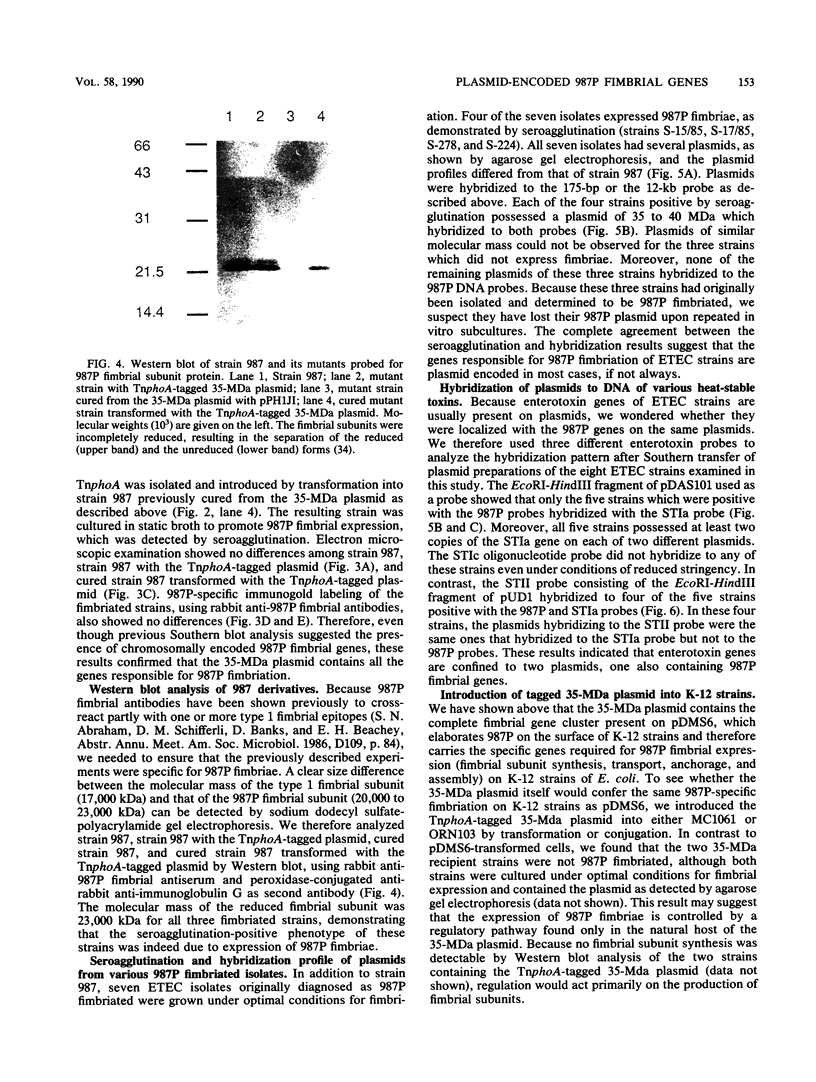
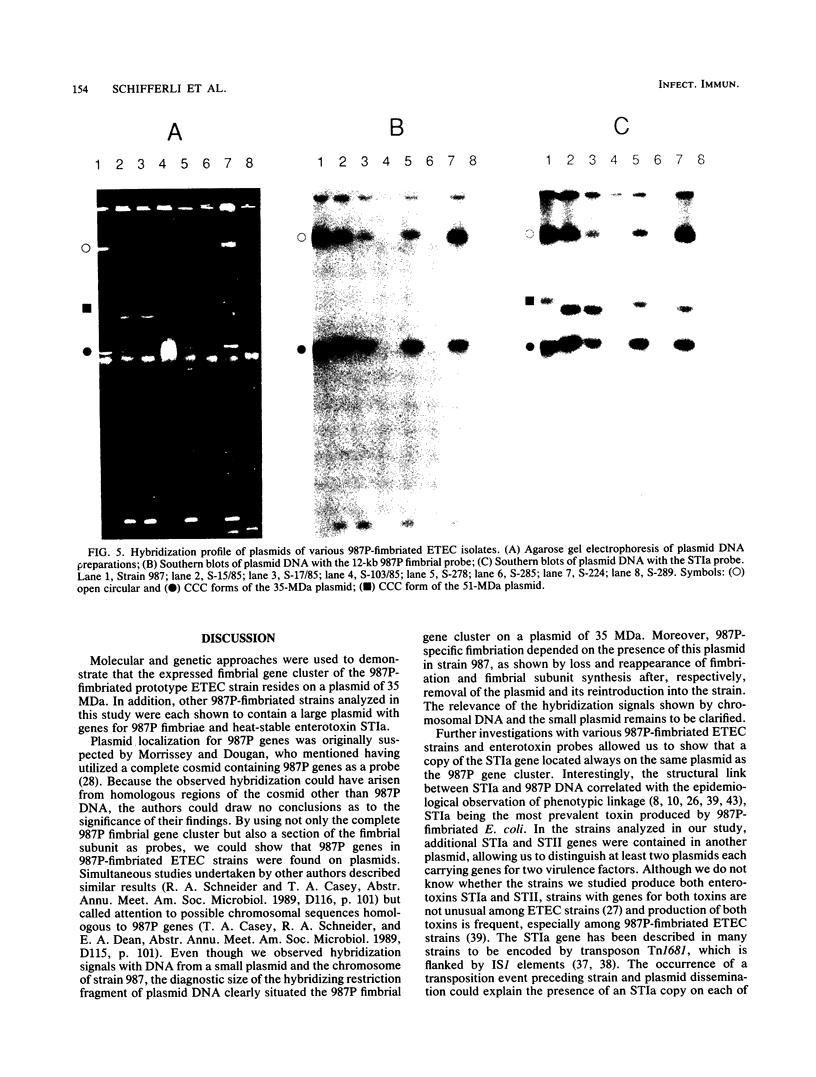
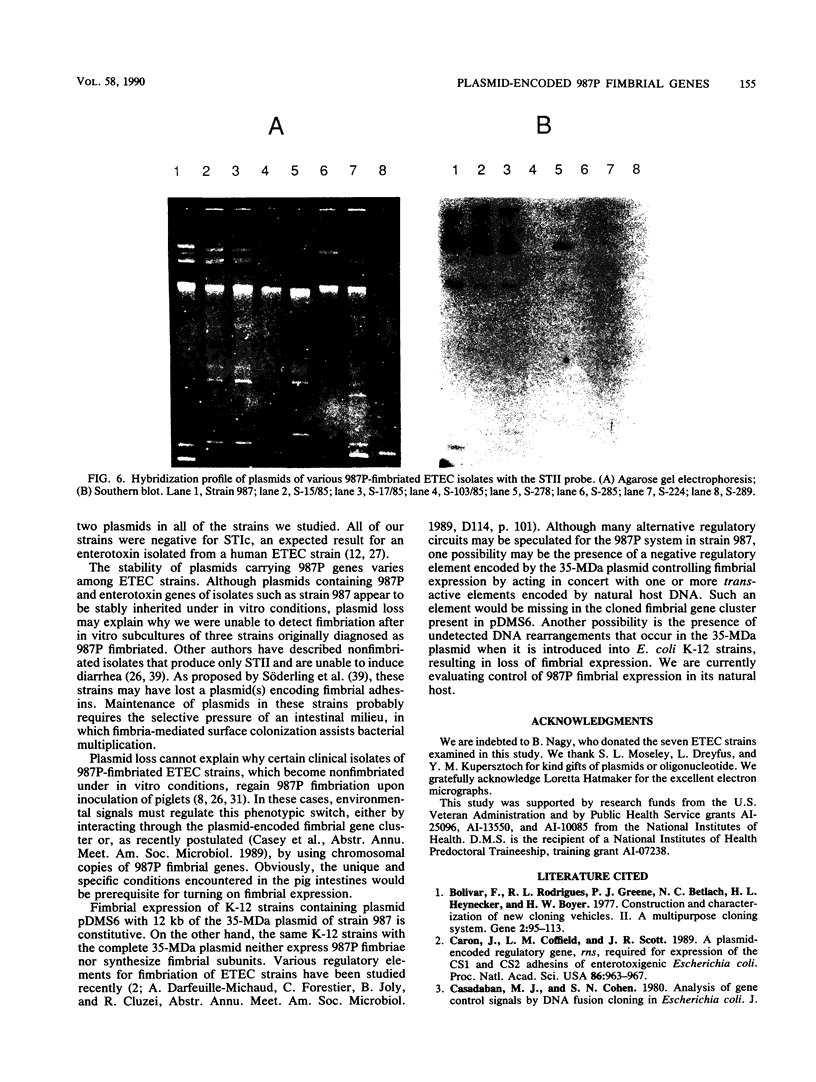
A clone containing the 987P fimbrial gene cluster was selected from a cosmid library of total DNA of the prototype Escherichia coli strain 987 by using 987P-specific antiserum. A subclone of 12 kilobases containing all of the genes required for fimbrial expression on a nonfimbriated K-12 strain of E. coli and a DNA fragment internal to the fimbrial subunit gene were used to probe the prototype strain and various isolates of 987P-fimbriated enterotoxigenic E. coli. All strains had several plasmids, as shown by agarose gel electrophoresis, and each of five strains which expressed 987P fimbriae showed a plasmid of 35 to 40 megadaltons (MDa) hybridizing to both 987P-specific probes. Hybridization to restricted DNA of strain 987 supported a plasmid origin for the cloned 987P gene cluster. Moreover, an isogenic strain which had lost its 35-MDa plasmid was no longer capable of synthesizing fimbrial subunits, but regained fimbrial expression after reintroduction of the TnphoA (Tn5 IS50L::phoA)-tagged 35-MDa plasmid. Absence of fimbrial subunit synthesis in K-12 strains transformed with the 35-MDa plasmid alone suggested the requirement of regulatory elements existing in strain 987 but missing in K-12 strains. A probe for the heat-stable enterotoxin STIa hybridized in each of the 987P-fimbriated strains to the plasmid containing the 987P genes and in most of these strains to an additional plasmid which contained the gene for the heat-stable enterotoxin STII. Occurrence of the 987P and STIa genes on the same replicon correlates with epidemiological observations, STIa being the most prevalent toxin produced by 987P-fimbriated E. coli.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caron J., Coffield L. M., Scott J. R. A plasmid-encoded regulatory gene, rns, required for expression of the CS1 and CS2 adhesins of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):963–967. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Graaf F. K., Mooi F. R. The fimbrial adhesins of Escherichia coli. Adv Microb Physiol. 1986;28:65–143. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60237-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean E. A., Whipp S. C., Moon H. W. Age-specific colonization of porcine intestinal epithelium by 987P-piliated enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):82–87. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.82-87.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbrother J. M., Larivière S., Johnson W. M. Prevalence of fimbrial antigens and enterotoxins in nonclassical serogroups of Escherichia coli isolated from newborn pigs with diarrhea. Am J Vet Res. 1988 Aug;49(8):1325–1328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. M., Long S. R., Brown S. E., Buikema W. J., Ausubel F. M. Construction of a broad host range cosmid cloning vector and its use in the genetic analysis of Rhizobium mutants. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):289–296. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinée P. A., Jansen W. H. Detection of enterotoxigenicity and attachment factors in Escherichia coli strains of human, porcine and bovine origin; a comparative study. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1979 Apr;243(2-3):245–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez C., Barondess J., Manoil C., Beckwith J. The use of transposon TnphoA to detect genes for cell envelope proteins subject to a common regulatory stimulus. Analysis of osmotically regulated genes in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 20;195(2):289–297. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90650-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzman-Verduzco L. M., Kupersztoch Y. M. Fusion of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin and heat-labile enterotoxin B subunit. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5201–5208. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5201-5208.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas D., Holloway B. W. R factor variants with enhanced sex factor activity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Mar 30;144(3):243–251. doi: 10.1007/BF00341722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintermann G., Fischer H. M., Crameri R., Hütter R. Simple procedure for distinguishing CCC, OC, and L forms of plasmid DNA by agarose gel electrophoresis. Plasmid. 1981 May;5(3):371–373. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch P. R., Beringer J. E. A physical map of pPH1JI and pJB4JI. Plasmid. 1984 Sep;12(2):139–141. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(84)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B., Collins J. A small cosmid for efficient cloning of large DNA fragments. Gene. 1980 Nov;11(3-4):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90069-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacson R. E., Fusco P. C., Brinton C. C., Moon H. W. In vitro adhesion of Escherichia coli to porcine small intestinal epithelial cells: pili as adhesive factors. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):392–397. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.392-397.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Isaacson R. E. Proteinaceous bacterial adhesins and their receptors. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1983;10(3):229–260. doi: 10.3109/10408418209113564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. H., Moseley S. L., Moon H. W., Whipp S. C., Gyles C. L., So M. Characterization of the gene encoding heat-stable toxin II and preliminary molecular epidemiological studies of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli heat-stable toxin II producers. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):264–268. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.264-268.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M. Escherichia coli that cause diarrhea: enterotoxigenic, enteropathogenic, enteroinvasive, enterohemorrhagic, and enteroadherent. J Infect Dis. 1987 Mar;155(3):377–389. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.3.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. TnphoA: a transposon probe for protein export signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8129–8133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooi F. R., de Graaf F. K. Molecular biology of fimbriae of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;118:119–138. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70586-1_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Kohler E. M., Schneider R. A., Whipp S. C. Prevalence of pilus antigens, enterotoxin types, and enteropathogenicity among K88-negative enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli from neonatal pigs. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):222–230. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.222-230.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Schneider R. A., Moseley S. L. Comparative prevalence of four enterotoxin genes among Escherichia coli isolated from swine. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Feb;47(2):210–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey P. M., Dougan G. Expression of a cloned 987P adhesion-antigen fimbrial determinant in Escherichia coli K-12 strain HB101. Gene. 1986;43(1-2):79–84. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Dougan G., Schneider R. A., Moon H. W. Cloning of chromosomal DNA encoding the F41 adhesin of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and genetic homology between adhesins F41 and K88. J Bacteriol. 1986 Sep;167(3):799–804. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.3.799-804.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Hardy J. W., Hug M. I., Echeverria P., Falkow S. Isolation and nucleotide sequence determination of a gene encoding a heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1167–1174. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1167-1174.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy B., Moon H. W., Isaacson R. E. Colonization of porcine intestine by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli: selection of piliated forms in vivo, adhesion of piliated forms to epithelial cells in vitro, and incidence of a pilus antigen among porcine enteropathogenic E. coli. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):344–352. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.344-352.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orndorff P. E., Spears P. A., Schauer D., Falkow S. Two modes of control of pilA, the gene encoding type 1 pilin in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):321–330. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.321-330.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F. Serology of Escherichia coli fimbriae. Prog Allergy. 1983;33:80–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifferli D. M., Abraham S. N., Beachey E. H. Use of monoclonal antibodies to probe subunit- and polymer-specific epitopes of 987P fimbriae of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1987 Apr;55(4):923–930. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.4.923-930.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So M., Atchison R., Falkow S., Moseley S., McCarthy B. J. A study of the dissemination of Tn1681: a bacterial transposon encoding a heat-stable toxin among enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolates. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):53–58. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So M., Heffron F., McCarthy B. J. The E. coli gene encoding heat stable toxin is a bacterial transposon flanked by inverted repeats of IS1. Nature. 1979 Feb 8;277(5696):453–456. doi: 10.1038/277453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommerfelt H., Kalland K. H., Raj P., Moseley S. L., Bhan M. K., Bjorvatn B. Cloned polynucleotide and synthetic oligonucleotide probes used in colony hybridization are equally efficient in the identification of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Nov;26(11):2275–2278. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.11.2275-2278.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderlind O., Thafvelin B., Möllby R. Virulence factors in Escherichia coli strains isolated from Swedish piglets with diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 May;26(5):879–884. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.5.879-884.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilghman S. M., Tiemeier D. C., Polsky F., Edgell M. H., Seidman J. G., Leder A., Enquist L. W., Norman B., Leder P. Cloning specific segments of the mammalian genome: bacteriophage lambda containing mouse globin and surrounding gene sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4406–4410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. A., Francis D. H. Fimbriae and enterotoxins associated with Escherichia coli serogroups isolated from pigs with colibacillosis. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Feb;47(2):213–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Graaf F. K., Klaasen P. Organization and expression of genes involved in the biosynthesis of 987P fimbriae. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Jul;204(1):75–81. doi: 10.1007/BF00330190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]