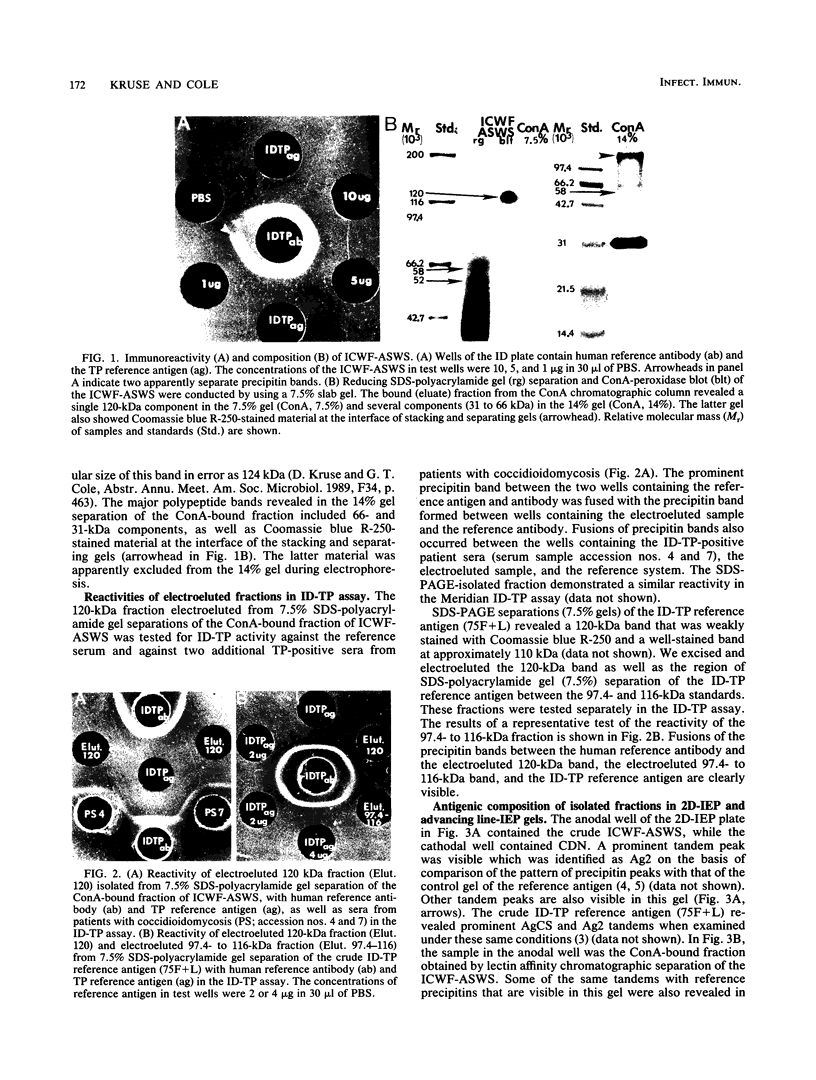
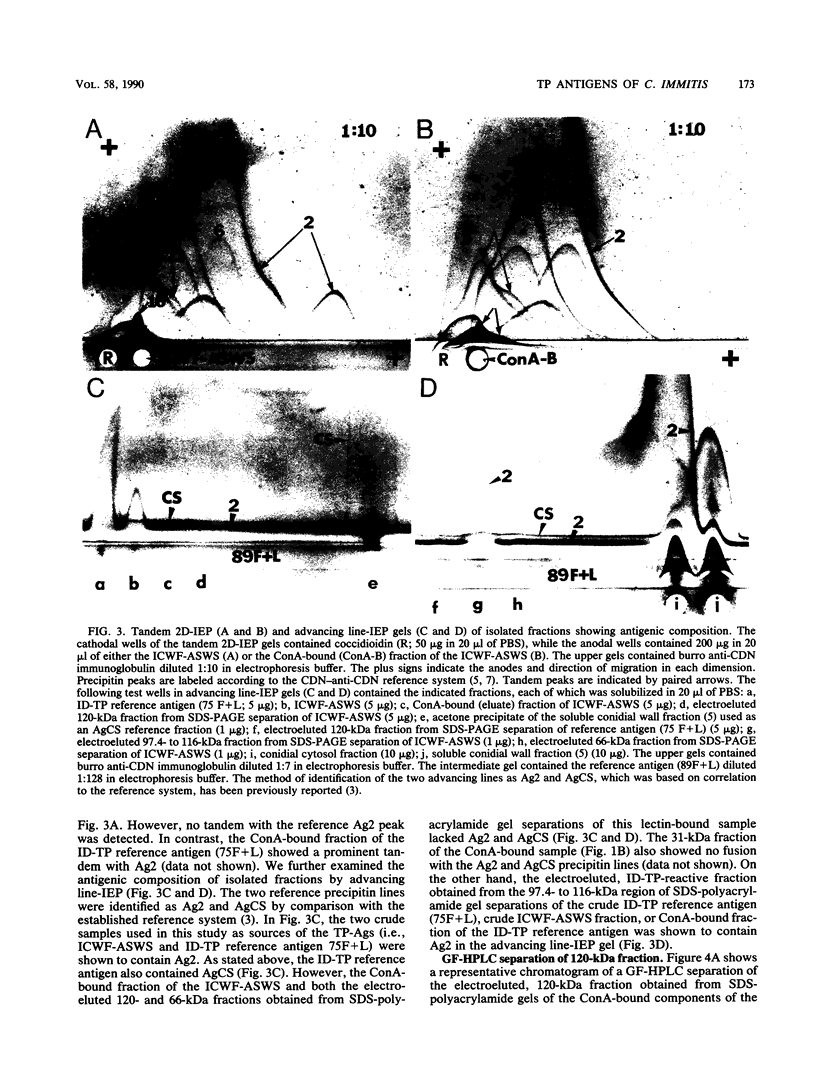
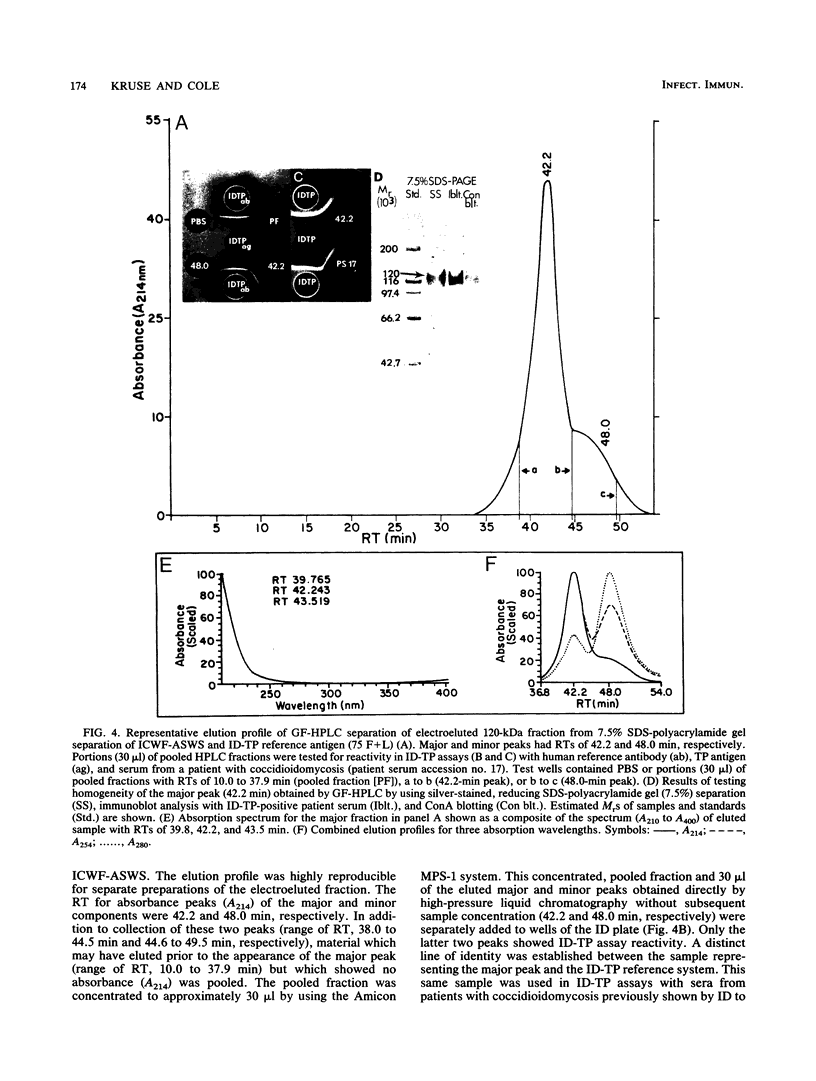
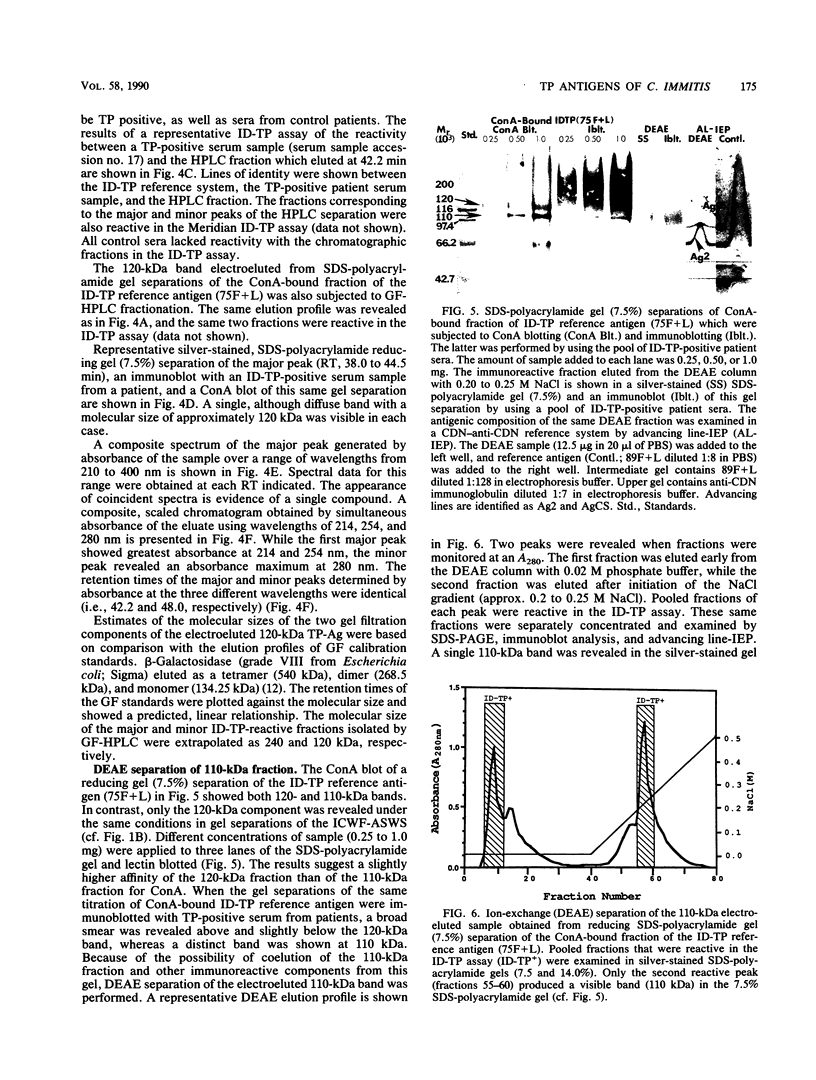
Abstract
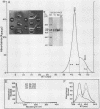
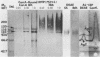
Patients presenting with primary coccidioidal infection have been shown by earlier investigators to produce immunoglobulin M (IgM) precipitin antibodies to lysates of mycelial and spherule phases of Coccidioides immitis. This humoral response has been detected by tube precipitin (TP) and immunodiffusion (ID)-TP assays of patient sera, which are valuable aids in early diagnosis of coccidioidomycosis. Several reports of antigenic fractions which show reactivity with patient TP antibody have been published. However, confusion persists with respect to the nature of the specific serologically reactive macromolecule(s). In this study we isolated two TP antibody-reactive antigens (TP-Ags) from an alkali-soluble, water-soluble fraction of the inner conidial wall and a culture filtrate plus toluene lysate of the mycelial phase of C. immitis. The crude antigens were first separated by concanavalin A (ConA) chromatography. The TP-Ags were identified in ID-TP assays as 120- and 110-kilodalton (kDa) fractions which were electroeluted from reducing sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis separations of the ConA-bound conidial wall extract and ConA-bound culture filtrate plus lysate preparation, respectively. Following electroelution, the 120-kDa fraction was subjected to gel filtration chromatography which yielded a major 240-kDa and minor 120-kDa component. The apparent dimer may be a product of disulfide bond formation resulting from reassociation of the reduced, monomeric components (120 kDa). The latter was suggested by the presence of cysteine in the isolated fraction. The electroeluted 110-kDa fraction was subjected to ion-exchange chromatography. The DEAE-isolated, TP antibody-reactive fraction was identified as antigen 2 in the coccidioidin-anti-coccidioidin reference system. Homogeneity of the TP-Ags was demonstrated in silver-stained sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels of the respective chromatographically isolated fractions. The two purified TP-Ags showed reactivity in the TP and ID-TP assays and were capable of binding patient IgM but comparatively little IgG antibody, as determined by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. It appears that the diagnostic TP reaction between sera from patients with coccidioidomycosis and the ID reference antigens examined in this study is a composite of IgM binding to both a 120-kDa and a 110-kDa antigen.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Calhoun D. L., Osir E. O., Dugger K. O., Galgiani J. N., Law J. H. Humoral antibody responses to specific antigens of Coccidioides immitis. J Infect Dis. 1986 Aug;154(2):265–272. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.2.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catanzaro A., Flatauer F. Detection of serum antibodies in coccidioidomycosis by solid-phase radioimmunoassay. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jan;147(1):32–39. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.1.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. T., Kirkland T. N., Franco M., Zhu S., Yuan L., Sun S. H., Hearn V. M. Immunoreactivity of a surface wall fraction produced by spherules of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2695–2701. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2695-2701.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. T., Kirkland T. N., Sun S. H. An immunoreactive, water-soluble conidial wall fraction of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):657–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.657-667.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. T., Kruse D., Zhu S. W., Seshan K. R., Wheat R. W. Composition, serologic reactivity, and immunolocalization of a 120-kilodalton tube precipitin antigen of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):179–188. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.179-188.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. T., Zhu S. W., Pan S. C., Yuan L., Kruse D., Sun S. H. Isolation of antigens with proteolytic activity from Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1524–1534. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1524-1534.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Britt L. A. Antigenic identity of biologically active antigens in coccidioidin and spherulin. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2590–2596. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2590-2596.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Britt L. A. Isolation of a coccidioidin component that reacts with immunoglobulin M precipitin antibody. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):449–453. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.449-453.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Huppert M., Starr P., Britt L. A. Reactivity of alkali-soluble, water-soluble cell wall antigen of Coccidioides immitis with anti-Coccidioides immunoglobulin M precipitin antibody. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):502–507. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.502-507.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolan M. J., Cox R. A., Williams V., Woolley S. Development and characterization of a monoclonal antibody against the tube precipitin antigen of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1035–1039. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1035-1039.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galgiani J. N., Dugger K. O., Ampel N. M., Sun S. H., Law J. H. Extraction of serologic and delayed hypersensitivity antigens from spherules of Coccidioides immitis. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;11(2):65–80. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(88)90075-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. J., Reichert C. M., Misaki A. Interaction of concanavalin A with model substrates. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974;234(0):283–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb53040.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millette C. F., Scott B. K. Identification of spermatogenic cell plasma membrane glycoproteins by two-dimensional electrophoresis and lectin blotting. J Cell Sci. 1984 Jan;65:233–248. doi: 10.1242/jcs.65.1.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAPPAGIANIS D., SMITH C. E., KOBAYASHI G. S., SAITO M. T. Studies of antigens from young mycelia of Coccidioides immitis. J Infect Dis. 1961 Jan-Feb;108:35–44. doi: 10.1093/infdis/108.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabilloud T., Carpentier G., Tarroux P. Improvement and simplification of low-background silver staining of proteins by using sodium dithionite. Electrophoresis. 1988 Jun;9(6):288–291. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150090608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeke G. N., Jr, Becker J. W., Cunningham B. A., Gunther G. R., Wang J. L., Edelman G. M. Relationships between the structure and activities of concanavalin A. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974;234(0):369–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb53049.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH C. E., SAITO M. T., BEARD R. R., KEPP R. M., CLARK R. W., EDDIE B. U. Serological tests in the diagnosis and prognosis of coccidioidomycosis. Am J Hyg. 1950 Jul;52(1):1–21. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH C. E., SAITO M. T., SIMONS S. A. Pattern of 39,500 serologic tests in coccidioidomycosis. J Am Med Assoc. 1956 Feb 18;160(7):546–552. doi: 10.1001/jama.1956.02960420026008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan L., Cole G. T. Isolation and characterization of an extracellular proteinase of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):1970–1978. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.1970-1978.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer B. L., Pappagianis D. Characterization of a soluble protein of Coccidiodes immitis with activity as an immunodiffusion-complement fixation antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Nov;26(11):2250–2256. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.11.2250-2256.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer B. L., Pappagianis D. Immunoaffinity isolation and partial characterization of the Coccidioides immitis antigen detected by the tube precipitin and immunodiffusion-tube precipitin tests. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Aug;27(8):1759–1766. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.8.1759-1766.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]