Abstract
The gene encoding a 75-kilodalton (kDa) protein of Chlamydia trachomatis was cloned, expressed, and sequenced. Genomic libraries from C. trachomatis serovar D DNA were constructed in vectors pUC18 and lambda gt11 and were screened with a panel of monoclonal antibodies against C. trachomatis antigens. The only recombinants identified were those that reacted with antibody UM-13, which has specificity for a genus-specific epitope on the 75-kDa protein. The gene was localized to a 2.9-kilobase DNA fragment and sequenced. The gene consists of a long open reading frame of 1,956 nucleotides, which translates into 652 amino acids totalling 70,558 daltons in mass. Putative promoter elements and a ribosome binding site were identified within 5'-flanking sequences, and a typical rho-independent terminator was identified within 3'-flanking sequences. Screening of the GenBank nucleic acid sequence data bank revealed extensive similarity between the chlamydial 75-kDa gene and the heat shock protein 70 (hsp70) family or proteins. In particular, 71 and 69% amino acid sequence similarities were identified with hsp70 of Escherichia coli and Bacillus megaterium, respectively. Polyclonal antibodies were produced to the recombinant antigen in rabbits and detected epitopes on elementary bodies in enzyme-linked immunosorbent and indirect microimmunofluorescence assays. Antibodies reacted with an antigen of identical molecular mass in L2 and C serovars in an immunoblot assay and neutralized these serovars in cell culture. The 75-kDa protein appears to be a chlamydial homolog of hsp70, is immunoaccessible on native elementary bodies, and is a target for neutralization.
Full text
PDF


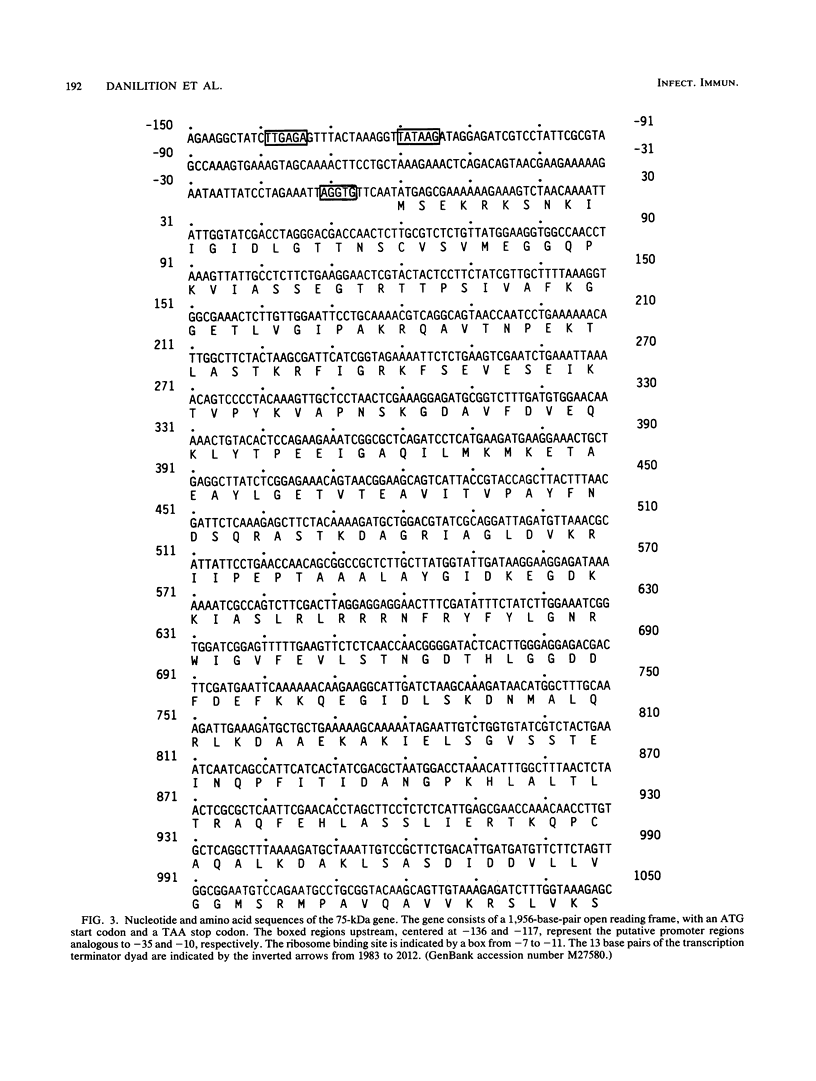
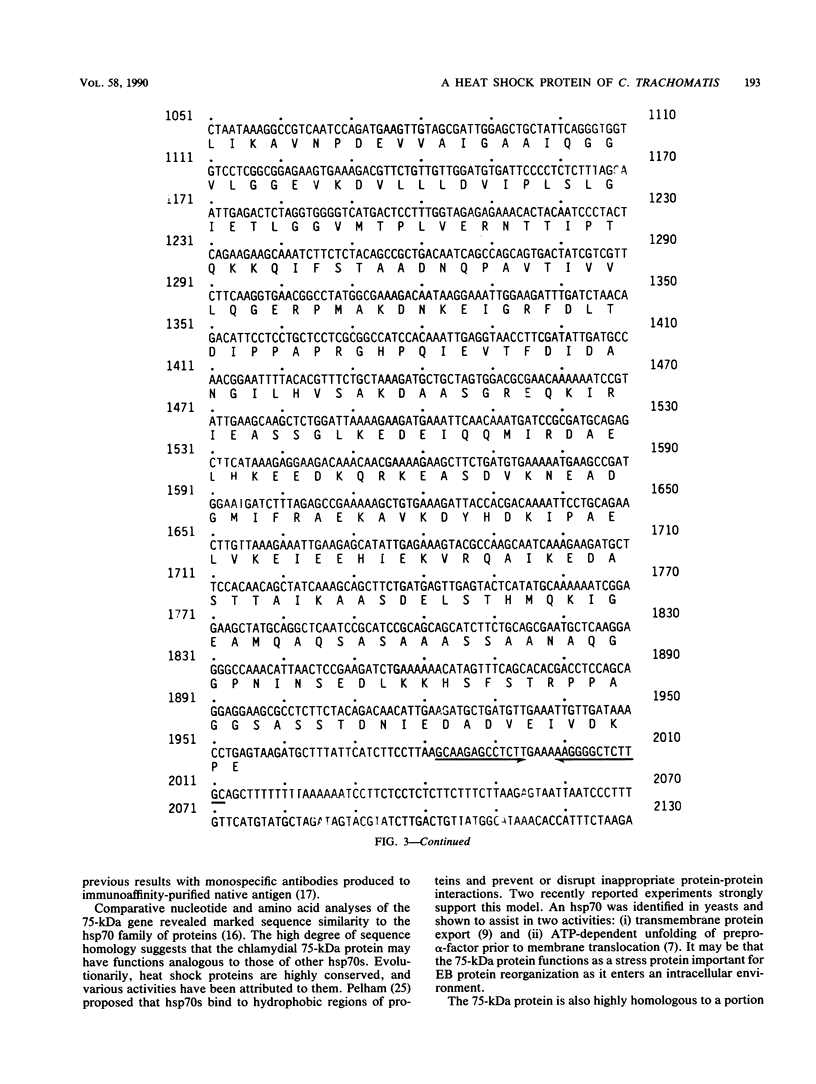



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bardwell J. C., Craig E. A. Major heat shock gene of Drosophila and the Escherichia coli heat-inducible dnaK gene are homologous. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):848–852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bavoil P., Ohlin A., Schachter J. Role of disulfide bonding in outer membrane structure and permeability in Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):479–485. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.479-485.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz M. Xenopus hsp 70 genes are constitutively expressed in injected oocytes. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2477–2483. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02159.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkelund S., Lundemose A. G., Christiansen G. Characterization of native and recombinant 75-kilodalton immunogens from Chlamydia trachomatis serovar L2. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2683–2690. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2683-2690.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunham R. C., Peeling R., Maclean I., McDowell J., Persson K., Osser S. Postabortal Chlamydia trachomatis salpingitis: correlating risk with antigen-specific serological responses and with neutralization. J Infect Dis. 1987 Apr;155(4):749–755. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.4.749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell H. D., Kromhout J., Schachter J. Purification and partial characterization of the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1161–1176. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1161-1176.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirico W. J., Waters M. G., Blobel G. 70K heat shock related proteins stimulate protein translocation into microsomes. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):805–810. doi: 10.1038/332805a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale R. M., McClure B. A., Houchins J. P. A rapid single-stranded cloning strategy for producing a sequential series of overlapping clones for use in DNA sequencing: application to sequencing the corn mitochondrial 18 S rDNA. Plasmid. 1985 Jan;13(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshaies R. J., Koch B. D., Werner-Washburne M., Craig E. A., Schekman R. A subfamily of stress proteins facilitates translocation of secretory and mitochondrial precursor polypeptides. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):800–805. doi: 10.1038/332800a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo L. H., Yang R. C., Wu R. An improved strategy for rapid direct sequencing of both strands of long DNA molecules cloned in a plasmid. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5521–5540. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P., Allan I., Pearce J. H. Structural and polypeptide differences between envelopes of infective and reproductive life cycle forms of Chlamydia spp. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):13–20. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.13-20.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P., Miceli M., Sublett J. E. Synthesis of disulfide-bonded outer membrane proteins during the developmental cycle of Chlamydia psittaci and Chlamydia trachomatis. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):379–385. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.379-385.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S. The heat-shock response. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1151–1191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maclean I. W., Peeling R. W., Brunham R. C. Characterization of Chlamydia trachomatis antigens with monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Feb;34(2):141–147. doi: 10.1139/m88-028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClenaghan M., Herring A. J., Aitken I. D. Comparison of Chlamydia psittaci isolates by DNA restriction endonuclease analysis. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):384–389. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.384-389.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S., Pelham H. R. An Hsp70-like protein in the ER: identity with the 78 kd glucose-regulated protein and immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90746-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newhall W. J., 5th Biosynthesis and disulfide cross-linking of outer membrane components during the growth cycle of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):162–168. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.162-168.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newhall W. J., Jones R. B. Disulfide-linked oligomers of the major outer membrane protein of chlamydiae. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):998–1001. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.998-1001.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer L., Falkow S. A common plasmid of Chlamydia trachomatis. Plasmid. 1986 Jul;16(1):52–62. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(86)90079-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeling R., Maclean I. W., Brunham R. C. In vitro neutralization of Chlamydia trachomatis with monoclonal antibody to an epitope on the major outer membrane protein. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):484–488. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.484-488.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Speculations on the functions of the major heat shock and glucose-regulated proteins. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):959–961. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90693-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardinia L. M., Engel J. N., Ganem D. Chlamydial gene encoding a 70-kilodalton antigen in Escherichia coli: analysis of expression signals and identification of the gene product. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):335–341. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.335-341.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman M. D., Setlow P. Nucleotide sequence of a Bacillus megaterium gene homologous to the dnaK gene of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 11;15(9):3923–3923. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.9.3923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D., Lathigra R., Hendrix R., Sweetser D., Young R. A. Stress proteins are immune targets in leprosy and tuberculosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4267–4270. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Stiegler P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):133–148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




