Abstract
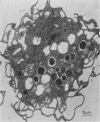
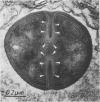
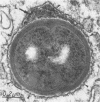
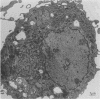
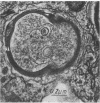
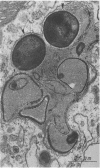
Clindamycin treatment of Staphylococcus aureus caused a remarkable thickening of the bacterial cell wall and made the bacterial wall much more resistant against lytic enzymes within bone marrow-derived macrophages as revealed by electron microscopy and radiolabeling experiments. This reduced wall degradability resulted from an increased number of O-acetyl groups in the murein. Furthermore, such clindamycin-treated bacteria were ingested by adherent bone marrow-derived macrophages at a higher rate than untreated bacteria. The medical aspects of these results are discussed.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R., Joone G., van Rensburg C. E. An in vitro investigation of the intracellular bioactivity of amoxicillin, clindamycin, and erythromycin for Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1986 Mar;153(3):593–600. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.3.593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassler M., Just H. M., Richter A., Zeller H., Daschner F. Antibakterielle Aktivität von Clindamycin und Linkomycin in Bouillon, Serum und in Kombination mit Polymorphkernigen Granulozyten gegen Staphylococcus aureus und Staphylococcus epidermidis. Infection. 1984 Jul-Aug;12(4):280–285. doi: 10.1007/BF01645962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blümel P., Uecker W., Giesbrecht P. Zero order kinetics of cell wall turnover in Staphylococcus aureus. Arch Microbiol. 1979 May;121(2):103–110. doi: 10.1007/BF00689972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easmon C. S., Crane J. P. Cellular uptake of clindamycin and lincomycin. Br J Exp Pathol. 1984 Dec;65(6):725–730. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming T. J., Wallsmith D. E., Rosenthal R. S. Arthropathic properties of gonococcal peptidoglycan fragments: implications for the pathogenesis of disseminated gonococcal disease. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):600–608. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.600-608.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giesbrecht P., Ruska H. Uber Veränderungen der Feinstrukturen von Bakterien unter der Einwirkung von Chloramphenicol. Klin Wochenschr. 1968 Jun 1;46(11):575–582. doi: 10.1007/BF01747836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giesbrecht P., Wecke J., Reinicke B. On the morphogenesis of the cell wall of staphylococci. Int Rev Cytol. 1976;44:225–318. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61651-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg I., Sela M. N. The role of leukocytes and their hydrolases in the persistence, degradation, and transport of bacterial constituents in tissues: relation to chronic inflammatory processes in staphylococcal, streptococcal, and mycobacterial infections and in chronic periodontal disease. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1976 Mar;4(3):249–322. doi: 10.3109/10408417609106944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand W. L., King-Thompson N. L. Contrasts between phagocyte antibiotic uptake and subsequent intracellular bactericidal activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jan;29(1):135–140. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.1.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs R. F., Wilson C. B. Intracellular penetration and antimicrobial activity of antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Oct;12 (Suppl 100):13–20. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.suppl_c.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempner M. S., Styrt B. Clindamycin uptake by human neutrophils. J Infect Dis. 1981 Nov;144(5):472–479. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.5.472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logardt I. M., Neujahr H. Y. Lysis of modified walls from Lactobacillus fermentum. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):73–77. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.73-77.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks M. I. In vitro activity of clindamycin and other antimicrobials against gram-positive bacteria and Hemophilus influenzae. Can Med Assoc J. 1975 Jan 25;112(2):170–173. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips L., Fernandes R., Warren C. In-vitro comparison of erythromycin, lincomycin, and clindamycin. Br Med J. 1970 Apr 11;2(5701):89–90. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5701.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prokesch R. C., Hand W. L. Antibiotic entry into human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Mar;21(3):373–380. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.3.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal R. S., Blundell J. K., Perkins H. R. Strain-related differences in lysozyme sensitivity and extent of O-acetylation of gonococcal peptidoglycan. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):826–829. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.826-829.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal R. S., Folkening W. J., Miller D. R., Swim S. C. Resistance of O-acetylated gonococcal peptidoglycan to human peptidoglycan-degrading enzymes. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):903–911. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.903-911.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab J. H., Ohanian S. H. Degradation of streptococcal cell wall antigens in vivo. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1346–1352. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1346-1352.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umeda A., Ueki Y., Amako K. Structure of the Staphylococcus aureus cell wall determined by the freeze-substitution method. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2482–2487. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2482-2487.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veringa E. M., Verhoef J. Influence of subinhibitory concentrations of clindamycin on opsonophagocytosis of Staphylococcus aureus, a protein-A-dependent process. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Nov;30(5):796–797. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.5.796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vosbeck K., James P. R., Zimmermann W. Antibiotic action on phagocytosed bacteria measured by a new method for determining viable bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jun;25(6):735–741. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.6.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wecke J., Lahav M., Ginsburg I., Giesbrecht P. Cell wall degradation of Staphylococcus aureus by lysozyme. Arch Microbiol. 1982 Mar;131(2):116–123. doi: 10.1007/BF01053992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wecke J., Lahav M., Ginsburg I., Kwa E., Giesbrecht P. Inhibition of wall autolysis of staphylococci by sodium polyanethole sulfonate "liquoid". Arch Microbiol. 1986 Mar;144(2):110–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00414719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]