Abstract
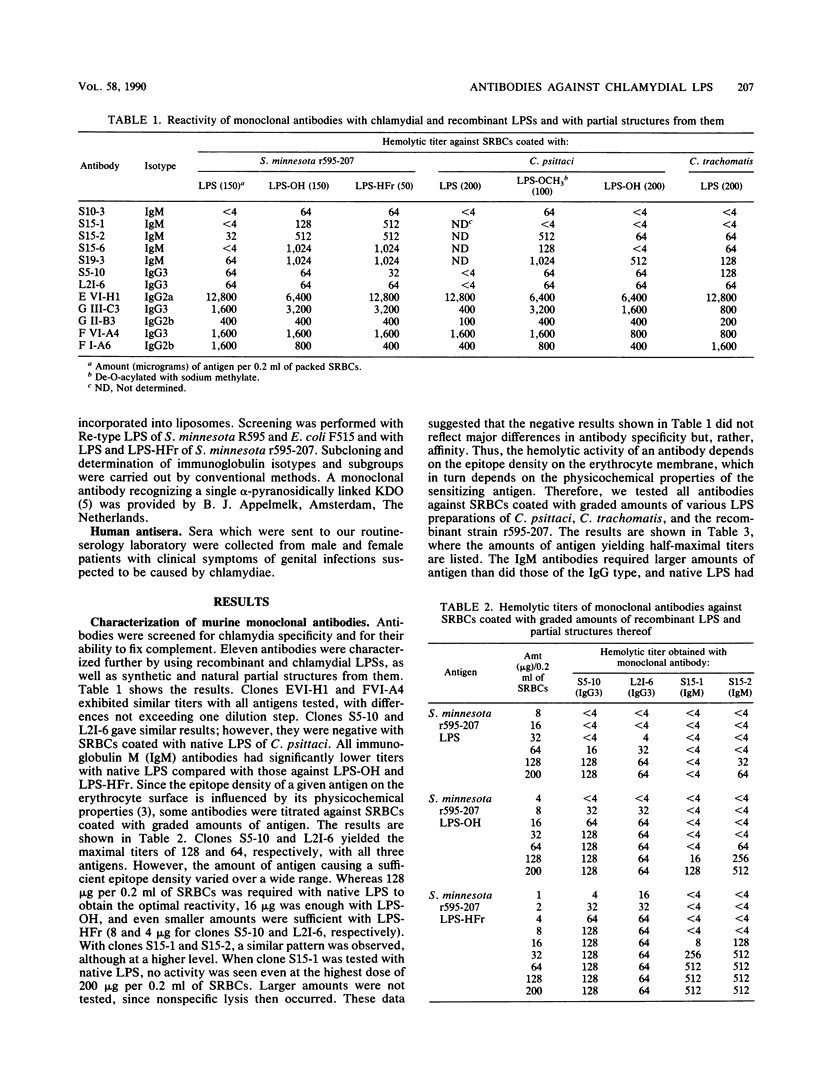
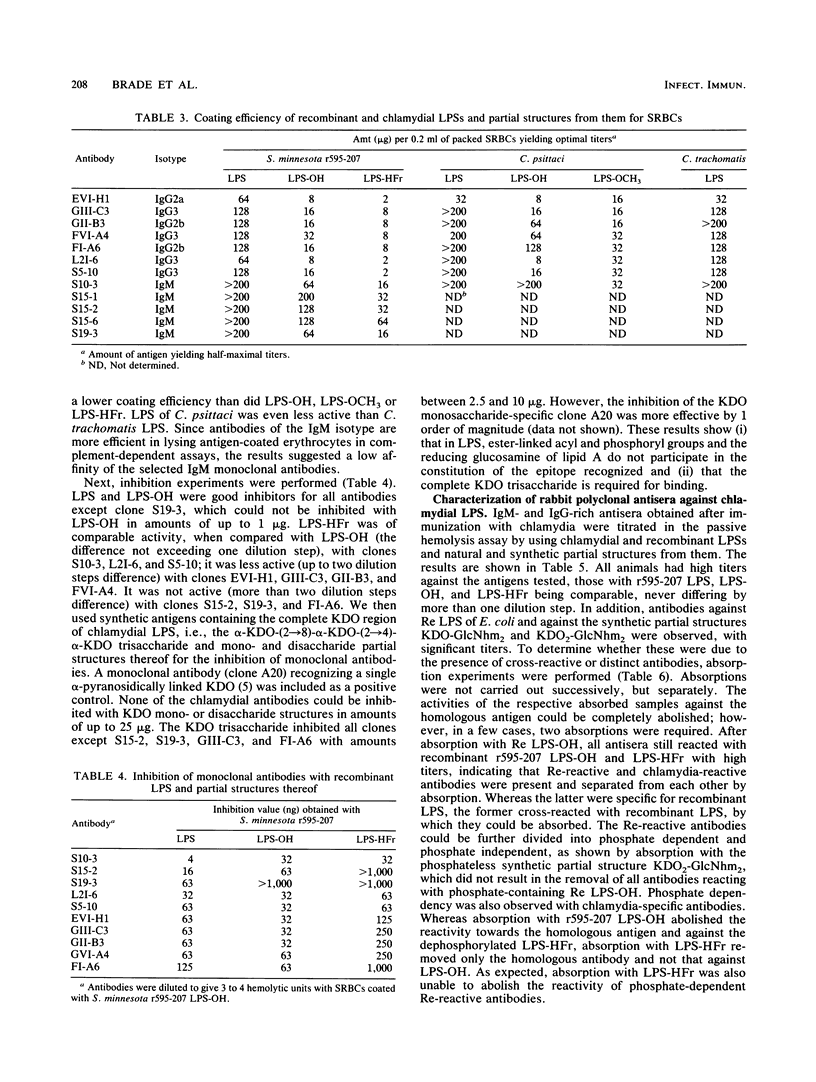
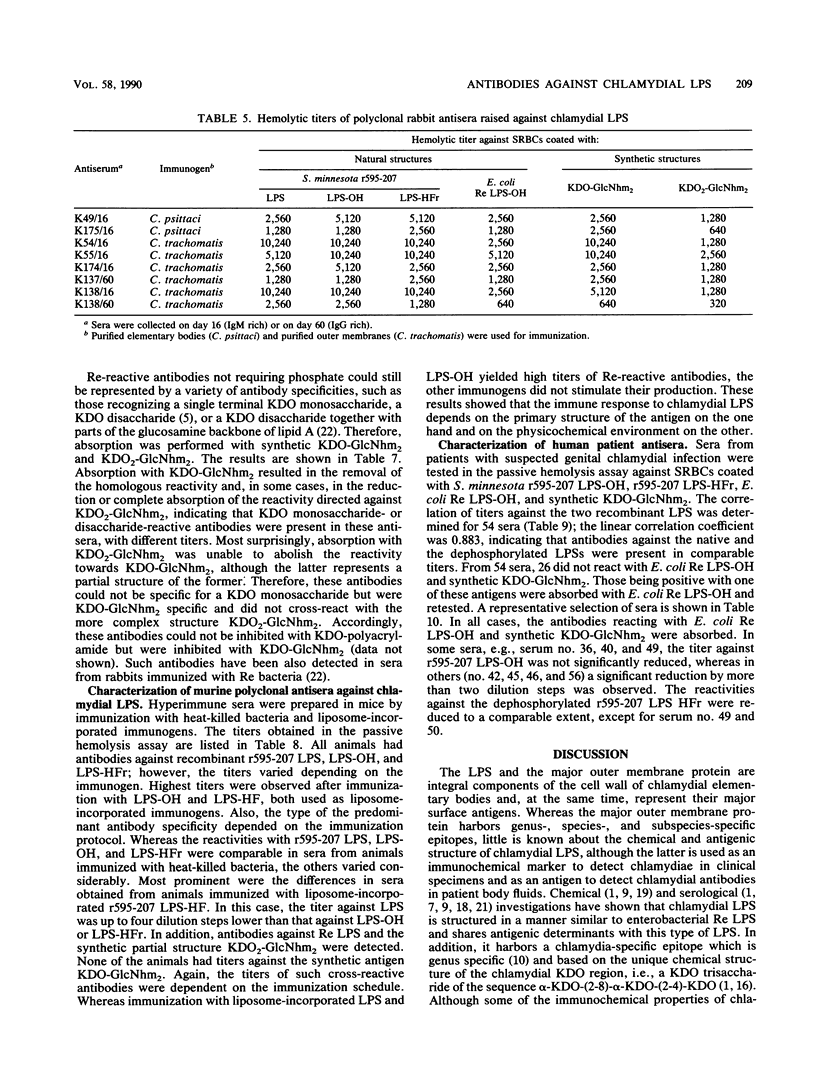
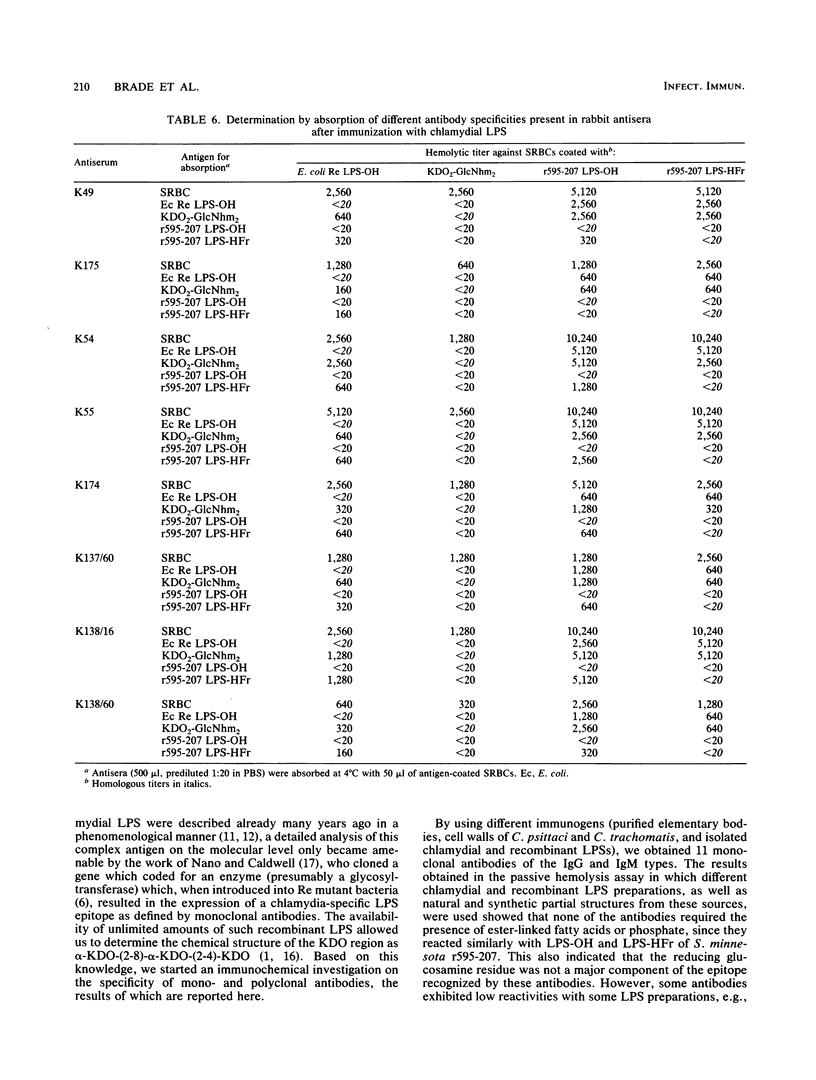
Murine monoclonal and rabbit, murine, and human polyclonal antibodies against chlamydial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) were characterized by the passive hemolysis and passive hemolysis inhibition assays and by absorption experiments with LPSs of Chlamydia psittaci, Chlamydia trachomatis, and a recombinant strain of Salmonella minnesota Re (r595-207) expressing the chlamydia-specific LPS epitope, as well as natural and synthetic partial structures of chlamydial LPS. Eleven monoclonal antibodies of the immunoglobulin M and G classes were characterized as chlamydia-specific by their failure to react with Re-type LPS, binding to a similar epitope for which the trisaccharide alpha-3-deoxy-D-manno-2-octulosonic acid (KDO)-(2-8)-alpha-KDO-(2-4)-alpha-KDO was an absolute prerequisite. For optimal binding, parts of the lipid A moiety were also involved; however, phosphoryl and ester-linked acyl groups and the reducing glucosamine residue of lipid A were dispensable. A similar antibody specificity was detected in lapine and murine hyperimmune sera after immunization with chlamydia, in addition to those recognizing more complex (e.g., those requiring the presence of phosphoryl residues) and less complex epitopes. Among the latter were those cross-reacting with Re-type LPS, which could be removed by absorption. The titers of different antibody specificities, in particular the ratio of chlamydia-specific to cross-reactive antibodies, present in murine polyclonal antisera depended on the immunization protocol. The preferential formation of chlamydia-specific antibodies was observed after immunization with liposome-incorporated immunogens. Human sera from patients with suspected genital chlamydial infections were also found to contain chlamydia-specific and cross-reactive antibodies, the latter of which could be removed by absorption with Re-type LPS.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brade H., Brade L., Nano F. E. Chemical and serological investigations on the genus-specific lipopolysaccharide epitope of Chlamydia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2508–2512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brade H., Brade L., Rietschel E. T. Structure-activity relationships of bacterial lipopolysaccharides (endotoxins). Current and future aspects. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1988 Apr;268(2):151–179. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(88)80001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brade H., Galanos C., Lüderitz O. Differential determination of the 3-Deoxy-D-mannooctulosonic acid residues in lipopolysaccharides of Salmonella minnesota rough mutants. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Mar 1;131(1):195–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07249.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brade H., Rietschel E. T. Alpha-2----4-interlinked 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid disaccharide. A common constituent of enterobacterial lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Dec 3;145(2):231–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08543.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brade L., Brandenburg K., Kuhn H. M., Kusumoto S., Macher I., Rietschel E. T., Brade H. The immunogenicity and antigenicity of lipid A are influenced by its physicochemical state and environment. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2636–2644. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2636-2644.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brade L., Kosma P., Appelmelk B. J., Paulsen H., Brade H. Use of synthetic antigens to determine the epitope specificities of monoclonal antibodies against the 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonate region of bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1987 Feb;55(2):462–466. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.2.462-466.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brade L., Nano F. E., Schlecht S., Schramek S., Brade H. Antigenic and immunogenic properties of recombinants from Salmonella typhimurium and Salmonella minnesota rough mutants expressing in their lipopolysaccharide a genus-specific chlamydial epitope. Infect Immun. 1987 Feb;55(2):482–486. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.2.482-486.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brade L., Nurminen M., Mäkelä P. H., Brade H. Antigenic properties of Chlamydia trachomatis lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):569–572. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.569-572.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brade L., Schramek S., Schade U., Brade H. Chemical, biological, and immunochemical properties of the Chlamydia psittaci lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):568–574. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.568-574.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell H. D., Hitchcock P. J. Monoclonal antibody against a genus-specific antigen of Chlamydia species: location of the epitope on chlamydial lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):306–314. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.306-314.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhir S. P., Hakomori S., Kenny G. E., Grayston J. T. Immunochemical studies on chlamydial group antigen (presence of a 2-keto-3-deoxycarbohydrate as immunodominant group). J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):116–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhir S. P., Kenny G. E., Grayston J. T. Characterization of the group antigen of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1971 Dec;4(6):725–730. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.6.725-730.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O. Electrodialysis of lipopolysaccharides and their conversion to uniform salt forms. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun;54(2):603–610. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04172.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosma P., Gass J., Schulz G., Christian R., Unger F. M. Artificial antigens. Synthesis of polyacrylamide copolymers containing 3-deoxy-D-manno-2-octulopyranosylonic acid (KDO) residues. Carbohydr Res. 1987 Sep 15;167:39–54. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(87)80266-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosma P., Schulz G., Brade H. Synthesis of a trisaccharide of 3-deoxy-D-manno-2-octulopyranosylonic acid (KDO) residues related to the genus-specific lipopolysaccharide epitope of Chlamydia. Carbohydr Res. 1988 Dec 1;183(2):183–199. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(88)84073-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nano F. E., Caldwell H. D. Expression of the chlamydial genus-specific lipopolysaccharide epitope in Escherichia coli. Science. 1985 May 10;228(4700):742–744. doi: 10.1126/science.2581315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurminen M., Leinonen M., Saikku P., Mäkelä P. H. The genus-specific antigen of Chlamydia: resemblance to the lipopolysaccharide of enteric bacteria. Science. 1983 Jun 17;220(4603):1279–1281. doi: 10.1126/science.6344216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurminen M., Rietschel E. T., Brade H. Chemical characterization of Chlamydia trachomatis lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):573–575. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.573-575.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurminen M., Wahlström E., Kleemola M., Leinonen M., Saikku P., Mäkelä P. H. Immunologically related ketodeoxyoctonate-containing structures in Chlamydia trachomatis, Re mutants of Salmonella species, and Acinetobacter calcoaceticus var. anitratus. Infect Immun. 1984 Jun;44(3):609–613. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.3.609-613.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozalski A., Brade L., Kosma P., Appelmelk B. J., Krogmann C., Brade H. Epitope specificities of murine monoclonal and rabbit polyclonal antibodies against enterobacterial lipopolysaccharides of the Re chemotype. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2645–2652. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2645-2652.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sádecký E., Trávnicek M., Balascák J., Brezina R., Kazár J., Urvölgyi J., Flesár I., Cizmár J. Enzootický potrat oviec v okrese Roznava. Vet Med (Praha) 1978 Jan;23(1):25–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


