Abstract
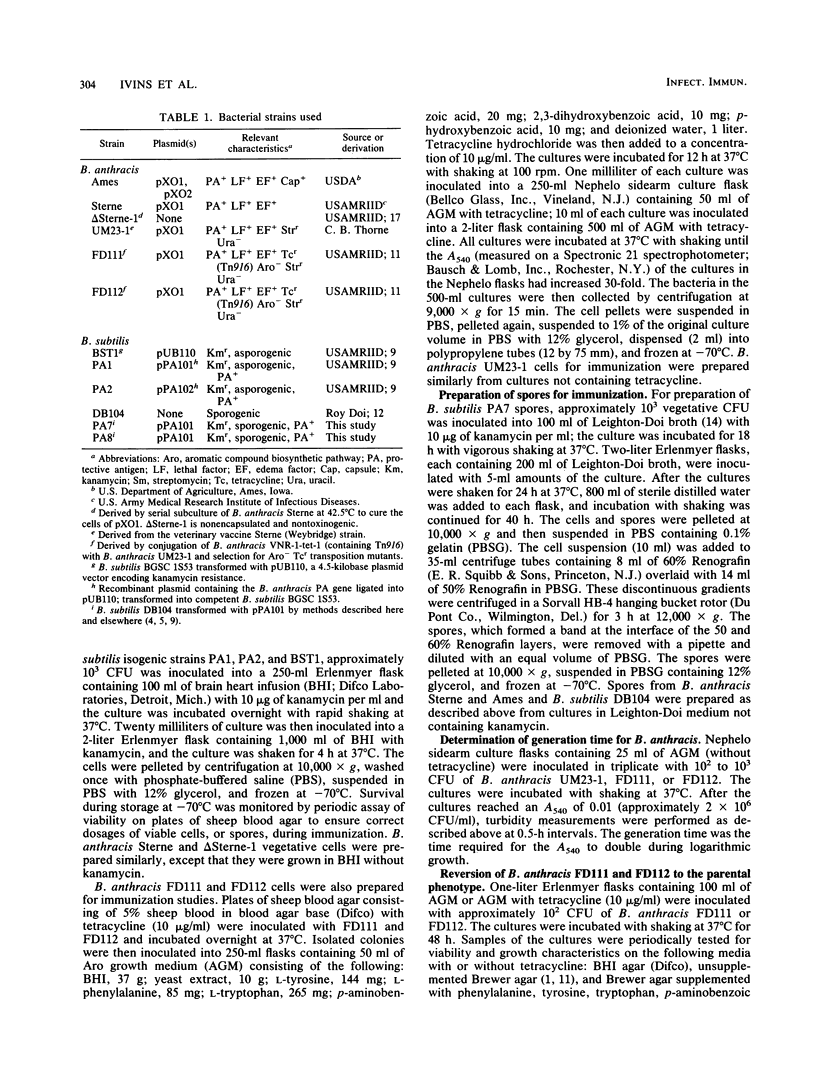
The safety and efficacy of five prototype, live anthrax vaccines were studied in Hartley guinea pigs and CBA/J and A/J mice. Two of the strains, Bacillus anthracis FD111 and FD112, are Aro- mutants derived by Tn916 mutagenesis of B. anthracis UM23-1. Bacillus subtilis PA1 and PA2 contain a recombinant plasmid, pPA101 or pPA102, respectively, that carries the gene from B. anthracis encoding synthesis of protective antigen (PA). The final strain, B. subtilis PA7, was isolated in this study from B. subtilis DB104 transformed with pPA101. All five strains were less virulent in guinea pigs and A/J and CBA/J mice than the toxinogenic, nonencapsulated B. anthracis veterinary vaccine Sterne strain. A/J and CBA/J inbred mice represent strains that are innately susceptible and resistant, respectively, to the Sterne strain. These differences in susceptibility are due to differences in ability to produce complement component 5. In guinea pigs, immunization with PA1 or PA2 vegetative cells or PA7 spores protected greater than or equal to 95% from an intramuscular spore challenge with the virulent, "vaccine-resistant" B. anthracis Ames strain. Strain PA2 vegetative cells and strain PA7 spores were as effective as the Sterne strain in Sterne-resistant CBA/J mice, protecting 70% of the mice from Ames strain spore challenge. Immunization with FD111 or FD112 vegetative cells fully protected guinea pigs from challenge. Immunization with FD111 cells protected up to 100% of CBA/J mice and up to 70% of A/J mice.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ezzell J. W., Ivins B. E., Leppla S. H. Immunoelectrophoretic analysis, toxicity, and kinetics of in vitro production of the protective antigen and lethal factor components of Bacillus anthracis toxin. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):761–767. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.761-767.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green B. D., Battisti L., Koehler T. M., Thorne C. B., Ivins B. E. Demonstration of a capsule plasmid in Bacillus anthracis. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):291–297. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.291-297.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryczan T. J., Contente S., Dubnau D. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus plasmids introduced by transformation into Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;134(1):318–329. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.1.318-329.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry P., LeBlanc D. J., Falkow S. General method for the isolation of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):1064–1066. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.1064-1066.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAINES B. W., KLEIN F., LINCOLN R. E. QUANTITATIVE ASSAY FOR CRUDE ANTHRAX TOXINS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jan;89:74–83. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.1.74-83.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiseth S. K., Stocker B. A. Aromatic-dependent Salmonella typhimurium are non-virulent and effective as live vaccines. Nature. 1981 May 21;291(5812):238–239. doi: 10.1038/291238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivins B. E., Ezzell J. W., Jr, Jemski J., Hedlund K. W., Ristroph J. D., Leppla S. H. Immunization studies with attenuated strains of Bacillus anthracis. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):454–458. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.454-458.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivins B. E., Welkos S. L. Cloning and expression of the Bacillus anthracis protective antigen gene in Bacillus subtilis. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):537–542. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.537-542.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivins B. E., Welkos S. L., Knudson G. B., Leblanc D. J. Transposon Tn916 mutagenesis in Bacillus anthracis. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):176–181. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.176-181.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivins B. E., Welkos S. L. Recent advances in the development of an improved, human anthrax vaccine. Eur J Epidemiol. 1988 Mar;4(1):12–19. doi: 10.1007/BF00152686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura F., Doi R. H. Construction of a Bacillus subtilis double mutant deficient in extracellular alkaline and neutral proteases. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):442–444. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.442-444.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leighton T. J., Doi R. H. The stability of messenger ribonucleic acid during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3189–3195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little S. F., Knudson G. B. Comparative efficacy of Bacillus anthracis live spore vaccine and protective antigen vaccine against anthrax in the guinea pig. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):509–512. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.509-512.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikesell P., Ivins B. E., Ristroph J. D., Dreier T. M. Evidence for plasmid-mediated toxin production in Bacillus anthracis. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):371–376. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.371-376.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasser D., Nester E. W. Aromatic amino acid biosynthesis: gene-enzyme relationships in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1706–1714. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1706-1714.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUZISS M., MANNING L. C., LYNCH J. W., BARCLAYE, ABELOW I., WRIGHT G. G. Large-scale production of protective antigen of Bacillus anthracis in anaerobic cultures. Appl Microbiol. 1963 Jul;11:330–334. doi: 10.1128/am.11.4.330-334.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ristroph J. D., Ivins B. E. Elaboration of Bacillus anthracis antigens in a new, defined culture medium. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):483–486. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.483-486.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH H., KEPPIE J., STANLEY J. L. The chemical basis of the virulence of Bacillus anthracis. V. The specific toxin produced by B. Anthracis in vivo. Br J Exp Pathol. 1955 Oct;36(5):460–472. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull P. C., Broster M. G., Carman J. A., Manchee R. J., Melling J. Development of antibodies to protective antigen and lethal factor components of anthrax toxin in humans and guinea pigs and their relevance to protective immunity. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):356–363. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.356-363.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vodkin M. H., Leppla S. H. Cloning of the protective antigen gene of Bacillus anthracis. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):693–697. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90402-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welkos S. L., Friedlander A. M. Comparative safety and efficacy against Bacillus anthracis of protective antigen and live vaccines in mice. Microb Pathog. 1988 Aug;5(2):127–139. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welkos S. L., Keener T. J., Gibbs P. H. Differences in susceptibility of inbred mice to Bacillus anthracis. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):795–800. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.795-800.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



