Abstract
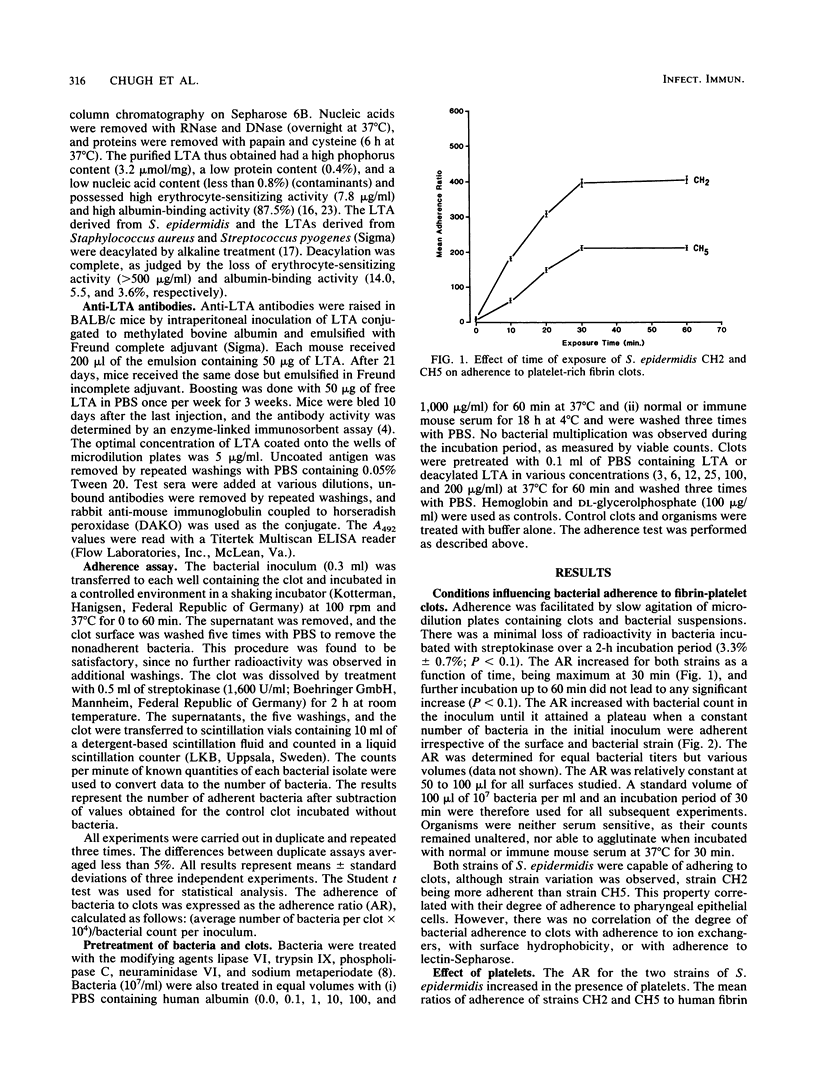
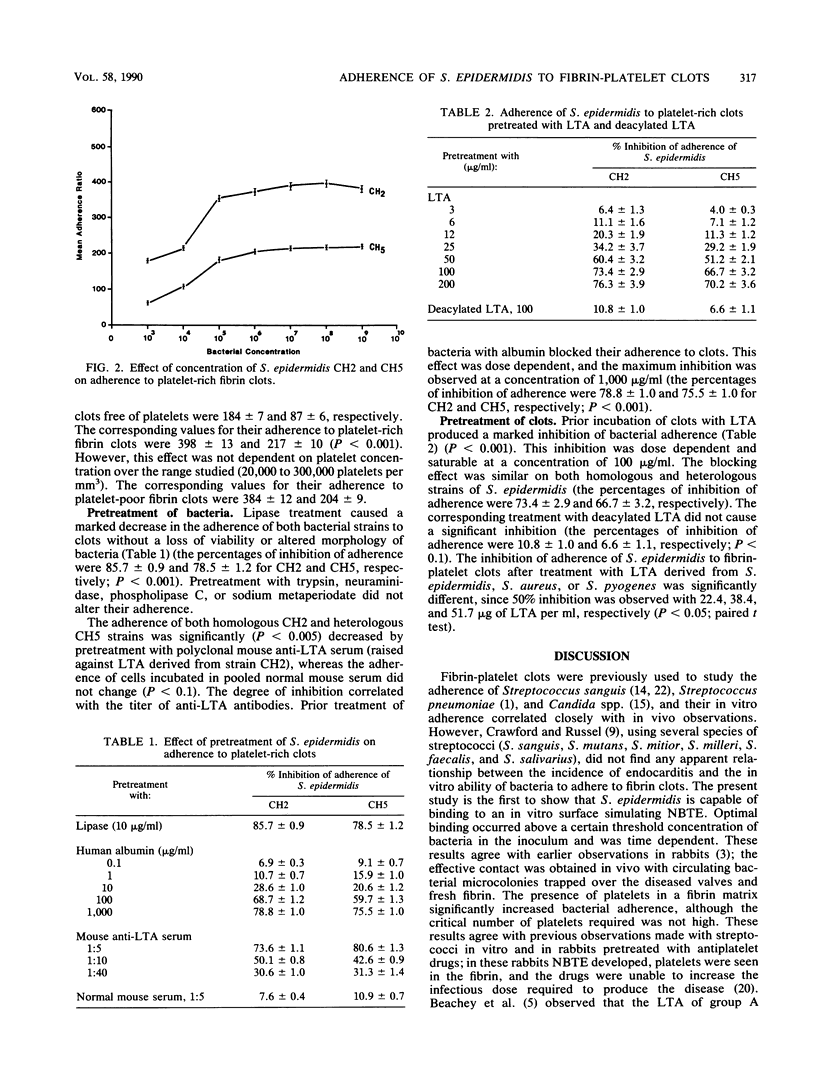
The adherence of two strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis to human fibrin-platelet clots in vitro was investigated. Both strains were noncapsulated, nonhemagglutinating, and nonslime producers. Binding was not related to surface charge, carbohydrate profile, or hydrophobicity of the bacteria. Adherence was reduced four- to sixfold (P less than 0.001) on pretreatment of bacteria with lipase, while neuraminidase, trypsin, phospholipase C, and sodium periodate did not alter their binding. Pretreatment of bacteria with substances known to bind lipoteichoic acid (LTA), such as human albumin and anti-LTA antibodies, also resulted in a fourfold (P less than 0.001) reduction in adherence. Prior incubation of clots with free LTA, but not with deacylated LTA, produced a fourfold (P less than 0.001) decrease in the adherence of homologous and heterologous strains of S. epidermidis. A similar reduction was also observed when LTAs derived from Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes were used. These data provide evidence that the lipid moiety of LTA has a central role in the adherence of S. epidermidis to fibrin-platelet clots in vitro.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANGRIST A. A., OKA M. Pathogenesis of bacterial endocarditis. JAMA. 1963 Jan 26;183:249–252. doi: 10.1001/jama.1963.63700040009010b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler S. W., 2nd, Selinger D. S., Reed W. P. Effect of immunization on the genesis of pneumococcal endocarditis in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):55–61. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.55-61.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baddour L. M., Christensen G. D., Hester M. G., Bisno A. L. Production of experimental endocarditis by coagulase-negative staphylococci: variability in species virulence. J Infect Dis. 1984 Nov;150(5):721–727. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.5.721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahr G. M., Rook G. A., al-Saffar M., Van Embden J., Stanford J. L., Behbehani K. Antibody levels to mycobacteria in relation to HLA type: evidence for non-HLA-linked high levels of antibody to the 65 kD heat shock protein of M. bovis in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Nov;74(2):211–215. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H., Chiang T. M., Ofek I., Kang A. H. Interaction of lipoteichoic acid of group A streptococci with human platelets. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):649–654. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.649-654.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carruthers M. M., Kabat W. J. Mediation of staphylococcal adherence to mucosal cells by lipoteichoic acid. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):444–446. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.444-446.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chugh T. D., Babaa E., Burns G., Shuhaiber H. Effect of sublethal concentration of antibiotics on the adherence of Staphylococcus epidermidis to eukaryotic cells. Chemotherapy. 1989;35(2):113–118. doi: 10.1159/000238656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford I., Russell C. Comparative adhesion of seven species of streptococci isolated from the blood of patients with sub-acute bacterial endocarditis to fibrin-platelet clots in vitro. J Appl Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;60(2):127–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1986.tb03369.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durack D. T., Gilliland B. C., Petersdorf R. G. Effect of immunization on susceptibility to experimental Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sanguis endocarditis. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):52–56. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.52-56.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K., Ramirez-Ronda C. H., Holmes R. K., Sanford J. P. Adherence of bacteria to heart valves in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1364–1370. doi: 10.1172/JCI108216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogt A. H., Dankert J., Hulstaert C. E., Feijen J. Cell surface characteristics of coagulase-negative staphylococci and their adherence to fluorinated poly(ethylenepropylene). Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):294–301. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.294-301.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph R., Shockman G. D. Cellular localization of lipoteichoic acid in Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):1375–1386. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.1375-1386.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy F. D., Chang D. S., Neuhaus E. G., Horne D. S., Tomasz A., Steigbigel N. H. Effect of penicillin on the adherence of Streptococcus sanguis in vitro and in the rabbit model of endocarditis. J Clin Invest. 1983 Mar;71(3):668–675. doi: 10.1172/JCI110813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisch P. A., Calderone R. A. Adherence of Candida albicans to a fibrin-platelet matrix formed in vitro. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):650–656. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.650-656.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz M. Separation and properties of a red cell sensitizing substance from streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2200–2204. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2200-2204.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Beachey E. H., Jefferson W., Campbell G. L. Cell membrane-binding properties of group A streptococcal lipoteichoic acid. J Exp Med. 1975 May 1;141(5):990–1003. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.5.990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Simpson W. A., Beachey E. H. Formation of molecular complexes between a structurally defined M protein and acylated or deacylated lipoteichoic acid of Streptococcus pyogenes. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):426–433. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.426-433.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez-Ronda C. H. Adherence of glucan-positive and glucan-negative streptococcal strains to normal and damaged heart valves. J Clin Invest. 1978 Oct;62(4):805–814. doi: 10.1172/JCI109192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sande M. A., Korzeniowski O. M., Scheld W. M. Factors influencing the pathogenesis and prevention of infective endocarditis. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1982;31:48–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheld W. M., Calderone R. A., Brodeur J. P., Sande M. A. Influence of preformed antibody on the pathogenesis of experimental Candida albicans endocarditis. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):950–955. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.950-955.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheld W. M., Valone J. A., Sande M. A. Bacterial adherence in the pathogenesis of endocarditis. Interaction of bacterial dextran, platelets, and fibrin. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1394–1404. doi: 10.1172/JCI109057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. A., Ofek I., Beachey E. H. Binding of streptococcal lipoteichoic acid to the fatty acid binding sites on serum albumin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6092–6097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teti G., Chiofalo M. S., Tomasello F., Fava C., Mastroeni P. Mediation of Staphylococcus saprophyticus adherence to uroepithelial cells by lipoteichoic acid. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):839–842. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.839-842.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tojo M., Yamashita N., Goldmann D. A., Pier G. B. Isolation and characterization of a capsular polysaccharide adhesin from Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):713–722. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



