Abstract
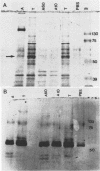
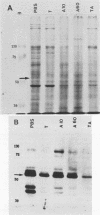
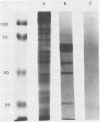
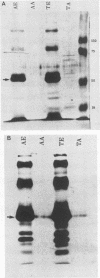
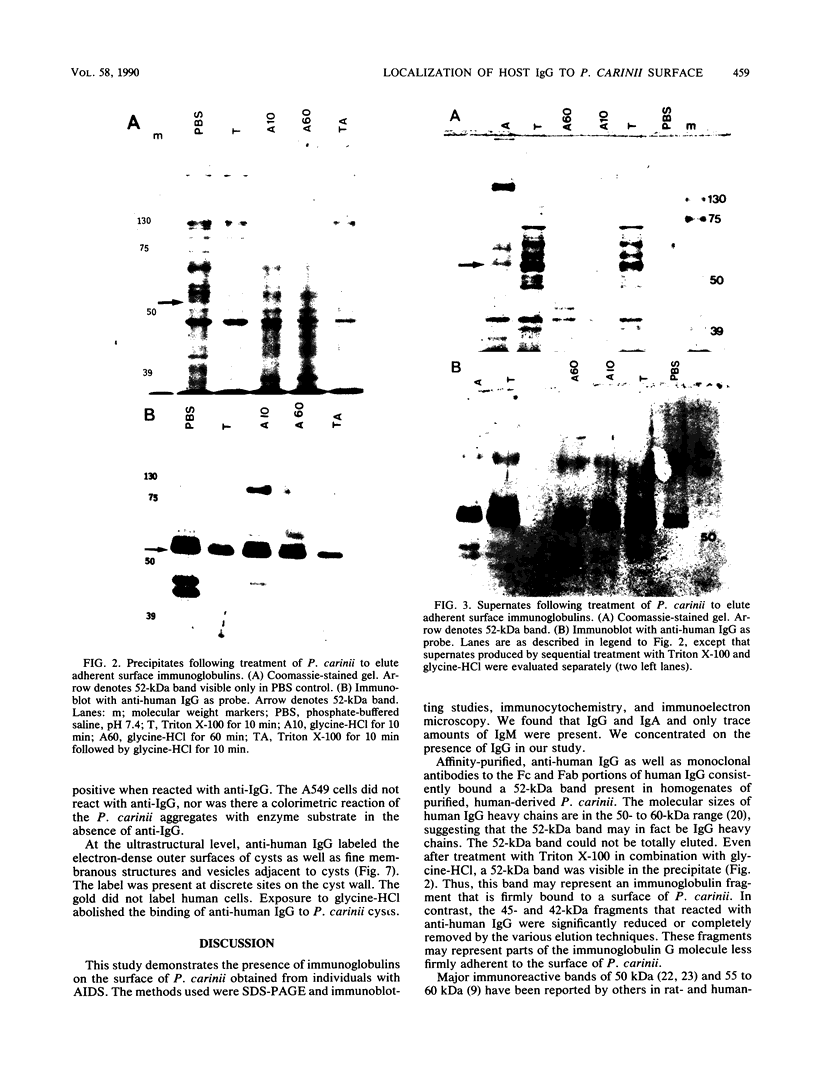
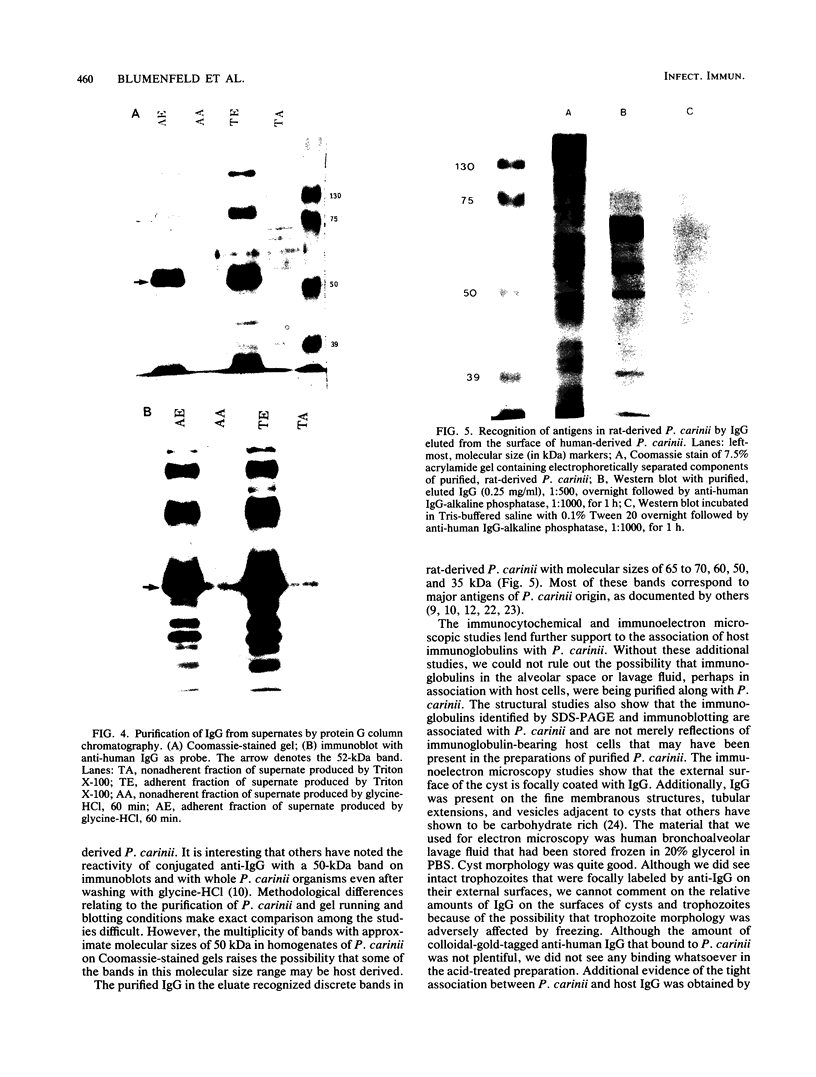
In immunoblotting studies of Pneumocystis carinii surface proteins, we found that a secondary antibody, anti-human immunoglobulin G (IgG), recognized a 52-kilodalton (kDa) band in homogenates of P. carinii purified from human autopsy lungs and bronchoalveolar lavage fluids, even when serum as a source of primary antibody was omitted. The electrophoretic mobility of the 52-kDa band is identical to that of IgG heavy chains. In addition to affinity-purified, anti-human IgG, monoclonal antibodies specific for the Fab and Fc regions of human IgG recognized the 52-kDa band. To determine whether the 52-kDa band represents IgG bound to the surface of P. carinii, we treated intact organisms with Triton X-100 and acid in order to elute immunoglobulin from the surface of P. carinii. After purification over a protein G column, the eluate comigrated with human IgG, was recognized by anti-IgG, and bound to discrete bands with molecular sizes of 65 to 70, 60, 50, and 35 kDa in purified, rat-derived P. carinii. To confirm the presence of human IgG on the surface of P. carinii, we performed immunocytochemical and immunoelectron microscopic studies. Staining of intact P. carinii aggregates by anti-human IgG was pronounced and was abolished by acid treatment. IgA was also present. Ultrastructural studies showed the presence of IgG on the cyst wall and on fine membranous structures and vesicles adjacent to cysts. We conclude that the surface of P. carinii is coated with human IgG. The close association of human IgG with P. carinii may have implications for the pathogenesis of P. carinii pneumonia in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allegra C. J., Kovacs J. A., Drake J. C., Swan J. C., Chabner B. A., Masur H. Activity of antifolates against Pneumocystis carinii dihydrofolate reductase and identification of a potent new agent. J Exp Med. 1987 Mar 1;165(3):926–931. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.3.926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenfeld W., Griffiss J. M. In vitro differentiation of human-derived Pneumocystis carinii. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Mar;27(3):480–485. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.3.480-485.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenfeld W., Kovacs J. A. Use of a monoclonal antibody to detect Pneumocystis carinii in induced sputum and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid by immunoperoxidase staining. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1988 Dec;112(12):1233–1236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brzosko W. J., Krawczyński K., Madaliński K., Nowoslawski A. Immunopathologic aspects of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in infants as revealed by immunofluorescence and electron microscopy. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1976 Oct;43:163–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brzosko W. J., Madaliński K., Krawczyński K., Nowoslawski A. Immunohistochemistry in studies on the pathogenesis of Pneumocystis pneumonia in infants. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Jun 21;177:156–170. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb35042.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushion M. T., Walzer P. D. Growth and serial passage of Pneumocystis carinii in the A549 cell line. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):245–251. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.245-251.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falus A., Merétey K., Bagdy D., Diószegi M., Böhm U., Csák E., Bozsóky S. Beta-2-microglobulin-specific autoantibodies cause platelet aggregation and interfere with ADP-induced aggregation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Jan;47(1):103–109. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves D. C. Immunological studies of Pneumocystis carinii. J Protozool. 1989 Jan-Feb;36(1):60–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1989.tb02700.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves D. C., McNabb S. J., Worley M. A., Downs T. D., Ivey M. H. Analyses of rat Pneumocystis carinii antigens recognized by human and rat antibodies by using western immunoblotting. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):96–103. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.96-103.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs J. A., Halpern J. L., Swan J. C., Moss J., Parrillo J. E., Masur H. Identification of antigens and antibodies specific for Pneumocystis carinii. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 15;140(6):2023–2031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linke M. J., Cushion M. T., Walzer P. D. Properties of the major antigens of rat and human Pneumocystis carinii. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1547–1555. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1547-1555.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddison S. E., Walls K. W., Haverkos H. W., Juranek D. D. Evaluation of serologic tests for Pneumocystis carinii antibody and antigenemia in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1984 Jan;2(1):69–73. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(84)90025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlier J. F., Valade S. P., Mayaud C. M., Rouquette A. M., Roland J. H. Immunohistological localization of immunoglobulins in pneumocystosis of adults. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1987 Jan-Feb;23(1):43–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuwissen J. H., Tauber I., Leeuwenberg A. D., Beckers P. J., Sieben M. Parasitologic and serologic observations of infection with Pneumocystis in humans. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jul;136(1):43–49. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. F., Garay S. M., Hopewell P. C., Mills J., Snider G. L., Stover D. E. NHLBI workshop summary. Pulmonary complications of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: an update. Report of the second National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute workshop. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Feb;135(2):504–509. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.2.504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pifer L. L., Hughes W. T., Stagno S., Woods D. Pneumocystis carinii infection: evidence for high prevalence in normal and immunosuppressed children. Pediatrics. 1978 Jan;61(1):35–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plata F., Autran B., Martins L. P., Wain-Hobson S., Raphaël M., Mayaud C., Denis M., Guillon J. M., Debré P. AIDS virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in lung disorders. Nature. 1987 Jul 23;328(6128):348–351. doi: 10.1038/328348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rankin J. A. Pulmonary immunology. Clin Chest Med. 1988 Sep;9(3):387–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Linke M. J. A comparison of the antigenic characteristics of rat and human Pneumocystis carinii by immunoblotting. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2257–2265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Stanforth D., Linke M. J., Cushion M. T. Pneumocystis carinii: immunoblotting and immunofluorescent analyses of serum antibodies during experimental rat infection and recovery. Exp Parasitol. 1987 Jun;63(3):319–328. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(87)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa H., Morioka H., Yoshida Y. Ultrastructural detection of carbohydrates in the pellicle of Pneumocystis carinii. Parasitol Res. 1988;74(6):537–543. doi: 10.1007/BF00531631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young K. R., Jr, Rankin J. A., Naegel G. P., Paul E. S., Reynolds H. Y. Bronchoalveolar lavage cells and proteins in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. An immunologic analysis. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Oct;103(4):522–533. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-4-522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]