Abstract
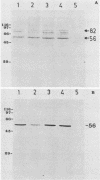
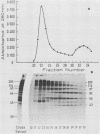
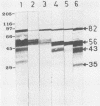
Eimeria maxima gametocytes contain two major antigens with molecular masses of 56 and 82 kilodaltons (kDa) which are recognized by convalescent sera from immune chickens. Preparations enriched in these two antigens were used to immunize mice, and several monoclonal antibodies which specifically reacted with the 56-kDa antigen were produced. One of these monoclonal antibodies of the immunoglobulin M subclass, along with immune chicken sera raised against affinity-purified 56- and 82-kDa antigens, was used to passively immunize chicks. On the basis of the parameter of total oocyst output, it was found that these antibodies provided partial protection (40 to 50% inhibition) against E. maxima challenge infections.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Crane M. S., Murray P. K., Gnozzio M. J., MacDonald T. T. Passive protection of chickens against Eimeria tenella infection by monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):972–976. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.972-976.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danforth H. D. Use of monoclonal antibodies directed against Eimeria tenella sporozoites to determine stage specificity and in vitro effect on parasite penetration and development. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Sep;44(9):1722–1727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaushal D. C., Carter R., Rener J., Grotendorst C. A., Miller L. H., Howard R. J. Monoclonal antibodies against surface determinants on gametes of Plasmodium gallinaceum block transmission of malaria parasites to mosquitoes. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2557–2562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennett R. H., Denis K. A., Tung A. S., Klinman N. R. Hybrid plasmacytoma production: fusions with adult spleen cells, monoclonal spleen fragments, neonatal spleen cells and human spleen cells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;81:77–91. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67448-8_13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskov R., Ishay-Michaeli R., Wallach M., Givol D., Kim K. J. Simultaneous expression of mu- and gamma-chain mRNA in cloned murine B-lymphoma cell lines. EMBO J. 1983;2(2):167–172. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01400.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laxer M. A., Healey M. C., Youssef N. N. Production of monoclonal antibodies specific for Eimeria tenella microgametocytes. J Parasitol. 1987 Jun;73(3):611–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long P. L., Millard B. J. Immunological differences in Eimeria maxima: effect of a mixed immunizing inoculum on heterologous challenge. Parasitology. 1979 Dec;79(3):451–457. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000053841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mencher D., Pugatsch T., Wallach M. Antigenic proteins of Eimeria maxima gametocytes: cell-free translation and detection with recovered chicken serum. Exp Parasitol. 1989 Jan;68(1):40–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(89)90006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugatsch T., Mencher D., Wallach M. Eimeria maxima: isolation of gametocytes and their immunogenicity in mice, rabbits, and chickens. Exp Parasitol. 1989 Feb;68(2):127–134. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(89)90089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSE M. E. SOME ASPECTS OF IMMUNITY TO EIMERIA INFECTIONS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Dec 30;113:383–399. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb40677.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. E. Immunity to coccidiosis: protective effect of transferred serum in Eimeria maxima infections. Parasitology. 1971 Feb;62(1):11–25. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000071249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagenbach G. E., Challey J. R., Burns W. C. A method for purifying coccidian oocysts employing clorox and sulfuric acid-dichromate solution. J Parasitol. 1966 Dec;52(6):1222–1222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach M. G., Mencher D., Yarus S., Pillemer G., Halabi A., Pugatsch T. Eimeria maxima: identification of gametocyte protein antigens. Exp Parasitol. 1989 Jan;68(1):49–56. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(89)90007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]