Abstract
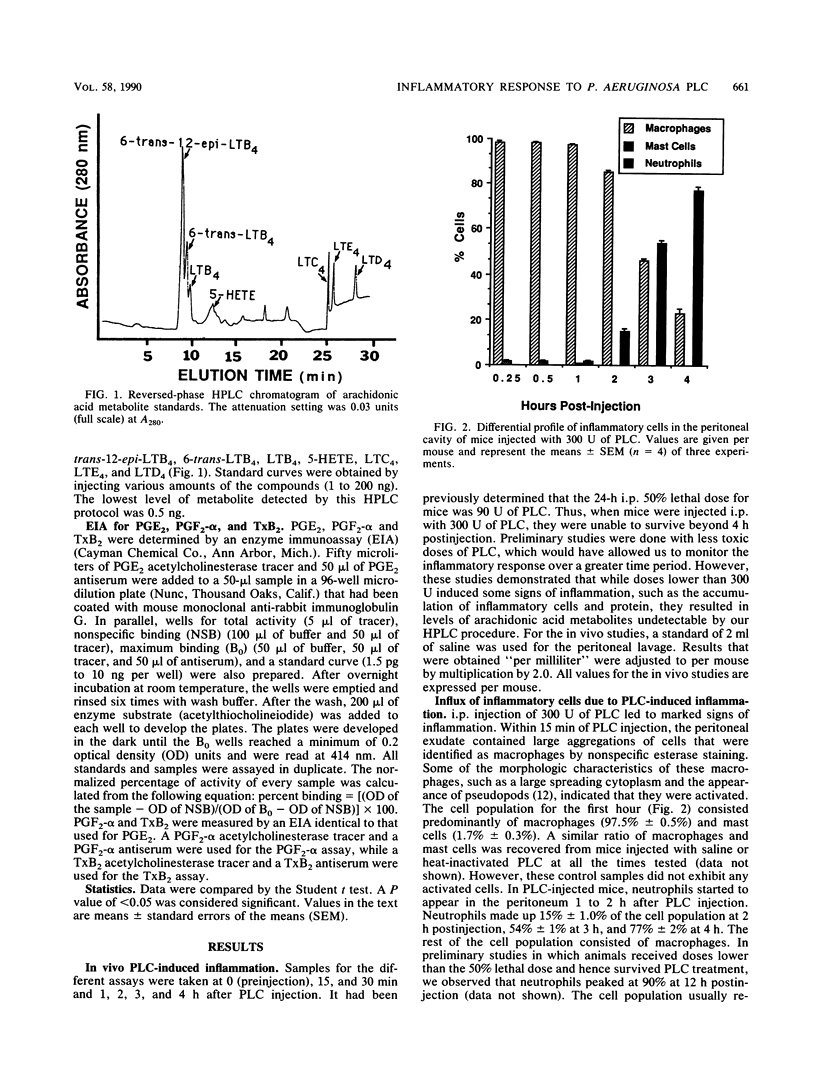
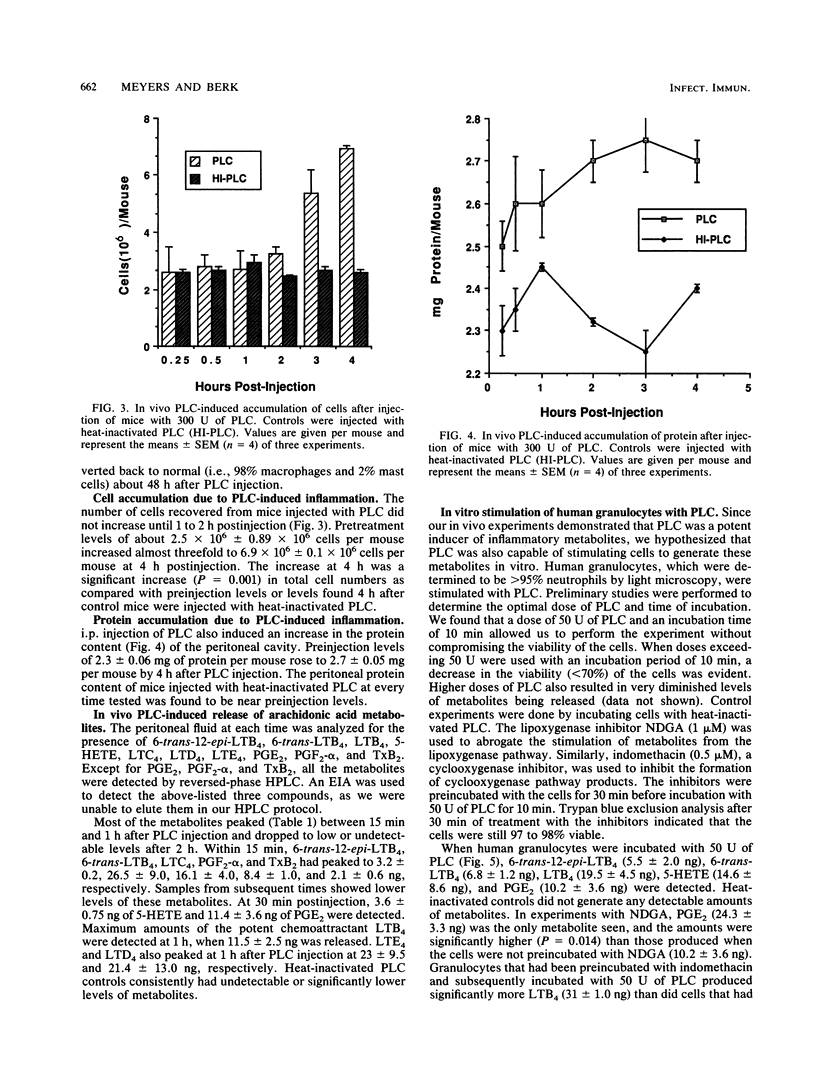
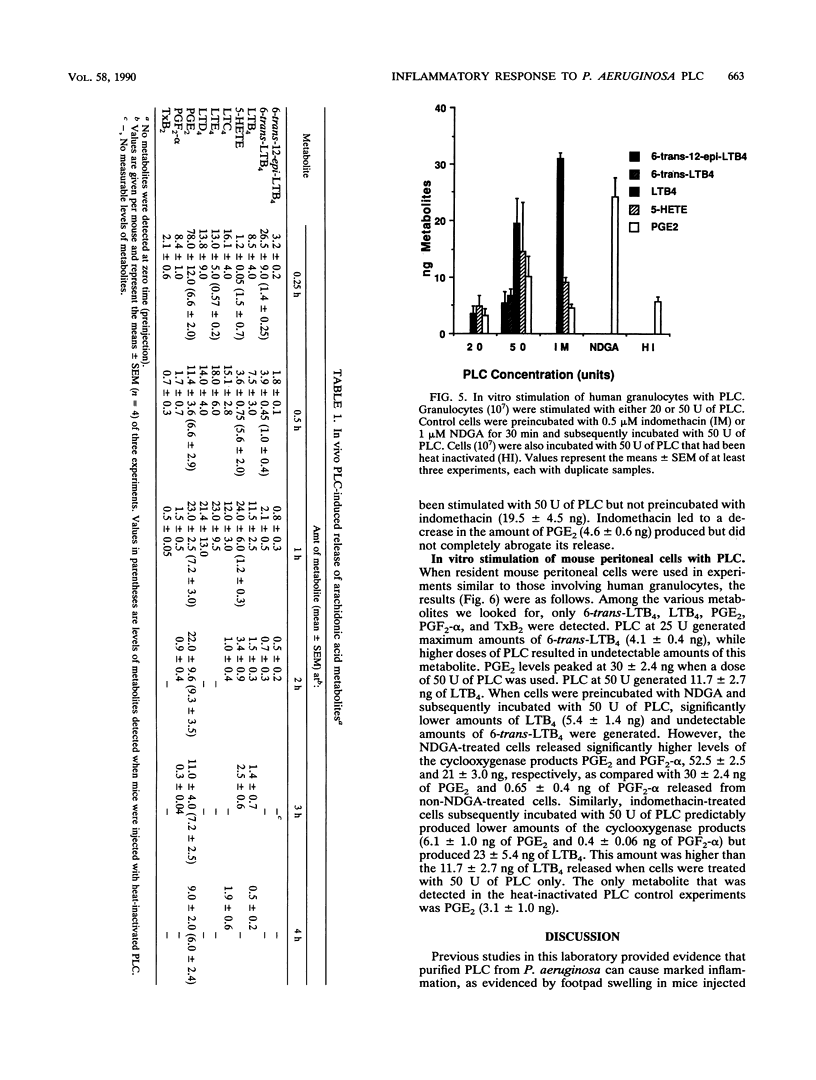
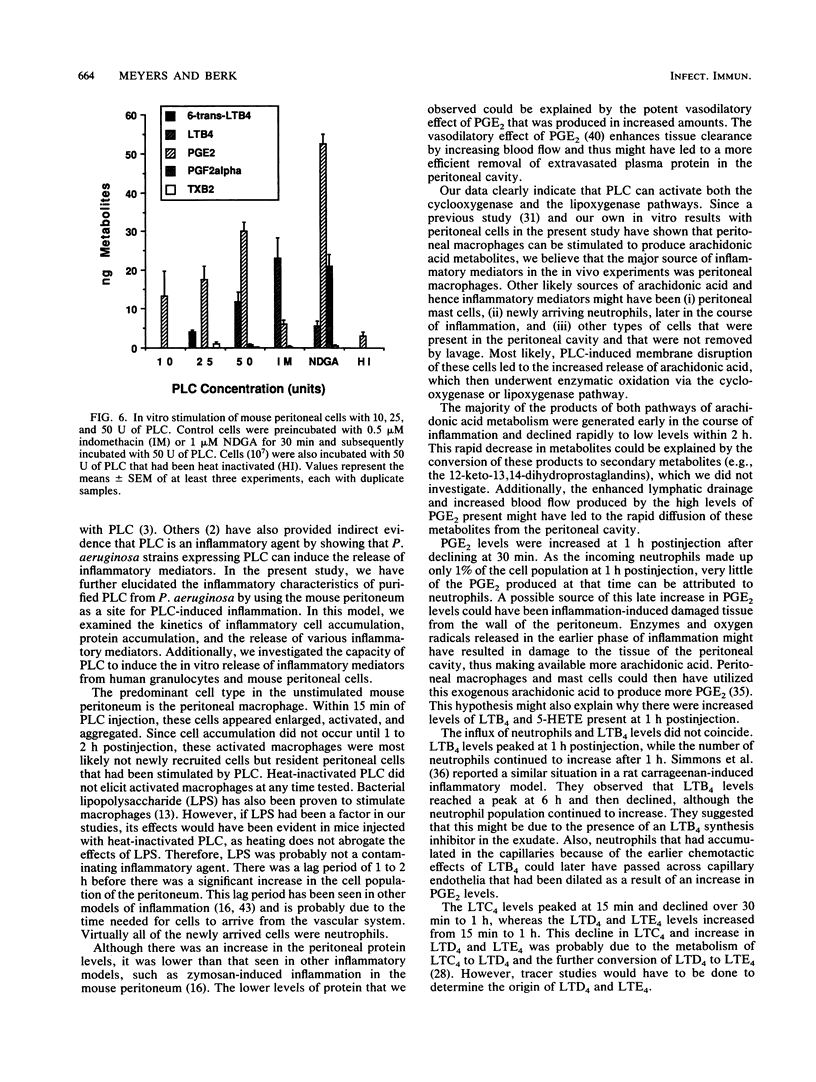
Phospholipase C (PLC) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa induced a marked inflammatory response when injected intraperitoneally in C3H/HeJ mice. This inflammation was characterized by the accumulation of inflammatory cells and plasma protein and the release of arachidonic acid metabolites (6-trans-12-epi-leukotriene B4 [LTB4], 6-trans-LTB4, LTB4, 5-HETE (5-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid), LTC4, LTD4, LTE4, prostaglandin E2 [PGE2], PGF2-alpha, and thromboxane B2 [TxB2]) in the peritoneal cavity of the mice. Heat-inactivated PLC did not evoke any of these effects, suggesting that enzyme activity is necessary for PLC-induced inflammation. When human granulocytes were incubated with PLC in vitro, 6-trans-12-epi-LTB4, 6-trans-LTB4, LTB4, 5-HETE, and PGE2 were generated. Mouse peritoneal cells stimulated with PLC released 6-trans-LTB4, LTB4, PGE2, PGF2-alpha, and TxB2. Both human granulocytes and mouse peritoneal cells stimulated with PLC generated significantly increased levels of arachidonic acid metabolites as compared with cells incubated with heat-inactivated PLC. Leukotriene production by both populations of cells was inhibited when the cells were preincubated with nordihydroguaiaretic acid and subsequently stimulated with PLC. Similarly, both cell types released significantly lower amounts of cyclooxygenase pathway products when they were preincubated with indomethacin and subsequently stimulated with PLC.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltch A. L., Hammer M. C., Smith R. P., Obrig T. G., Conroy J. V., Bishop M. B., Egy M. A., Lutz F. Effects of Pseudomonas aeruginosa cytotoxin on human serum and granulocytes and their microbicidal, phagocytic, and chemotactic functions. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):498–506. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.498-506.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann U., Scheffer J., Köller M., Schönfeld W., Erbs G., Müller F. E., König W. Induction of inflammatory mediators (histamine and leukotrienes) from rat peritoneal mast cells and human granulocytes by Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains from burn patients. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):2187–2195. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.2187-2195.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk R. S., Brown D., Coutinho I., Meyers D. In vivo studies with two phospholipase C fractions from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1728–1730. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1728-1730.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berka R. M., Vasil M. L. Phospholipase C (heat-labile hemolysin) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: purification and preliminary characterization. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):239–245. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.239-245.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgeat P., Fruteau de Laclos B., Rabinovitch H., Picard S., Braquet P., Hébert J., Laviolette M. Eosinophil-rich human polymorphonuclear leukocyte preparations characteristically release leukotriene C4 on ionophore A23187 challenge. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1984 Sep;74(3 Pt 2):310–315. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(84)90122-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgeat P., Samuelsson B. Arachidonic acid metabolism in polymorphonuclear leukocytes: effects of ionophore A23187. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2148–2152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremm K. D., Brom H. J., Alouf J. E., König W., Spur B., Crea A., Peters W. Generation of leukotrienes from human granulocytes by alveolysin from Bacillus alvei. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):188–193. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.188-193.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A., BENSON B. THE DIFFERENTIATION OF MONONUCLEAR PHAGOCYTES. MORPHOLOGY, CYTOCHEMISTRY, AND BIOCHEMISTRY. J Exp Med. 1965 Jan 1;121:153–170. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.1.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn Z. A. Activation of mononuclear phagocytes: fact, fancy, and future. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):813–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coutinho I. R., Berk R. S., Mammen E. Platelet aggregation by a phospholipase C from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Thromb Res. 1988 Sep 1;51(5):495–505. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(88)90115-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cromwell O., Walport M. J., Morris H. R., Taylor G. W., Hodson M. E., Batten J., Kay A. B. Identification of leukotrienes D and B in sputum from cystic fibrosis patients. Lancet. 1981 Jul 25;2(8239):164–165. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90353-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty N. S., Poubelle P., Borgeat P., Beaver T. H., Westrich G. L., Schrader N. L. Intraperitoneal injection of zymosan in mice induces pain, inflammation and the synthesis of peptidoleukotrienes and prostaglandin E2. Prostaglandins. 1985 Nov;30(5):769–789. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(85)90006-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durkin J. P., Shier W. T. Staphylococcal delta toxin stimulates endogenous phospholipase A2 activity and prostaglandin synthesis in fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 23;663(2):467–479. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90175-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engineer D. M., Niederhauser U., Piper P. J., Sirois P. Release of mediators of anaphylaxis: inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis and the modification of release of slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis and histamine. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 Jan;62(1):61–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1978.tb07006.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford-Hutchinson A. W., Bray M. A., Doig M. V., Shipley M. E., Smith M. J. Leukotriene B, a potent chemokinetic and aggregating substance released from polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Nature. 1980 Jul 17;286(5770):264–265. doi: 10.1038/286264a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granström M., Ericsson A., Strandvik B., Wretlind B., Pavlovskis O. R., Berka R., Vasil M. L. Relation between antibody response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoproteins and colonization/infection in patients with cystic fibrosis. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1984 Nov;73(6):772–777. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1984.tb17774.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humes J. L., Bonney R. J., Pelus L., Dahlgren M. E., Sadowski S. J., Kuehl F. A., Jr, Davies P. Macrophages synthesis and release prostaglandins in response to inflammatory stimuli. Nature. 1977 Sep 8;269(5624):149–151. doi: 10.1038/269149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Kabat D. NAD-dependent inhibition of protein synthesis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin,. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2284–2288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent C., Evers A., Haun S. S. Diacylglycerol metabolism in phospholipase C-treated mammalian cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Nov 1;250(2):519–525. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90757-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König B., König W., Scheffer J., Hacker J., Goebel W. Role of Escherichia coli alpha-hemolysin and bacterial adherence in infection: requirement for release of inflammatory mediators from granulocytes and mast cells. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):886–892. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.886-892.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicas T. I., Bradley J., Lochner J. E., Iglewski B. H. The role of exoenzyme S in infections with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1985 Oct;152(4):716–721. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.4.716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Driscoll B. R., Cromwell O., Kay A. B. Sputum leukotrienes in obstructive airways diseases. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Feb;55(2):397–404. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostroff R. M., Wretlind B., Vasil M. L. Mutations in the hemolytic-phospholipase C operon result in decreased virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 grown under phosphate-limiting conditions. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1369–1373. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1369-1373.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. W., Falkenhein S. F., Huber M. M. Sequential conversion of the glutathionyl side chain of slow reacting substance (SRS) to cysteinyl-glycine and cysteine in rat basophilic leukemia cells stimulated with A-23187. Prostaglandins. 1980 Nov;20(5):863–886. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(80)90139-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck M. J., Piper P. J., Williams T. J. The effect of leukotrienes C4 and D4 on the microvasculature of guinea-pig skin. Prostaglandins. 1981 Feb;21(2):315–321. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(81)90149-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosoff P. M., Savage N., Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 stimulates diacylglycerol production in T lymphocytes by a novel mechanism. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):73–81. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90181-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouzer C. A., Scott W. A., Cohn Z. A., Blackburn P., Manning J. M. Mouse peritoneal macrophages release leukotriene C in response to a phagocytic stimulus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4928–4932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouzer C. A., Scott W. A., Hamill A. L., Liu F. T., Katz D. H., Cohn Z. A. Secretion of leukotriene C and other arachidonic acid metabolites by macrophages challenged with immunoglobulin E immune complexes. J Exp Med. 1982 Oct 1;156(4):1077–1086. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.4.1077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salari H., Braquet P., Borgeat P. Comparative effects of indomethacin, acetylenic acids, 15-HETE, nordihydroguaiaretic acid and BW755C on the metabolism of arachidonic acid in human leukocytes and platelets. Prostaglandins Leukot Med. 1984 Jan;13(1):53–60. doi: 10.1016/0262-1746(84)90102-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffer J., König W., Braun V., Goebel W. Comparison of four hemolysin-producing organisms (Escherichia coli, Serratia marcescens, Aeromonas hydrophila, and Listeria monocytogenes) for release of inflammatory mediators from various cells. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):544–551. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.544-551.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott W. A., Pawlowski N. A., Andreach M., Cohn Z. A. Resting macrophages produce distinct metabolites from exogenous arachidonic acid. J Exp Med. 1982 Feb 1;155(2):535–547. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.2.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons P. M., Salmon J. A., Moncada S. The release of leukotriene B4 during experimental inflammation. Biochem Pharmacol. 1983 Apr 15;32(8):1353–1359. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(83)90446-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttorp N., Seeger W., Uhl J., Lutz F., Roka L. Pseudomonas aeruginosa cytotoxin stimulates prostacyclin production in cultured pulmonary artery endothelial cells: membrane attack and calcium influx. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Apr;123(1):64–72. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041230111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Sulavik M. C., Johnson K. J. Activated rat neutrophils. Correlation of arachidonate products with enzyme secretion but not with O(2)- generation. Am J Pathol. 1985 Jul;120(1):112–120. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittle B. J., Oren-Wolman N., Guth P. H. Gastric vasoconstrictor actions of leukotriene C4, PGF2 alpha, and thromboxane mimetic U-46619 on rat submucosal microcirculation in vivo. Am J Physiol. 1985 May;248(5 Pt 1):G580–G586. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1985.248.5.G580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. J. Prostaglandin E2, prostaglandin I2 and the vascular changes of inflammation. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Mar;65(3):517–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb07860.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Cryz S. J., Friedman R. L., Iglewski B. H. Contribution of toxin A and elastase to virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in chronic lung infections of rats. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1223–1228. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1223-1228.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wretlind B., Pavlovskis O. R. The role of proteases and exotoxin A in the pathogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1981;29:13–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita T., Ishibashi Y., Nagaoka I., Kasuya K., Masuda K., Warabi H., Shiokawa Y. Studies of glycogen-induced inflammation of mice. Dynamics of inflammatory responses and influence of antiinflammatory drugs and protease inhibitors. Inflammation. 1982 Mar;6(1):87–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00910722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



