Abstract
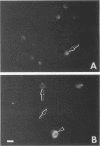
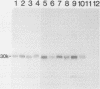
A monoclonal antibody (MAb) produced against trophozoites of Entamoeba histolytica strain HM-1:IMSS, reacted with all of 42 isolates and 4 clones showing pathogenic zymodeme (Z) patterns, i.e., Z-II, Z-II alpha-, Z-II (glucose phosphate isomerase: gamma +), Z-VII, Z-VII (glucose phosphate isomerase: alpha lack, gamma +), Z-XI, Z-XIV, and Z-XIX, regardless of culture conditions, geographical origins, or host symptoms in an indirect fluorescence antibody test. In contrast, the MAb failed to react with 14 isolates possessing nonpathogenic zymodemes Z-I and Z-VIII and did not react with other enteric protozoan parasites, such as E. histolytica-like Laredo, Entamoeba hartmanni, Entamoeba coli, Endolimax nana, Dientamoeba fragilis, Trichomonas hominis, and Giardia lamblia. Western immunoblotting analysis showed that the molecular weight of the antigenic component recognized by the MAb was exclusively 30,000 in pathogenic isolates of different zymodemes. These results suggest that the 30,000-molecular-weight antigen is a marker of pathogenic isolates and that the indirect fluorescent-antibody test with the MAb is useful for the accurate discrimination of pathogenic amebae.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Diamond L. S., Harlow D. R., Cunnick C. C. A new medium for the axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and other Entamoeba. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(4):431–432. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel L. I., Giladi M., Huber M., Gitler C., Mirelman D., Revel M., Rozenblatt S. DNA probes specific for Entamoeba histolytica possessing pathogenic and nonpathogenic zymodemes. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):926–931. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.926-931.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keister D. B. Axenic culture of Giardia lamblia in TYI-S-33 medium supplemented with bile. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1983;77(4):487–488. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(83)90120-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D., Bracha R., Chayen A., Aust-Kettis A., Diamond L. S. Entamoeba histolytica: effect of growth conditions and bacterial associates on isoenzyme patterns and virulence. Exp Parasitol. 1986 Aug;62(1):142–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(86)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D., Bracha R., Wexler A., Chayen A. Changes in isoenzyme patterns of a cloned culture of nonpathogenic Entamoeba histolytica during axenization. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):827–832. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.827-832.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D. Effect of culture conditions and bacterial associates on the zymodemes of Entamoeba histolytica. Parasitol Today. 1987 Feb;3(2):37–37. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(87)90210-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orozco E., Suárez M. E., Sánchez T. Differences in adhesion, phagocytosis and virulence of clones from Entamoeba histolytica, strain HM1:IMSS. Int J Parasitol. 1985 Dec;15(6):655–660. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(85)90012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson G. L. The laboratory diagnosis of human parasitic amoebae. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1968;62(2):285–294. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(68)90170-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargeaunt P. G., Baveja U. K., Nanda R., Anand B. S. Influence of geographical factors in the distribution of pathogenic zymodemes of Entamoeba histolytica: identification of zymodeme XIV in India. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1984;78(1):96–101. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(84)90185-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargeaunt P. G., Williams J. E., Bhojnani R., Kumate J., Jiménez E. A review of isoenzyme characterization of Entamoeba histolytica with particular reference to pathogenic and non-pathogenic stocks isolated in Mexico. Arch Invest Med (Mex) 1982;13 (Suppl 3):89–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargeaunt P. G., Williams J. E., Grene J. D. The differentiation of invasive and non-invasive Entamoeba histolytica by isoenzyme electrophoresis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(5):519–521. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90174-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargeaunt P. G. Zymodemes expressing possible genetic exchange in Entamoeba histolytica. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1985;79(1):86–89. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(85)90244-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana H., Nagakura K., Kaneda Y. Species-specific monoclonal antibodies for a membrane antigen(s) in all developmental forms of Trypanosoma cruzi. Z Parasitenkd. 1986;72(4):433–441. doi: 10.1007/BF00927887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannich E., Horstmann R. D., Knobloch J., Arnold H. H. Genomic DNA differences between pathogenic and nonpathogenic Entamoeba histolytica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5118–5122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Young T. M., Lu L. P., Unkeless J. C., Cohn Z. A. Characterization of a membrane pore-forming protein from Entamoeba histolytica. J Exp Med. 1982 Dec 1;156(6):1677–1690. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.6.1677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]