Abstract
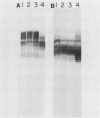
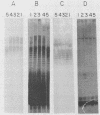
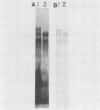
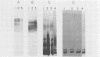
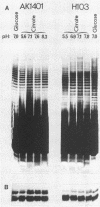
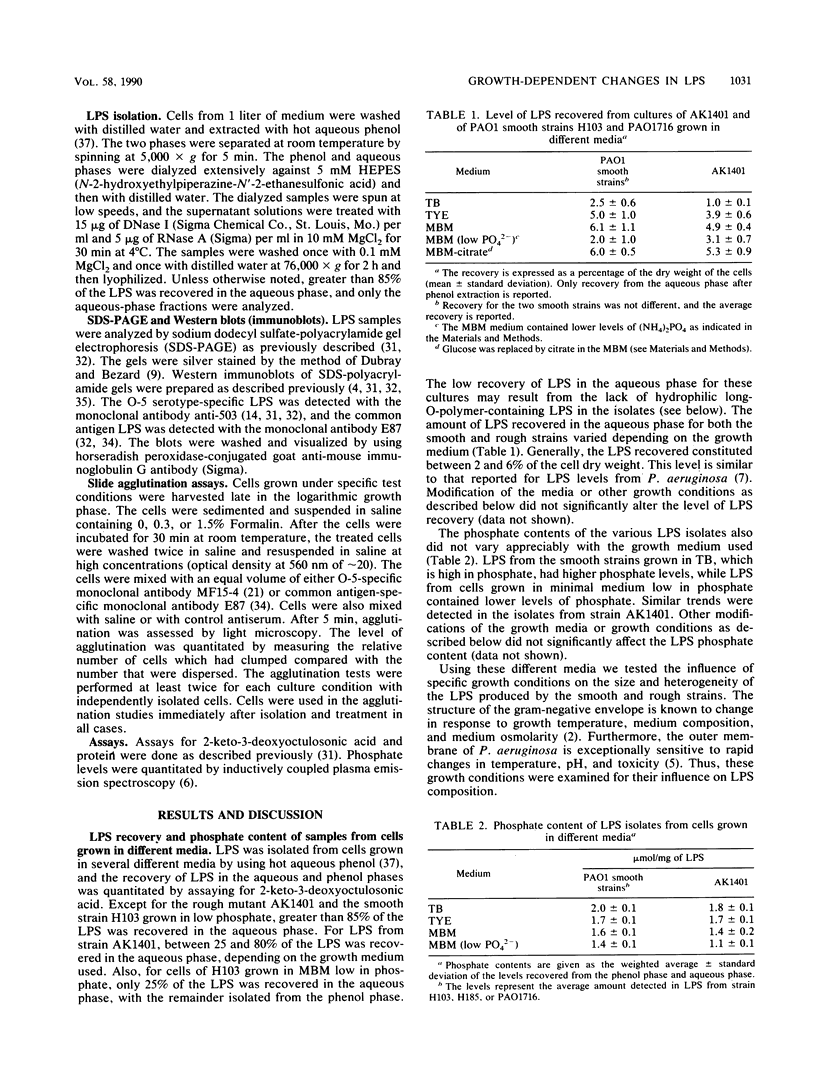
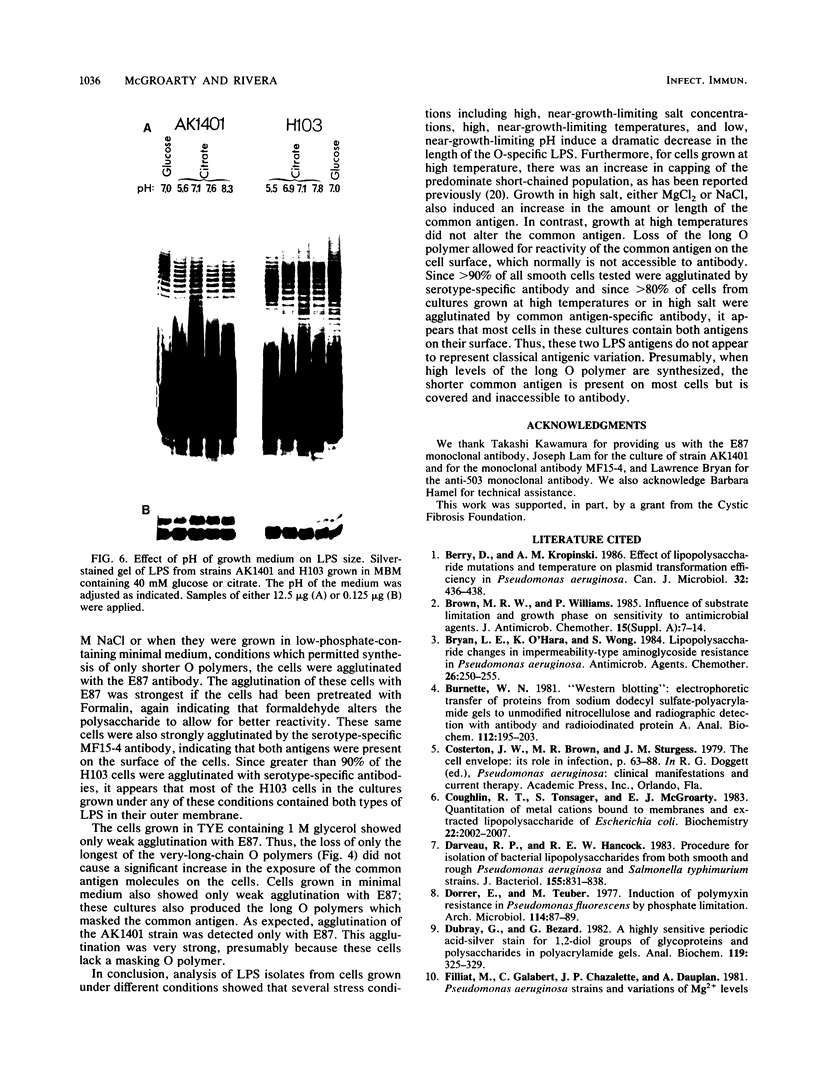
Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 was grown in various media and at different temperatures, and the heterogeneity of the extracted lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was characterized by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The size distributions of the serotype-specific LPS and the common antigen LPS were analyzed on Western blots (immunoblots). Cells grown at high, near-growth-limiting temperatures, at low pH, in low concentrations of phosphate, or in high concentrations of NaCl, MgCl2, glycerol, or sucrose produced decreased amounts of the very long chain population of O-antigen LPS molecules. Lower temperatures and lowered glycerol, lowered sucrose, low sulfate, lower salt concentrations, and elevated pH did not significantly affect the level of this LPS population. The size and amount of common antigen LPS was either unaffected or increased slightly when the cells were grown under the above stress conditions. Cells grown under normal, nonstressed conditions were agglutinated only by serotype-specific antibodies. In contrast, cells grown under stress conditions, in which the long-O-polymer LPS was absent, were agglutinated by both serotype-specific and common antigen-specific antibodies. The results indicate that the long O polymers cover and mask the shorter common antigen. However, specific growth conditions limit the production of the long O polymer, allowing the exposure and reactivity of the common antigen on the cell surface.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berry D., Kropinski A. M. Effect of lipopolysaccharide mutations and temperature on plasmid transformation efficiency in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Can J Microbiol. 1986 May;32(5):436–438. doi: 10.1139/m86-082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. R., Williams P. Influence of substrate limitation and growth phase on sensitivity to antimicrobial agents. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jan;15 (Suppl A):7–14. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.suppl_a.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., O'Hara K., Wong S. Lipopolysaccharide changes in impermeability-type aminoglycoside resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Aug;26(2):250–255. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.2.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin R. T., Tonsager S., McGroarty E. J. Quantitation of metal cations bound to membranes and extracted lipopolysaccharide of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 12;22(8):2002–2007. doi: 10.1021/bi00277a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darveau R. P., Hancock R. E. Procedure for isolation of bacterial lipopolysaccharides from both smooth and rough Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Salmonella typhimurium strains. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):831–838. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.831-838.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorrer E., Teuber M. Induction of polymyxin resistance in Pseudomonas fluorescens by phosphate limitation. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Jul 26;114(1):87–89. doi: 10.1007/BF00429636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubray G., Bezard G. A highly sensitive periodic acid-silver stain for 1,2-diol groups of glycoproteins and polysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 15;119(2):325–329. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90593-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fomsgaard A., Conrad R. S., Galanos C., Shand G. H., Høiby N. Comparative immunochemistry of lipopolysaccharides from typable and polyagglutinable Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 May;26(5):821–826. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.5.821-826.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilleland H. E., Jr Adaptive alterations in the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria during human infection. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Apr;34(4):499–502. doi: 10.1139/m88-085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey A. J., Hatlelid L., Bryan L. E. Correlation between lipopolysaccharide structure and permeability resistance in beta-lactam-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Aug;26(2):181–186. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.2.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey A. J., Shahrabadi M. S., Bryan L. E. Distribution of porin and lipopolysaccharide antigens on a Pseudomonas aeruginosa permeability mutant. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Nov;30(5):802–805. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.5.802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Mutharia L. M., Chan L., Darveau R. P., Speert D. P., Pier G. B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from patients with cystic fibrosis: a class of serum-sensitive, nontypable strains deficient in lipopolysaccharide O side chains. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):170–177. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.170-177.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Raffle V. J., Nicas T. I. Involvement of the outer membrane in gentamicin and streptomycin uptake and killing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 May;19(5):777–785. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.5.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenward M. A., Brown M. R., Fryer J. J. The influence of calcium or manganese on the resistance to EDTA, polymyxin B or cold shock, and the composition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa grown in glucose- or magnesium-depleted batch cultures. J Appl Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;47(3):489–503. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1979.tb01210.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koval S. F., Meadow P. M. The isolation and characterization of lipopolysaccharide-defective mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAC1. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Feb;98(2):387–398. doi: 10.1099/00221287-98-2-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropinski A. M., Lewis V., Berry D. Effect of growth temperature on the lipids, outer membrane proteins, and lipopolysaccharides of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):1960–1966. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.1960-1966.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam J. S., MacDonald L. A., Lam M. Y., Duchesne L. G., Southam G. G. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against serotype strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1051–1057. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1051-1057.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam M. Y., McGroarty E. J., Kropinski A. M., MacDonald L. A., Pedersen S. S., Høiby N., Lam J. S. Occurrence of a common lipopolysaccharide antigen in standard and clinical strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 May;27(5):962–967. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.5.962-967.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzar M. A., Montie T. C. Avirulence and altered physiological properties of cystic fibrosis strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):572–576. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.572-576.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnell M., Wright A. Variation in the structure and bacteriophage-inactivating capacity of Salmonella anatum lipopolysaccharide as a function of growth temperature. J Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;137(2):746–751. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.2.746-751.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills B. J., Holloway B. W. Mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa that show specific hypersensitivity to aminoglycosides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Sep;10(3):411–416. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.3.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicas T. I., Hancock R. E. Outer membrane protein H1 of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: involvement in adaptive and mutational resistance to ethylenediaminetetraacetate, polymyxin B, and gentamicin. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):872–878. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.872-878.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojeniyi B., Baek L., Høiby N. Polyagglutinability due to loss of O-antigenic determinants in Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from cystic fibrosis patients. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1985 Feb;93(1):7–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1985.tb02844.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penketh A., Pitt T., Roberts D., Hodson M. E., Batten J. C. The relationship of phenotype changes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa to the clinical condition of patients with cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 May;127(5):605–608. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.5.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole K., Braun V. Influence of growth temperature and lipopolysaccharide on hemolytic activity of Serratia marcescens. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5146–5152. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5146-5152.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivera M., Bryan L. E., Hancock R. E., McGroarty E. J. Heterogeneity of lipopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: analysis of lipopolysaccharide chain length. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):512–521. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.512-521.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivera M., McGroarty E. J. Analysis of a common-antigen lipopolysaccharide from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):2244–2248. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.2244-2248.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said A. A., Livermore D. M., Williams R. J. Expression of H1 outer-membrane protein of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in relation to sensitivity to EDTA and polymyxin B. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Nov;24(3):267–274. doi: 10.1099/00222615-24-3-267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada S., Kawamura T., Masuho Y., Tomibe K. A new common polysaccharide antigen of strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa detected with a monoclonal antibody. J Infect Dis. 1985 Dec;152(6):1290–1299. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.6.1290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Hutzler M., Kao L. Environmental modulation of lipopolysaccharide chain length alters the sensitivity of Escherichia coli to the neutrophil bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):594–599. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.594-599.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson S. G. Composition and structure of lipopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Nov-Dec;5 (Suppl 5):S941–S949. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_5.s941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]