Abstract
The exotoxin A gene (toxA) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 was expressed from the lac promoter in Escherichia coli, and the localization of the toxin A protein was determined. Throughout the growth cycle, the ADP-ribosyltransferase activity of toxin A was gradually reduced in the periplasm of E. coli, with no apparent degradation of the toxin A protein. This suggests the presence of an E. coli periplasmic factor that interferes with the ADP-ribosyltransferase activity in toxin A. Such an inactivating factor was found in the periplasmic extract from control E. coli cells. The processing of toxin A in E. coli was examined by pulse-chase immunoprecipitation experiments. Mature toxin was detected in both the periplasm and cytoplasm, whereas the membranes contained both mature and precursor forms. Toxin A precursor appears to be processed in both the cytoplasm and the periplasm of E. coli. Toxin A proteins from P. aeruginosa PAO1, PA103, and PAK were compared for their secretion in E. coli. Despite the differences in the amino acid sequences of their leader peptides, toxin A proteins from strains PAO1, PA103, and PAK were processed and secreted to the periplasm of E. coli.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angus B. L., Carey A. M., Caron D. A., Kropinski A. M., Hancock R. E. Outer membrane permeability in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: comparison of a wild-type with an antibiotic-supersusceptible mutant. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Feb;21(2):299–309. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung D. W., Collier R. J. Enzymatically active peptide from the adenosine diphosphate-ribosylating toxin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):832–841. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.832-841.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B. Nature of Col E 1 plasmid replication in Escherichia coli in the presence of the chloramphenicol. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):667–676. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.667-676.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalbey R. E., Wickner W. The role of the polar, carboxyl-terminal domain of Escherichia coli leader peptidase in its translocation across the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13844–13849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas C. M., Guidi-Rontani C., Collier R. J. Exotoxin A of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: active, cloned toxin is secreted into the periplasmic space of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):4962–4966. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.4962-4966.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg J. B., Ohman D. E. Cloning and expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa of a gene involved in the production of alginate. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1115–1121. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1115-1121.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. L., Smith D. H., Baldridge J. S., Harkins R. N., Vasil M. L., Chen E. Y., Heyneker H. L. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression in Escherichia coli of the exotoxin A structural gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2645–2649. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
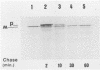
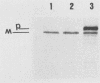
- Hamood A. N., Olson J. C., Vincent T. S., Iglewski B. H. Regions of toxin A involved in toxin A excretion in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):1817–1824. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.1817-1824.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Kabat D. NAD-dependent inhibition of protein synthesis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin,. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2284–2288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Bassford P. J., Jr, Beckwith J. Protein localization in E. coli: is there a common step in the secretion of periplasmic and outer-membrane proteins? Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):707–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn R., Schiebler W., Greengard P. A quantitative dot-immunobinding assay for proteins using nitrocellulose membrane filters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1684–1687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler E., Safrin M. Synthesis, processing, and transport of Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5241–5247. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5241-5247.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland D., Botstein D. Secretion of beta-lactamase requires the carboxy end of the protein. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):749–760. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90321-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lory S., Strom M. S., Johnson K. Expression and secretion of the cloned Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):714–719. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.714-719.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lory S., Tai P. C., Davis B. D. Mechanism of protein excretion by gram-negative bacteria: Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):695–702. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.695-702.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALAMY M. H., HORECKER B. L. RELEASE OF ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE FROM CELLS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI UPON LYSOZYME SPHEROPLAST FORMATION. Biochemistry. 1964 Dec;3:1889–1893. doi: 10.1021/bi00900a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizusawa S., Nishimura S., Seela F. Improvement of the dideoxy chain termination method of DNA sequencing by use of deoxy-7-deazaguanosine triphosphate in place of dGTP. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1319–1324. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pages J. M., Anba J., Bernadac A., Shinagawa H., Nakata A., Lazdunski C. Normal precursors of periplasmic proteins accumulated in the cytoplasm are not exported post-translationally in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Sep 17;143(3):499–505. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08398.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palva E. T., Hirst T. R., Hardy S. J., Holmgren J., Randall L. Synthesis of a precursor to the B subunit of heat-labile enterotoxin in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):325–330. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.325-330.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine M. J. Response of intracellular proteolysis to alteration of bacterial protein and the implications in metabolic regulation. J Bacteriol. 1967 May;93(5):1527–1533. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.5.1527-1533.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray P., Dev I., MacGregor C., Bassford P., Jr Signal peptidases. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;125:75–102. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71251-7_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M., Roa M., Débarbouillé M. Mutations that affect lamB gene expression at a posttranscriptional level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2937–2941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauch K. L., Beckwith J. An Escherichia coli mutation preventing degradation of abnormal periplasmic proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1576–1580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasil M. L., Kabat D., Iglewski B. H. Structure-activity relationships of an exotoxin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):353–361. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.353-361.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick M. J., Iglewski B. H. Determination of the amino acid change responsible for the nontoxic, cross-reactive exotoxin A protein (CRM 66) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO-PR1. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5385–5388. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5385-5388.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]