Abstract
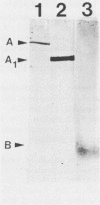
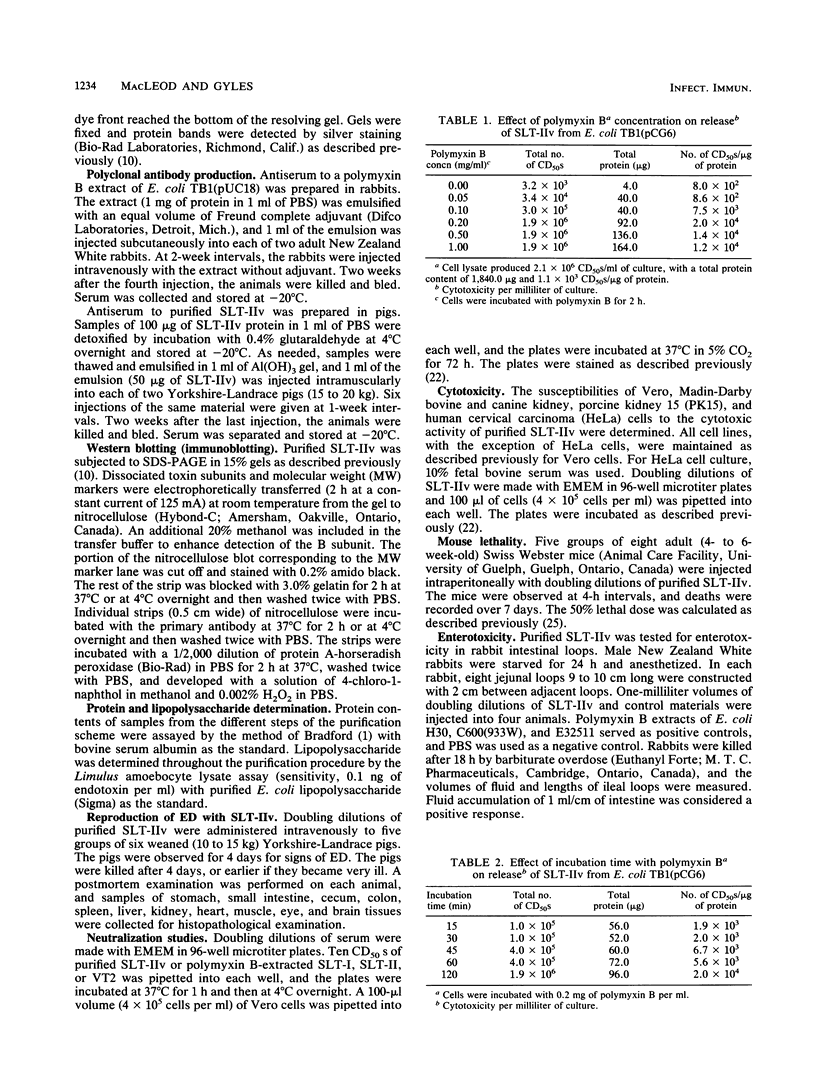
A Shiga-like toxin II variant was purified to homogeneity from Escherichia coli TB1(pCG6), which contained the toxin genes cloned in multicopy plasmid pUC18. The purification scheme involved polymyxin B extraction of the toxin from bacterial cells, followed by differential (NH4)2SO4 precipitation, anion- and cation-exchange fast-protein liquid chromatography, and immunoaffinity exclusion chromatography. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of purified toxin revealed three protein bands that migrated with calculated molecular weights of 33,000, 27,500, and 7,500. These bands correspond to values for the A, A1, and B subunits, respectively, that would be expected on the basis of the nucleotide sequence and comparison with data for Shiga toxin and other Shiga-like toxins. Electrophoresis under nonreducing conditions resulted in disappearance of the 27,000-molecular-weight band. Western blot (immunoblot) analysis revealed three protein bands with molecular weights of 33,000, 27,500, and 7,500. The purified toxin induced typical signs of edema disease in pigs injected intravenously with doses as small as 3 ng/kg of body weight. The 50% cytotoxic doses for Vero, PK15, and Madin-Darby bovine and canine kidney cells were 0.5, 2.0, 8.0, and 8.0 pg, respectively. The 50% lethal dose of purified toxin for mice was 0.9 pg by the intraperitoneal route. Approximately 75 micrograms of purified toxin was required to induce a 1-ml/cm fluid response in rabbit ileal loops. Antiserum to the Shiga-like toxin II variant neutralized homologous toxin, Shiga-like toxin II, and Verotoxin 2 but not Shiga-like toxin I.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderwood S. B., Auclair F., Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G. T., Mekalanos J. J. Nucleotide sequence of the Shiga-like toxin genes of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4364–4368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerny G., Teuber M. Differential release of periplasmic versus cytoplasmic enzymes from Escherichia coli B by polymixin B. Arch Mikrobiol. 1971;78(2):166–179. doi: 10.1007/BF00424873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clugston R. E., Nielsen N. O. Experimental edema disease of swine (E. coli enterotoxemia). I. Dectection and preparation of an active principle. Can J Comp Med. 1974 Jan;38(1):22–28. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS J. W., ALLEN R. C., SMIBERT R. M. Studies on hemolytic Escherichia coli associated with edema disease of swine, I. Separation and properties of a toxin of hemolytic Escherichia coli. Am J Vet Res. 1961 Jul;22:736–740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobrescu L. New biological effect of edema disease principle (Escherichia coli-neurotoxin) and its use as an in vitro for this toxin. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Jan;44(1):31–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobrescu L., van Wijnendaele F. Immunological studies in mice with swine edema disease principle (neurotoxin). Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1979 Apr;26(3):239–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.1979.tb00811.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G. T., Edson C., Thorley-Lawson D., Jacewicz M. Pathogenesis of Shigella diarrhea. IX. Simplified high yield purification of Shigella toxin and characterization of subunit composition and function by the use of subunit-specific monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies. J Exp Med. 1984 Dec 1;160(6):1767–1781. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.6.1767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G. T. Shigella dysenteriae 1 cytotoxin: periplasmic protein releasable by polymyxin B and osmotic shock. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):270–274. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.270-274.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes F. P., Barrett T. J., Green J. H., Aloisio C. H., Spika J. S., Strockbine N. A., Wachsmuth I. K. Affinity purification and characterization of Shiga-like toxin II and production of toxin-specific monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1926–1933. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1926-1933.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon V. P., Gyles C. L., Wilcock B. P. Effects of Escherichia coli Shiga-like toxins (verotoxins) in pigs. Can J Vet Res. 1989 Jul;53(3):306–312. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin D. E., Gemski P. Release of Shiga toxin from Shigella dysenteriae 1 by polymyxin B. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):425–428. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.425-428.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C. L., De Grandis S. A., MacKenzie C., Brunton J. L. Cloning and nucleotide sequence analysis of the genes determining verocytotoxin production in a porcine edema disease isolate of Escherichia coli. Microb Pathog. 1988 Dec;5(6):419–426. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90003-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A., de Grandis S., Friesen J., Karmali M., Petric M., Congi R., Brunton J. L. Cloning and expression of the genes specifying Shiga-like toxin production in Escherichia coli H19. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):375–379. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.375-379.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A. Infection by verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jan;2(1):15–38. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Petric M., Louie S., Cheung R. Antigenic heterogeneity of Escherichia coli verotoxins. Lancet. 1986 Jan 18;1(8473):164–165. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92307-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konowalchuk J., Dickie N., Stavric S., Speirs J. I. Comparative studies of five heat-labile toxic products of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):644–648. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.644-648.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konowalchuk J., Speirs J. I., Stavric S. Vero response to a cytotoxin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):775–779. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.775-779.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod D. L., Gyles C. L. Effects of culture conditions on yield of Shiga-like toxin-IIv from Escherichia coli. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Jun;35(6):623–629. doi: 10.1139/m89-100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Holmes R. K. Shiga and Shiga-like toxins. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):206–220. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.206-220.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., LaVeck G. D. Purification and characterization of a Shigella dysenteriae 1-like toxin produced by Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):675–683. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.675-683.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., LaVeck G. D., Thompson M. R., Formal S. B. Production of Shigella dysenteriae type 1-like cytotoxin by Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1982 Dec;146(6):763–769. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.6.763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padhye V. V., Kittell F. B., Doyle M. P. Purification and physicochemical properties of a unique Vero cell cytotoxin from Escherichia coli O157:H7. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Sep 14;139(2):424–430. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scotland S. M., Smith H. R., Rowe B. Two distinct toxins active on Vero cells from Escherichia coli O157. Lancet. 1985 Oct 19;2(8460):885–886. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90146-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Green P., Parsell Z. Vero cell toxins in Escherichia coli and related bacteria: transfer by phage and conjugation and toxic action in laboratory animals, chickens and pigs. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Oct;129(10):3121–3137. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-10-3121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Jackson M. P., Sung L. M., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Cloning and sequencing of the genes for Shiga toxin from Shigella dysenteriae type 1. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1116–1122. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1116-1122.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Marques L. R., Newland J. W., Smith H. W., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Two toxin-converting phages from Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain 933 encode antigenically distinct toxins with similar biologic activities. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):135–140. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.135-140.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein D. L., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Effects of iron and temperature on Shiga-like toxin I production by Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):106–111. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.106-111.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein D. L., Jackson M. P., Samuel J. E., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Cloning and sequencing of a Shiga-like toxin type II variant from Escherichia coli strain responsible for edema disease of swine. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4223–4230. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4223-4230.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yutsudo T., Honda T., Miwatani T., Takeda Y. Characterization of purified Shiga toxin from Shigella dysenteriae 1. Microbiol Immunol. 1986;30(11):1115–1127. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1986.tb03041.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yutsudo T., Nakabayashi N., Hirayama T., Takeda Y. Purification and some properties of a Vero toxin from Escherichia coli O157:H7 that is immunologically unrelated to Shiga toxin. Microb Pathog. 1987 Jul;3(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]