Abstract
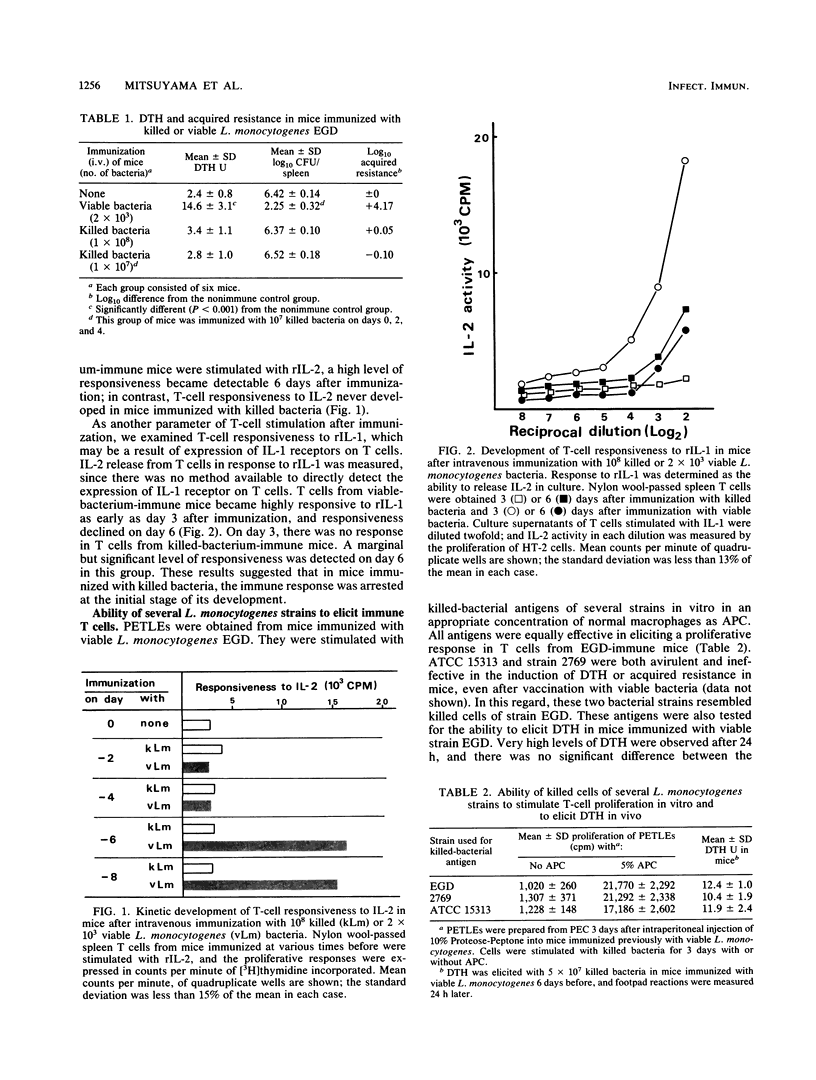
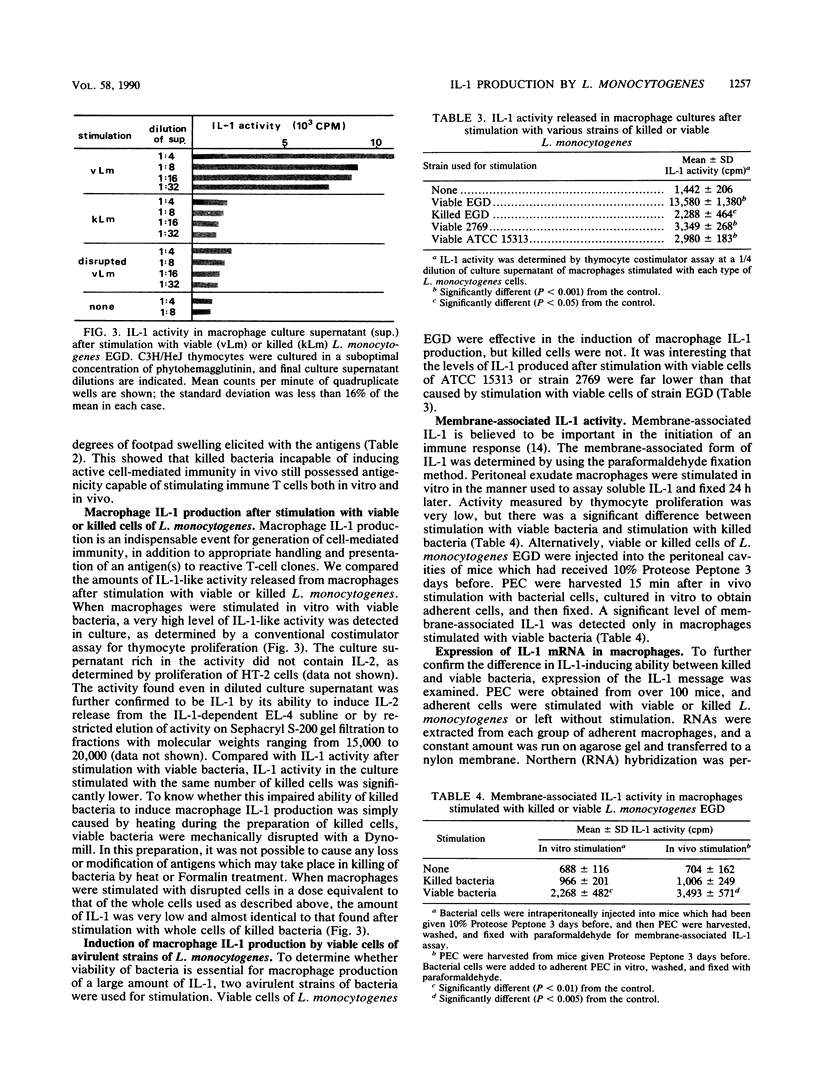
T-cell-mediated immunity to Listeria monocytogenes in mice, as determined by delayed-type hypersensitivity and acquired resistance, was induced by immunization with viable bacteria but not with killed bacteria, even when killed cells were injected in a high dose or repeatedly. T cells obtained from mice immunized with viable L. monocytogenes were readily stimulated with killed-bacterial antigens, resulting in T-cell proliferation in vitro and expression of a delayed footpad reaction in vivo. After immunization with killed-bacterial vaccine, T-cell responsiveness to interleukin 2 (IL-2) never developed but a lower level of responsiveness to IL-1 appeared later than with T cells from mice immunized with viable bacteria. When IL-1 production by macrophages was examined in vitro, viable L. monocytogenes stimulated a high level of IL-1 release while killed bacteria did not. Avirulent strains which were ineffective in the induction of T-cell mediated immunity were incapable of inducing IL-1 production as well. The impaired ability of killed bacteria to stimulate IL-1 production was confirmed by the level of IL-1 mRNA expression. These results suggested that the ineffectiveness of killed L. monocytogenes vaccine is not due to loss or lack of antigenic epitopes but may be ascribed to insufficient induction of IL-1 production in the initial stage of the immune response in vivo.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berche P., Gaillard J. L., Sansonetti P. J. Intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes as a prerequisite for in vivo induction of T cell-mediated immunity. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2266–2271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanden R. V., Langman R. E. Cell-mediated immunity to bacterial infection in the mouse. Thymus-derived cells as effectors of acquired resistance to Listeria monocytogenes. Scand J Immunol. 1972;1(4):379–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1972.tb03304.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanden R. V., Lefford M. J., Mackaness G. B. The host response to Calmette-Guérin bacillus infection in mice. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):1079–1107. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanden R. V., Mackaness G. B., Collins F. M. Mechanisms of acquired resistance in mouse typhoid. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):585–600. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breiman R. F., Horwitz M. A. Guinea pigs sublethally infected with aerosolized Legionella pneumophila develop humoral and cell-mediated immune responses and are protected against lethal aerosol challenge. A model for studying host defense against lung infections caused by intracellular pathogens. J Exp Med. 1987 Mar 1;165(3):799–811. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.3.799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty T., Goebel W. Recent developments in the study of virulence in Listeria monocytogenes. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1988;138:41–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlon P. J., Grabstein K. H., Alpert A., Prickett K. S., Hopp T. P., Gillis S. Localization of human mononuclear cell interleukin 1. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 1;139(1):98–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr A. G., Kiely J. M., Unanue E. R. Macrophage-T cell interactions involving Listeria monocytogenes--role of the H-2 gene complex. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2395–2404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Sansonetti P. Transposon mutagenesis as a tool to study the role of hemolysin in the virulence of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):50–55. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.50-55.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J., PICKETT M. J. A cellular basis of immunity in experimental Brucella infection. J Exp Med. 1958 Sep 1;108(3):343–360. doi: 10.1084/jem.108.3.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn H., Kaufmann S. H. The role of cell-mediated immunity in bacterial infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Nov-Dec;3(6):1221–1250. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.6.1221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handa T., Mitsuyama M., Watanabe Y., Koga T., Nomoto K. A significant role of the macrophage accumulation induced by MCF in the protection of mice against Listeria monocytogenes in vivo. Cell Immunol. 1987 May;106(2):330–342. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(87)90176-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurme M. Membrane-associated interleukin 1 is required for the activation of T cells in the anti-CD3 antibody-induced T cell response. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 15;139(4):1168–1172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kathariou S., Metz P., Hof H., Goebel W. Tn916-induced mutations in the hemolysin determinant affecting virulence of Listeria monocytogenes. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1291–1297. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1291-1297.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato K., Yamamoto K. Suppression of BCG cell wall-induced delayed-type hypersensitivity by BCG pre-treatment. II. Induction of suppressor T cells by heat-killed BCG injection. Immunology. 1982 Apr;45(4):655–661. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H. Acquired resistance to facultative intracellular bacteria: relationship between persistence, cross-reactivity at the T-cell level, and capacity to stimulate cellular immunity of different Listeria strains. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):234–241. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.234-241.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H. Effective antibacterial protection induced by a Listeria monocytogenes-specific T cell clone and its lymphokines. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1265–1270. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1265-1270.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H., Hahn H., Berger R., Kirchner H. Interferon-gamma production by Listeria monocytogenes-specific T cells active in cellular antibacterial immunity. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Mar;13(3):265–268. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H., Hahn H. Biological functions of t cell lines with specificity for the intracellular bacterium Listeria monocytogenes in vitro and in vivo. J Exp Med. 1982 Jun 1;155(6):1754–1765. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.6.1754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H., Hahn H., Simon M. M., Röllinghoff M., Wagner H. Interleukin 2 induction in Lyt 1+ 23- T cells from Listeria monocytogenes-immune mice. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):1292–1294. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.1292-1294.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H., Hug E., Väth U., Müller I. Effective protection against Listeria monocytogenes and delayed-type hypersensitivity to listerial antigens depend on cooperation between specific L3T4+ and Lyt 2+ T cells. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):263–266. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.263-266.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H. Immunity against intracellular bacteria: biological effector functions and antigen specificity of T lymphocytes. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1988;138:141–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killar L. M., Eisenstein T. K. Delayed-type hypersensitivity and immunity to Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):504–508. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.504-508.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurt-Jones E. A., Beller D. I., Mizel S. B., Unanue E. R. Identification of a membrane-associated interleukin 1 in macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1204–1208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurt-Jones E. A., Virgin H. W., 4th, Unanue E. R. In vivo and in vitro expression of macrophage membrane interleukin 1 in response to soluble and particulate stimuli. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):10–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefford M. J., McGregor D. D., Mackaness G. B. Immune response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis in rats. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):182–189. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.182-189.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepe-Zuniga J. L., Gery I. Production of intra- and extracellular interleukin-1 (IL-1) by human monocytes. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1984 May;31(2):222–230. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(84)90242-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomedico P. T., Gubler U., Hellmann C. P., Dukovich M., Giri J. G., Pan Y. C., Collier K., Semionow R., Chua A. O., Mizel S. B. Cloning and expression of murine interleukin-1 cDNA in Escherichia coli. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):458–462. doi: 10.1038/312458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenthal J. W., Cerottini J. C., MacDonald H. R. Interleukin 1-dependent induction of both interleukin 2 secretion and interleukin 2 receptor expression by thymoma cells. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 15;137(4):1226–1231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. THE IMMUNOLOGICAL BASIS OF ACQUIRED CELLULAR RESISTANCE. J Exp Med. 1964 Jul 1;120:105–120. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIKI K., MACKANESS G. B. THE PASSIVE TRANSFER OF ACQUIRED RESISTANCE TO LISTERIA MONOCYTOGENES. J Exp Med. 1964 Jul 1;120:93–103. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuyama M., Watanabe Y., Sano M., Amako K., Nomoto K. Generation of Listeria monocytogenes-specific T cells mediating delayed footpad reaction and protection in neonatally thymectomized mice but not in nude mice. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1988;177(4):207–217. doi: 10.1007/BF00211220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B. Interleukin 1 and T cell activation. Immunol Rev. 1982;63:51–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Näher H., Sperling U., Hahn H. H-2K-restricted granuloma formation by Ly-2+ T cells in antibacterial protection to facultative intracellular bacteria. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):569–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M., Collins F. M. Protection against Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection by adoptive immunotherapy. Requirement for T cell-deficient recipients. J Exp Med. 1983 Jul 1;158(1):74–83. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.1.74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedrazzini T., Louis J. A. Functional analysis in vitro and in vivo of Mycobacterium bovis strain BCG-specific T cell clones. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 1;136(5):1828–1834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralston D. J., Elberg S. S. Sensitization and recall of anti-Brucella immunity in Guinea pig macrophages by attenuated and virulent Brucella. Infect Immun. 1971 Feb;3(2):200–208. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.2.200-208.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakawa F., Tanaka Y., Ota T., Suzuki H., Eto S., Yamashita U. Expression of interleukin 1 receptors on human peripheral T cells. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4243–4248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperling U., Kaufmann S. H., Hahn H. Production of macrophage-activating and migration-inhibition factors in vitro by serologically selected and cloned Listeria monocytogenes-specific T cells of the Lyt 1+2- phenotype. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):111–115. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.111-115.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Beller D. I., Lu C. Y., Allen P. M. Antigen presentation: comments on its regulation and mechanism. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):1–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Meer C., Hofhuis F. M., Willers J. M. Killed Listeria monocytogenes vaccine becomes protective on addition of polyanions. Nature. 1977 Oct 13;269(5629):594–595. doi: 10.1038/269594a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y., Mitsuyama M., Koga T., Handa T., Yoshikai Y., Nomoto K. Protective immunity to Listeria monocytogenes in neonatally thymectomized (NTx) mice: involvement of T cells distinct from those in sham-thymectomized mice. Immunology. 1988 Apr;63(4):649–655. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Kato K., Kimura T. Killed Listeria-induced suppressor T cells involved in suppression of delayed-type hypersensitivity and protection against Listeria infection. Immunology. 1985 Aug;55(4):609–619. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dijk H., Hofhuis F. M., Berns E. M., van der Meer C., Willers J. M. Killed Listeria monocytogenes vaccine is protective in C3H/HeJ mice without addition of adjuvants. Nature. 1980 Aug 14;286(5774):713–714. doi: 10.1038/286713a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Koenig C. H., Finger H., Hof H. Failure of killed Listeria monocytogenes vaccine to produce protective immunity. Nature. 1982 May 20;297(5863):233–234. doi: 10.1038/297233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



