Abstract
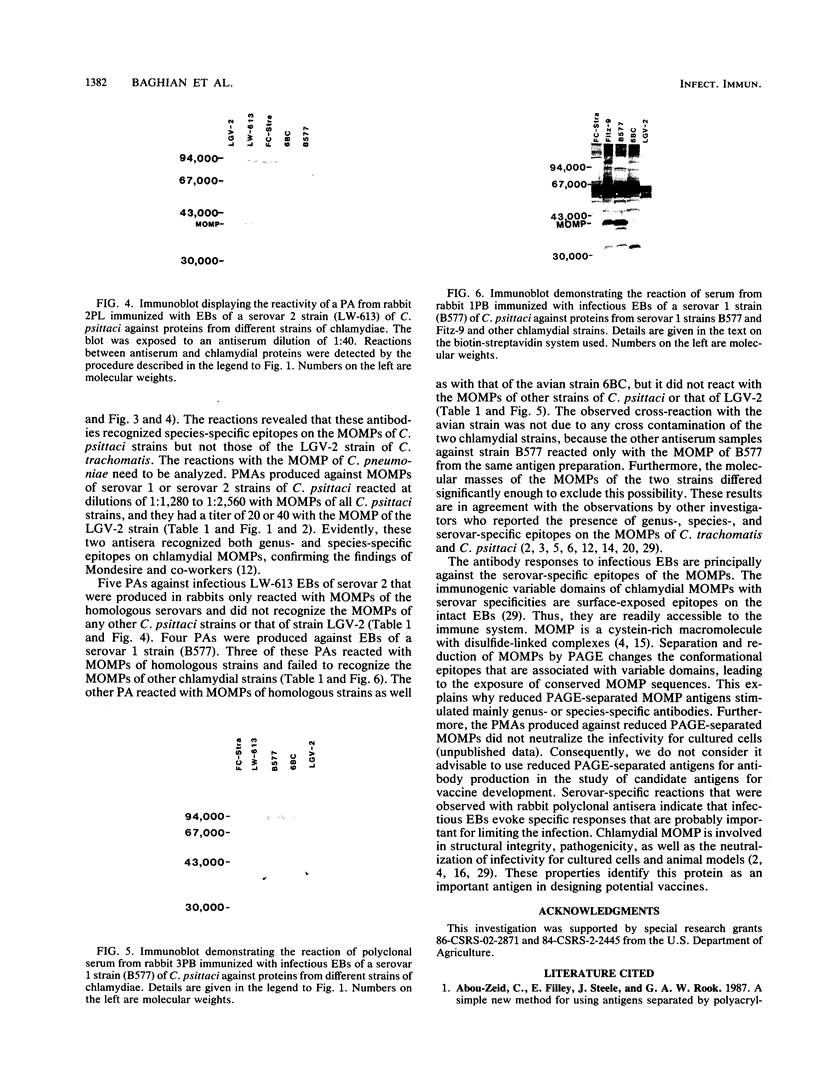
Approximately 60% of the outer membrane of chlamydial elementary bodies (EBs) consists of the major outer membrane protein (MOMP) that has structural and metabolic functions. The antigenic properties of MOMPs from mammalian strains of serovars 1 and 2 and an avian strain of Chlamydia psittaci were analyzed. Polyclonal-monospecific antisera (PMAs), one monoclonal antibody (MAb), and polyclonal antisera (PAs) were produced against reduced polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis-separated MOMPs and against infectious EBs. Three PMAs and the MAb, which were induced by reduced polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis-separated MOMPs, reacted strongly in Western blot (immunoblot) assays with MOMPs of serovar 1 and 2 strains as well as with that of the avian strain 6BC, and two of these PMAs reacted weakly (dilution, 1:20) with the MOMP of strain LGV-2. The third PMA and the MAb against the MOMP of the serovar 2 strain did not react with the MOMP of LGV-2. Four PAs were produced against infectious EBs of the serovar 1 strain. One of these PAs reacted with the homologous MOMP and that of the avian strain 6BC but did not recognize MOMPs of other chlamydial strains. Three of the PAs reacted with MOMPs of homologous strains only and failed to recognize MOMPs of avian, serovar 2, and LGV-2 strains. Five PAs induced against infectious EBs of the serovar strain 2 reacted only with the MOMPs of the homologous strains and failed to recognize MOMPs of other strains of chlamydiae. Consequently, MOMPs of C. psittaci strains possess genus-, species-, and serovar-specific epitopes whereby the immune response to serovar-specific epitopes of MOMP predominate when infectious EBs are used for immunization.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abou-Zeid C., Filley E., Steele J., Rook G. A. A simple new method for using antigens separated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis to stimulate lymphocytes in vitro after converting bands cut from Western blots into antigen-bearing particles. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Apr 2;98(1):5–10. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90429-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baehr W., Zhang Y. X., Joseph T., Su H., Nano F. E., Everett K. D., Caldwell H. D. Mapping antigenic domains expressed by Chlamydia trachomatis major outer membrane protein genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):4000–4004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.4000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batteiger B. E., Newhall W. J., 5th, Terho P., Wilde C. E., 3rd, Jones R. B. Antigenic analysis of the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis with murine monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):530–533. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.530-533.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bavoil P., Ohlin A., Schachter J. Role of disulfide bonding in outer membrane structure and permeability in Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):479–485. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.479-485.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell H. D., Kromhout J., Schachter J. Purification and partial characterization of the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1161–1176. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1161-1176.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushi H., Hirai K. Immunochemical diversity of the major outer membrane protein of avian and mammalian Chlamydia psittaci. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Apr;26(4):675–680. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.4.675-680.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfrè G., Milstein C. Preparation of monoclonal antibodies: strategies and procedures. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):3–46. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grayston J. T., Wang S. New knowledge of chlamydiae and the diseases they cause. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jul;132(1):87–105. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.1.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondesire R. R., Maclean I. W., Shewen P. E., Winston S. E. Identification of genus-specific epitopes on the outer membrane complexes of Chlamydia trachomatis and Chlamydia psittaci immunotypes 1 and 2. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2914–2918. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2914-2918.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W., Levy N. J., Schulman L. P. Persistent infection of mouse fibroblasts (L cells) with Chlamydia psittaci: evidence for a cryptic chlamydial form. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):874–883. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.874-883.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newhall W. J., 5th, Terho P., Wilde C. E., 3rd, Batteiger B. E., Jones R. B. Serovar determination of Chlamydia trachomatis isolates by using type-specific monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Feb;23(2):333–338. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.2.333-338.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newhall W. J., Jones R. B. Disulfide-linked oligomers of the major outer membrane protein of chlamydiae. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):998–1001. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.998-1001.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeling R., Maclean I. W., Brunham R. C. In vitro neutralization of Chlamydia trachomatis with monoclonal antibody to an epitope on the major outer membrane protein. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):484–488. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.484-488.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Martinez J. A., Storz J. Antigenic diversity of Chlamydia psittaci of mammalian origin determined by microimmunofluorescence. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):905–910. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.905-910.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spears P., Storz J. Biotyping of Chlamydia psittaci based on inclusion morphology and response to diethylaminoethyl-dextran and cycloheximide. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):224–232. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.224-232.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. S., Tam M. R., Kuo C. C., Nowinski R. C. Monoclonal antibodies to Chlamydia trachomatis: antibody specificities and antigen characterization. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1083–1089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su H., Zhang Y. X., Barrera O., Watkins N. G., Caldwell H. D. Differential effect of trypsin on infectivity of Chlamydia trachomatis: loss of infectivity requires cleavage of major outer membrane protein variable domains II and IV. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):2094–2100. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.2094-2100.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. P., Grayston J. T. Immunologic relationship between genital TRIC, lymphogranuloma venereum, and related organisms in a new microtiter indirect immunofluorescence test. Am J Ophthalmol. 1970 Sep;70(3):367–374. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(70)90096-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. P., Kuo C. C., Barnes R. C., Stephens R. S., Grayston J. T. Immunotyping of Chlamydia trachomatis with monoclonal antibodies. J Infect Dis. 1985 Oct;152(4):791–800. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.4.791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan Y., Zhang Y. X., Watkins N. G., Caldwell H. D. Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences for the four variable domains of the major outer membrane proteins of the 15 Chlamydia trachomatis serovars. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1040–1049. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1040-1049.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. X., Morrison S. G., Caldwell H. D., Baehr W. Cloning and sequence analysis of the major outer membrane protein genes of two Chlamydia psittaci strains. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1621–1625. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1621-1625.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. X., Stewart S., Joseph T., Taylor H. R., Caldwell H. D. Protective monoclonal antibodies recognize epitopes located on the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 15;138(2):575–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]









