Abstract
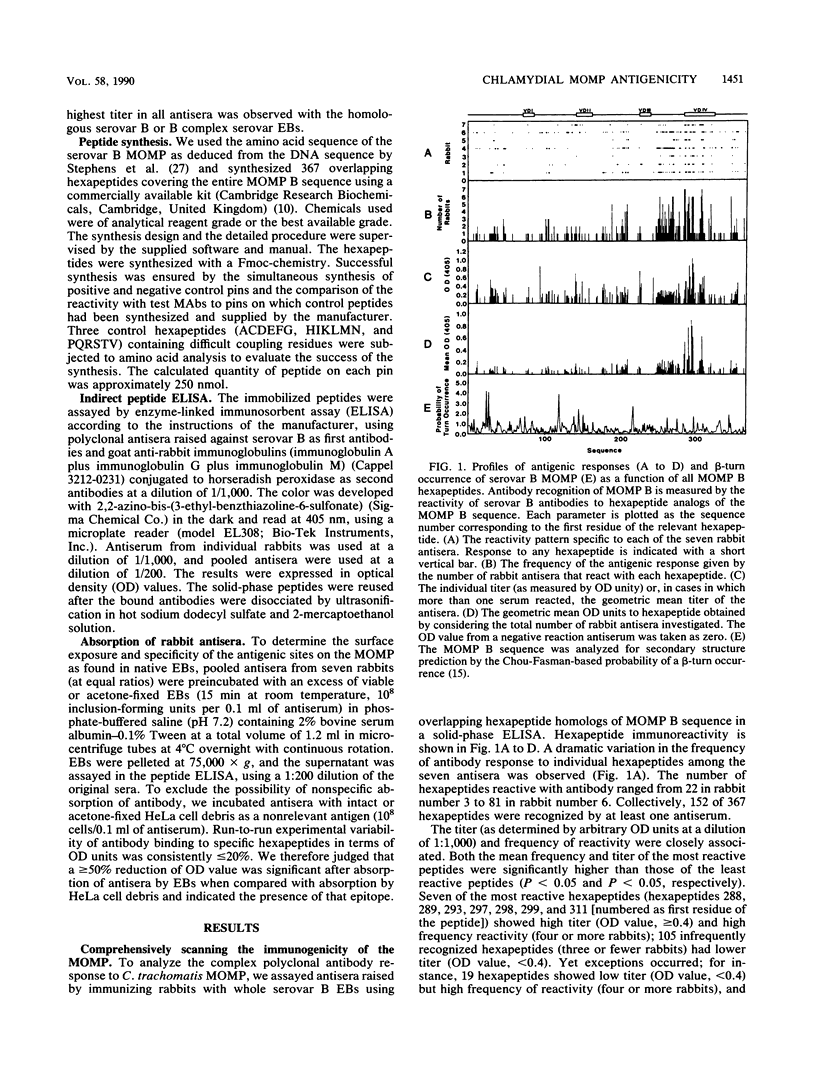
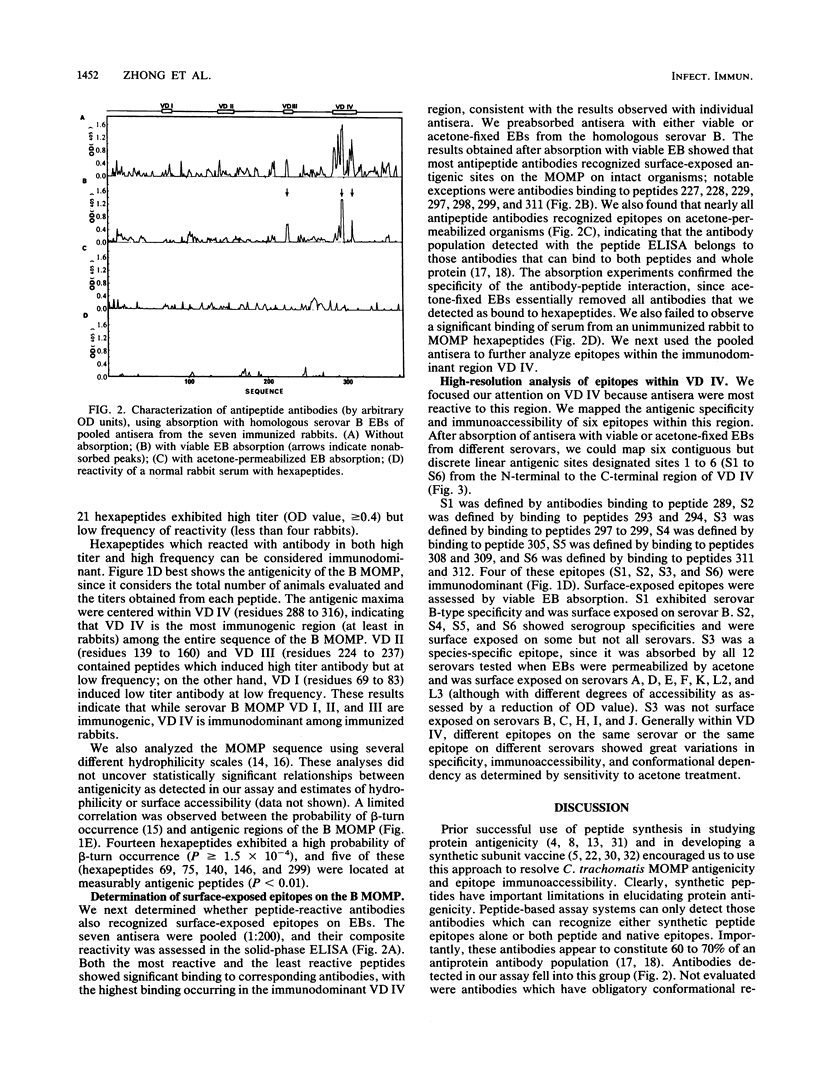
The antigenicity of the major outer membrane protein (MOMP) of Chlamydia trachomatis was comprehensively evaluated by using overlapping hexapeptide homologs of serovar B MOMP and polyclonal rabbit antisera in a peptide enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Of 367 hexapeptides, 152 showed reactivities with at least one antiserum. Seven hexapeptides located within variable domain (VD) IV (residues 288 to 316) were found to be most reactive in terms of their binding titer and frequency, suggesting that VD IV is the immunodominant region within the MOMP as detected by this assay. Peptide-reactive antibodies could also recognize corresponding epitopes on either viable or acetone-permeabilized organisms. The antigenic specificity and immunoaccessibility of epitopes located in VD IV were resolved by absorbing antisera with chlamydial elementary bodies. Six antigenic sites were found in this region and included a B-type-specific site (S1), four subserogroup-specific sites (S2 and S4 to 6), and one species-specific site (S3), each displaying varying degrees of surface exposures on elementary bodies from different C. trachomatis serovars.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amit A. G., Mariuzza R. A., Phillips S. E., Poljak R. J. Three-dimensional structure of an antigen-antibody complex at 2.8 A resolution. Science. 1986 Aug 15;233(4765):747–753. doi: 10.1126/science.2426778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baehr W., Zhang Y. X., Joseph T., Su H., Nano F. E., Everett K. D., Caldwell H. D. Mapping antigenic domains expressed by Chlamydia trachomatis major outer membrane protein genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):4000–4004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.4000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batteiger B. E., Newhall W. J., 5th, Terho P., Wilde C. E., 3rd, Jones R. B. Antigenic analysis of the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis with murine monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):530–533. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.530-533.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolwell C., Clarke B. E., Parry N. R., Ouldridge E. J., Brown F., Rowlands D. J. Epitope mapping of foot-and-mouth disease virus with neutralizing monoclonal antibodies. J Gen Virol. 1989 Jan;70(Pt 1):59–68. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke B. E., Newton S. E., Carroll A. R., Francis M. J., Appleyard G., Syred A. D., Highfield P. E., Rowlands D. J., Brown F. Improved immunogenicity of a peptide epitope after fusion to hepatitis B core protein. 1987 Nov 26-Dec 2Nature. 330(6146):381–384. doi: 10.1038/330381a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlan J. W., Clarke I. N., Ward M. E. Epitope mapping with solid-phase peptides: identification of type-, subspecies-, species- and genus-reactive antibody binding domains on the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Sep;2(5):673–679. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00076.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlan J. W., Kajbaf M., Clarke I. N., Chantler S., Ward M. E. The major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis: critical binding site and conformation determine the specificity of antibody binding to viable chlamydiae. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Mar;3(3):311–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00176.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAYSTON J. T., WOOLRIDGE R. L., WANG S. P., YEN C. H., YANG C. Y., CHENG K. H., CHANG I. H. Field studies of protection from infection by experimental trachoma virus vaccine in preschool-aged children on Taiwan. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Mar;112:589–595. doi: 10.3181/00379727-112-28112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Meloen R. H., Barteling S. J. Use of peptide synthesis to probe viral antigens for epitopes to a resolution of a single amino acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):3998–4002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.3998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Rodda S. J., Mason T. J., Tribbick G., Schoofs P. G. Strategies for epitope analysis using peptide synthesis. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Sep 24;102(2):259–274. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90085-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Tainer J. A., Rodda S. J., Mason T. J., Alexander H., Getzoff E. D., Lerner R. A. Chemistry of antibody binding to a protein. Science. 1987 Mar 6;235(4793):1184–1190. doi: 10.1126/science.3823878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krchnák V., Mach O., Malý A. Computer prediction of potential immunogenic determinants from protein amino acid sequence. Anal Biochem. 1987 Aug 15;165(1):200–207. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90220-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lando G., Berzofsky J. A., Reichlin M. Antigenic structure of sperm whale myoglobin. I. Partition of specificities between antibodies reactive with peptides and native protein. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):206–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lando G., Reichlin M. Antigenic structure of sperm whale myoglobin. II. Characterization of antibodies preferentially reactive with peptides arising in response to immunization with the native protein. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):212–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucero M. E., Kuo C. C. Neutralization of Chlamydia trachomatis cell culture infection by serovar-specific monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):595–597. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.595-597.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J. J., Chen K. C., Kuo C. C. Identification of conserved regions for species and subspecies specific epitopes on the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis. Microb Pathog. 1987 Oct;3(4):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotný J., Haber E. Static accessibility model of protein antigenicity: the case of scorpion neurotoxin. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 4;25(22):6748–6754. doi: 10.1021/bi00370a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patarroyo M. E., Amador R., Clavijo P., Moreno A., Guzman F., Romero P., Tascon R., Franco A., Murillo L. A., Ponton G. A synthetic vaccine protects humans against challenge with asexual blood stages of Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):158–161. doi: 10.1038/332158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeling R., Maclean I. W., Brunham R. C. In vitro neutralization of Chlamydia trachomatis with monoclonal antibody to an epitope on the major outer membrane protein. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):484–488. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.484-488.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson E. M., Zhong G. M., Carlson E., de la Maza L. M. Protective role of magnesium in the neutralization by antibodies of Chlamydia trachomatis infectivity. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):885–891. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.885-891.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz G. E. A critical evaluation of methods for prediction of protein secondary structures. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1988;17:1–21. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.17.060188.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. S., Kuo C. C., Newport G., Agabian N. Molecular cloning and expression of Chlamydia trachomatis major outer membrane protein antigens in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):713–718. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.713-718.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. S., Sanchez-Pescador R., Wagar E. A., Inouye C., Urdea M. S. Diversity of Chlamydia trachomatis major outer membrane protein genes. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):3879–3885. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.3879-3885.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. S., Tam M. R., Kuo C. C., Nowinski R. C. Monoclonal antibodies to Chlamydia trachomatis: antibody specificities and antigen characterization. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1083–1089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. S., Wagar E. A., Schoolnik G. K. High-resolution mapping of serovar-specific and common antigenic determinants of the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):817–831. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strynadka N. C., Redmond M. J., Parker J. M., Scraba D. G., Hodges R. S. Use of synthetic peptides to map the antigenic determinants of glycoprotein D of herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3474–3483. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3474-3483.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam J. P. Synthetic peptide vaccine design: synthesis and properties of a high-density multiple antigenic peptide system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5409–5413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton J. M., Edwards M. S., Taylor W. R., Barlow D. J. Location of 'continuous' antigenic determinants in the protruding regions of proteins. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):409–413. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04226.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. C., Noda M., Adamik R., Chang P. P., Chen H. C., Moss J., Vaughan M. Stimulation of choleragen enzymatic activities by GTP and two soluble proteins purified from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1768–1772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. P., Grayston J. T., Alexander E. R. Trachoma vaccine studies in monkeys. Am J Ophthalmol. 1967 May;63(5 Suppl):1615–1630. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(67)94155-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. P., Grayston J. T. Immunologic relationship between genital TRIC, lymphogranuloma venereum, and related organisms in a new microtiter indirect immunofluorescence test. Am J Ophthalmol. 1970 Sep;70(3):367–374. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(70)90096-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westhof E., Altschuh D., Moras D., Bloomer A. C., Mondragon A., Klug A., Van Regenmortel M. H. Correlation between segmental mobility and the location of antigenic determinants in proteins. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):123–126. doi: 10.1038/311123a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan Y., Zhang Y. X., Watkins N. G., Caldwell H. D. Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences for the four variable domains of the major outer membrane proteins of the 15 Chlamydia trachomatis serovars. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1040–1049. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1040-1049.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. X., Stewart S., Joseph T., Taylor H. R., Caldwell H. D. Protective monoclonal antibodies recognize epitopes located on the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 15;138(2):575–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



