Abstract
A deltalike toxin produced by a clinical isolate of Staphylococcus epidermidis was purified, and the amino acid sequence was determined. The toxin molecule consisted of 25 amino acid residues and shared a high degree of molecular homology with delta toxin purified from a Staphylococcus aureus human isolate.
Full text
PDF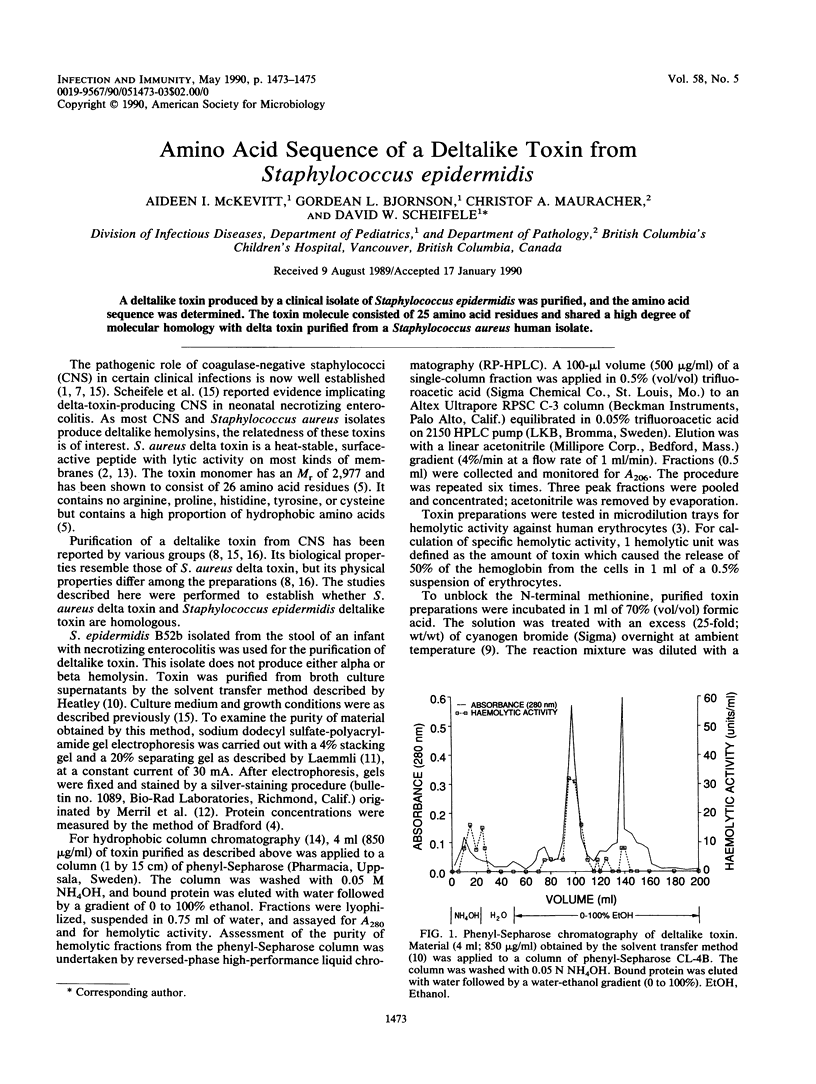

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumgart S., Hall S. E., Campos J. M., Polin R. A. Sepsis with coagulase-negative staphylococci in critically ill newborns. Am J Dis Child. 1983 May;137(5):461–463. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1983.02140310043012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkbeck T. H., Freer J. H. Purification and assay of staphylococcal delta-lysin. Methods Enzymol. 1988;165:16–22. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(88)65006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitton J. E., Dell A., Shaw W. V. The amino acid sequence of the delta haemolysin of Staphylococcus aureus. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jun 30;115(2):209–212. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81170-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleer A., Senders R. C., Visser M. R., Bijlmer R. P., Gerards L. J., Kraaijeveld C. A., Verhoef J. Septicemia due to coagulase-negative staphylococci in a neonatal intensive care unit: clinical and bacteriological features and contaminated parenteral fluids as a source of sepsis. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1983 Nov-Dec;2(6):426–431. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198311000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heatley N. G. A new method for the preparation and some properties of staphylococcal delta-haemolysin. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Dec;69(2):269–278. doi: 10.1099/00221287-69-2-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolte F. S., Kapral F. A. Hydrophobic interaction chromatography of Staphylococcus aureus delta-toxin. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1094–1098. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1094-1098.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheifele D. W., Bjornson G. L., Dyer R. A., Dimmick J. E. Delta-like toxin produced by coagulase-negative staphylococci is associated with neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2268–2273. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2268-2273.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


