Abstract
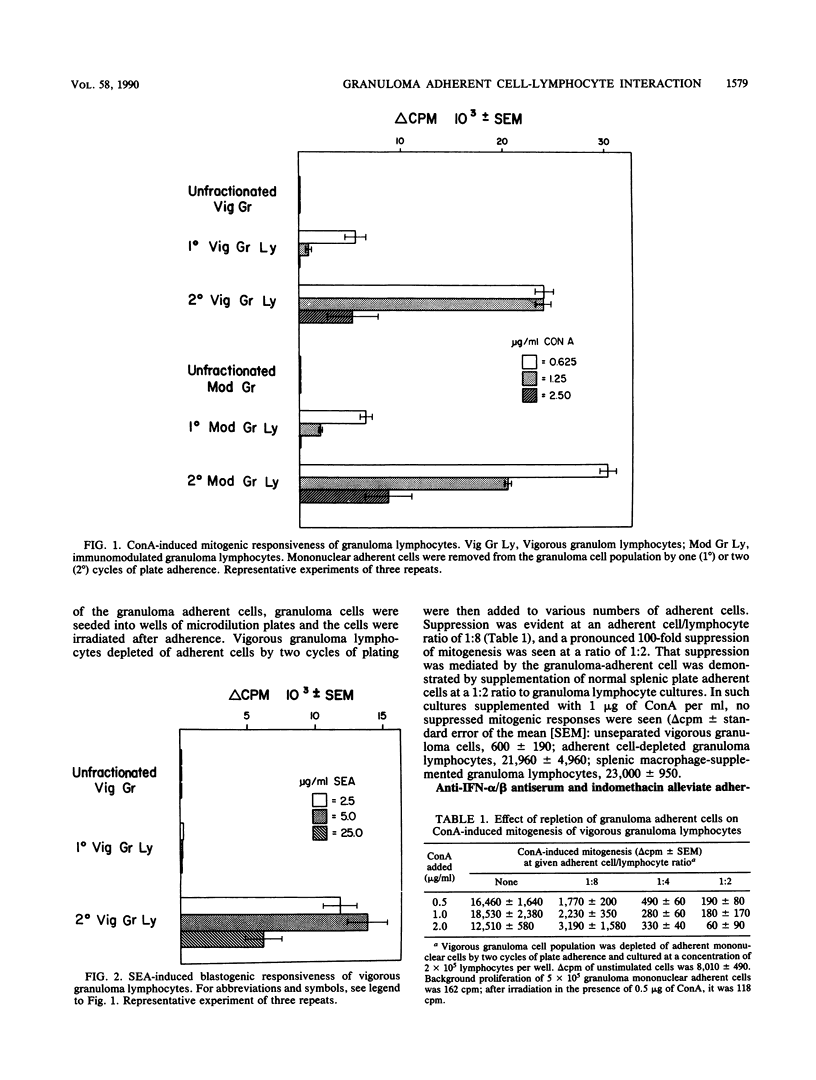
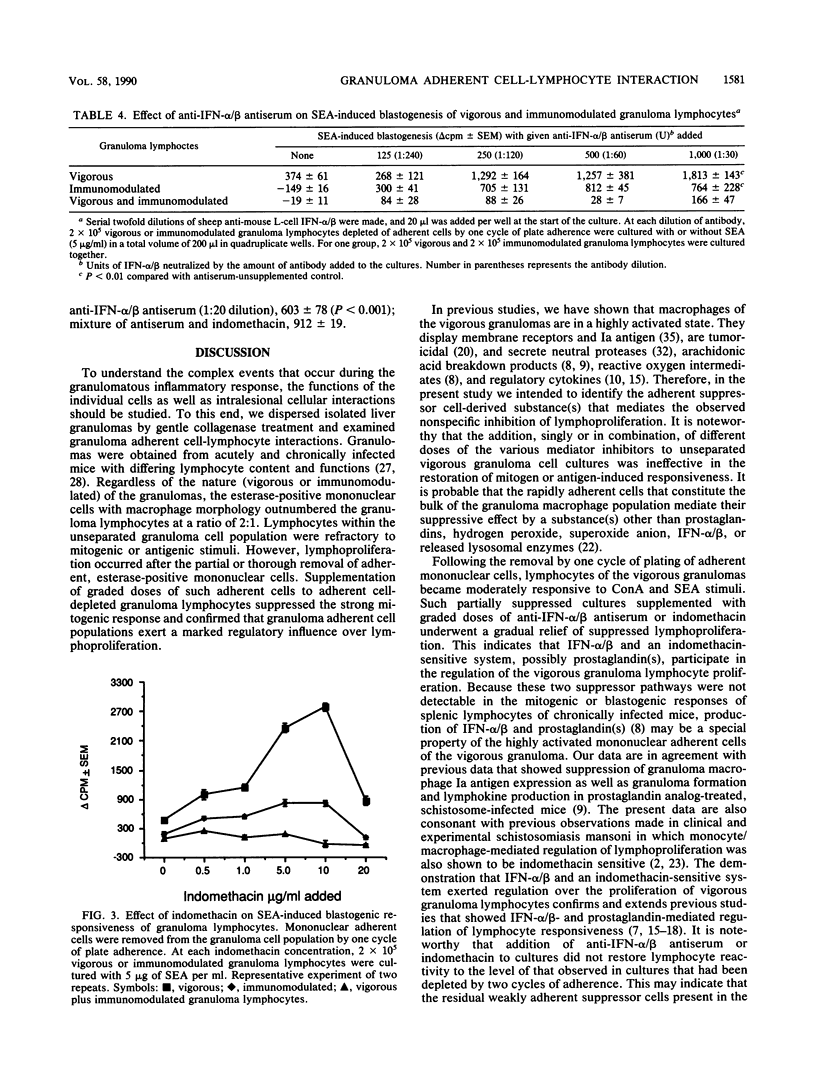
T-lymphocyte-adherent mononuclear cell interaction was analyzed in the vigorous and immunomodulated liver granulomas of Schistosoma mansoni-infected mice. Collagenase-dispersed granulomas contained 15% lymphocytes, 30% macrophages, 50% eosinophilis, and some neutrophils. Dispersed granuloma cells stimulated with concanavalin A or soluble worm egg antigens (SEA) did not proliferate unless plate-adherent, esterase-positive mononuclear cells were removed before culture. To analyze the granuloma adherent cell-mediated suppression, vigorous granuloma cell cultures partially depleted of adherent mononuclear cells were supplemented with indomethacin, catalase, superoxide dismutase, levamisole, and anti-murine alpha/beta interferon antiserum. In concanavalin A and SEA-stimulated cultures, only the addition of indomethacin or anti-alpha/beta interferon antiserum alleviated the adherent cell-mediated suppression of vigorous granuloma lymphocyte response. In contrast, these agents only minimally alleviated the suppressed response of SEA-stimulated, immunomodulated granuloma lymphocytes. Moreover, coculture of equal numbers of vigorous and immunomodulated granuloma cells partially depleted of adherent suppressor cells abrogated the alleviated response of vigorous granuloma lymphocytes. These findings indicate that, within the schistosome egg-induced vigorous granulomas, the adherent mononuclear cells exert regulation over lymphocyte responsiveness by alpha/beta-interferon and an indomethacin-sensitive, probably prostaglandin-mediated pathway. Within the immunomodulated granulomas, the adherent suppressor cell-mediated regulation of lymphocyte proliferation appears to play a lesser role.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe T., Colley D. G. Modulation of Schistosoma mansoni egg-induced granuloma formation. III. Evidence for an anti-idiotypic, I-J-positive, I-J-restricted, soluble T suppressor factor. J Immunol. 1984 Apr;132(4):2084–2088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barsoum I. S., Todd C. W., Habib M., El Alamy M. A., Colley D. G. The effects of indomethacin on in vitro peripheral blood mononuclear cell reactivity in human schistosomiasis. Parasite Immunol. 1983 Sep;5(5):441–447. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1983.tb00759.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boros D. L. Immunopathology of Schistosoma mansoni infection. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jul;2(3):250–269. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.3.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boros D. L. Immunoregulation of granuloma formation in murine schistosomiasis mansoni. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;465:313–323. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb18507.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boros D. L., Pelley R. P., Warren K. S. Spontaneous modulation of granulomatous hypersensitivity in schistosomiasis mansoni. J Immunol. 1975 May;114(5):1437–1441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boros D. L., Warren K. S. Delayed hypersensitivity-type granuloma formation and dermal reaction induced and elicited by a soluble factor isolated from Schistosoma mansoni eggs. J Exp Med. 1970 Sep 1;132(3):488–507. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.3.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chensue S. W., Kunkel S. L., Higashi G. I., Ward P. A., Boros D. L. Production of superoxide anion, prostaglandins, and hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids by macrophages from hypersensitivity-type (Schistosoma mansoni egg) and foreign body-type granulomas. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1116–1125. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1116-1125.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chensue S. W., Remick D. G., Higashi G. I., Boros D. L., Kunkel S. L. Modulation of murine schistosomiasis by exogenously administered prostaglandins. Am J Pathol. 1986 Oct;125(1):28–34. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark C. R., Chen B. D., Boros D. L. Macrophage progenitor cell and colony-stimulating factor production during granulomatous schistosomiasis mansoni in mice. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2680–2685. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2680-2685.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colley D. G. Immune responses to a soluble schistosomal egg antigen preparation during chronic primary infection with Schistosoma mansoni. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):150–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulis P. A., Lewert R. M., Fitch F. W. Splenic suppressor cells and cell-mediated cytotoxicity in murine schistosomiasis. J Immunol. 1978 Mar;120(3):1074–1076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doughty B. L., Phillips S. M. Delayed hypersensitivity granuloma formation and modulation around Schistosoma mansoni eggs in vitro. II. Regulatory T cell subsets. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):37–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott D. E., Boros D. L. Schistosome egg antigen(s) presentation and regulatory activity by macrophages isolated from vigorous or immunomodulated liver granulomas of Schistosoma mansoni-infected mice. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1506–1510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott D. E., Righthand V. F., Boros D. L. Characterization of regulatory (interferon-alpha/beta) and accessory (LAF/IL 1) monokine activities from liver granuloma macrophages of Schistosoma mansoni-infected mice. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 15;138(8):2653–2662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin J. S., Messner R. P., Peake G. T. Prostaglandin suppression of mitogen-stimulated lymphocytes in vitro. Changes with mitogen dose and preincubation. J Clin Invest. 1978 Oct;62(4):753–760. doi: 10.1172/JCI109186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D., Bray M. A., Morley J. Control of lymphokine secretion by prostaglandins. Nature. 1976 Jul 29;262(5567):401–402. doi: 10.1038/262401a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Chensue S. W., Mouton C., Higashi G. I. Role of lipoxygenase products in murine pulmonary granuloma formation. J Clin Invest. 1984 Aug;74(2):514–524. doi: 10.1172/JCI111449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl-Magnusson P., Leary P., Gresser I. Interferon inhibits DNA synthesis induced in mouse lymphocyte suspensions by phytohaemagglutinin or by allogeneic cells. Nat New Biol. 1972 May 24;237(73):120–121. doi: 10.1038/newbio237120a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loveless S. E., Wellhausen S. R., Boros D. L., Heppner G. H. Tumoricidal macrophages isolated from liver granulomas of Schistosoma mansoni-infected mice. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):284–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew R. C., Boros D. L. Regulation of granulomatous inflammation in murine schistosomiasis. III. Recruitment of antigen-specific I-J+ T suppressor cells of the granulomatous response by I-J+ soluble suppressor factor. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):1093–1099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikulíková D., Trnavský K. Effect of levamisole on lysosomal enzyme release from polymorphonuclear leukocytes and intracellular levels of cAMP and cGMP after phagocytosis of monosodium urate crystals. Agents Actions. 1980 Sep;10(4):374–377. doi: 10.1007/BF01971443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olds G. R., Kholy A. E., Ellner J. J. Two distinctive patterns of monocyte immunoregulatory and effector functions in heavy human infections with Schistosoma mansoni. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):954–958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottesen E. A. Modulation of the host response in human schistosomiasis. I. Adherent suppressor cells that inhibit lymphocyte proliferative responses to parasite antigens. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1639–1644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin P. J., Phillips S. M. The molecular basis of granuloma formation in schistosomiasis. I. A T cell-derived suppressor effector factor. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1714–1719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragheb S., Boros D. L. Characterization of granuloma T lymphocyte function from Schistosoma mansoni-infected mice. J Immunol. 1989 May 1;142(9):3239–3246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragheb S., Mathew R. C., Boros D. L. Establishment and characterization of an antigen-specific T-cell line from liver granulomas of Schistosoma mansoni-infected mice. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2625–2630. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2625-2630.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schook L. B., Wellhausen S. R., Boros D. L., Niederhuber J. E. Accessory cell function of liver granuloma macrophages of Schistosoma mansoni-infected mice. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):882–886. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.882-886.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadecker M. J., Wyler D. J., Wright J. A. Ia antigen expression and antigen-presenting function by macrophages isolated from hypersensitivity granulomas. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2739–2744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd C. W., Goodgame R. W., Colley D. G. Immune responses during human schistosomiasis mansoni. V. Suppression of schistosome antigen-specific lymphocyte blastogenesis by adherent/phagocytic cells. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1440–1446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truden J. L., Boros D. L. Detection of alpha 2-macroglobulin, alpha 1-protease inhibitor, and neutral protease-antiprotease complexes within liver granulomas of Schistosoma mansoni-infected mice. Am J Pathol. 1988 Feb;130(2):281–288. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tweardy D. J., Osman G. S., el Kholy A., Ellner J. J. Failure of immunosuppressive mechanisms in human Schistosoma mansoni infection with hepatosplenomegaly. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 May;25(5):768–773. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.5.768-773.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. S. The secret of the immunopathogenesis of schistosomiasis: in vivo models. Immunol Rev. 1982;61:189–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellhausen S. R., Boros D. L. Comparison of Fc, C3 receptors and Ia antigens on the inflammatory macrophage isolated from vigorous or immunomodulated liver granulomas of schistosome-infected mice. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1981 Sep;30(3):191–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



