Abstract
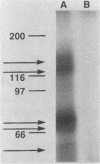
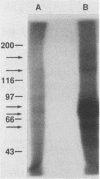
The structure of rat intestinal cell receptors for Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin (ST) was investigated by affinity cross-linking to 125I-ST and analysis by denaturing gel electrophoresis. Cross-linking of labeled toxin to intestinal membranes and analysis by nonreducing sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) revealed five specifically labeled proteins with molecular masses of 160, 136, 78, 71, and 56 (kilodaltons) kDa. Exhaustive reduction of these samples resulted in a similar pattern of labeling. Affinity-labeled proteins were further analyzed by nonreducing SDS-PAGE, reduction of the resulting separated proteins, and further separation by SDS-PAGE in the presence of beta-mercaptoethanol. Thus, the 160-kDa band on nonreducing gels consisted of two different receptors: a 160-kDa polypeptide not further reducible and one composed of at least two subunits, one of which was the 78-kDa subunit. Similarly, the 136-kDa band on nonreducing gels consisted of a 136-kDa polypeptide not further reducible and one composed of at least two subunits, one of which was the 71-kDa subunit. The 78-, 71-, and 56-kDa subunits were not further reducible. These data suggest heterogeneity of the ST receptor subunit structure and organization in rat intestinal epithelia.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. B., Thompson M. R., Overmann G. J., Giannella R. A. Association and dissociation of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin from rat brush border membrane receptors. Infect Immun. 1987 Feb;55(2):329–334. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.2.329-334.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus L. A., Robertson D. C. Solubilization and partial characterization of the intestinal receptor for Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):537–543. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.537-543.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Graf L. H., Jr, Laird W. J., Smith P. L. Heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: in vitro effects on guanylate cyclase activity, cyclic GMP concentration, and ion transport in small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2800–2804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frantz J. C., Jaso-Friedman L., Robertson D. C. Binding of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin to rat intestinal cells and brush border membranes. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):622–630. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.622-630.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gariépy J., Schoolnik G. K. Design of a photoreactive analogue of the Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin STIb: use in identifying its receptor on rat brush border membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):483–487. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino A., Cohen M. B., Overmann G., Thompson M. R., Giannella R. A. Binding of E. coli heat-stable enterotoxin to rat intestinal brush borders and to basolateral membranes. Dig Dis Sci. 1987 Sep;32(9):1017–1026. doi: 10.1007/BF01297193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Hughes J. M., Chang B., Robertson D. C., Murad F. Activation of intestinal guanylate cyclase by heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: studies of tissue specificity, potential receptors, and intermediates. J Infect Dis. 1980 Aug;142(2):220–228. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.2.220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. M., Murad F., Chang B., Guerrant R. L. Role of cyclic GMP in the action of heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1978 Feb 23;271(5647):755–756. doi: 10.1038/271755a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno T., Kamisaki Y., Waldman S. A., Gariepy J., Schoolnik G., Murad F. Characterization of the receptor for heat-stable enterotoxin from Escherichia coli in rat intestine. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1470–1476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitman D. C., Murad F. Atrial natriuretic factor receptor heterogeneity and stimulation of particulate guanylate cyclase and cyclic GMP accumulation. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 1987 Mar;16(1):79–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Caplan E. S., Waterman D., Cash R. A., Hornick R. B., Snyder M. J. Diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli that produce only heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):78–82. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.78-82.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radany E. W., Gerzer R., Garbers D. L. Purification and characterization of particulate guanylate cyclase from sea urchin spermatozoa. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8346–8351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B. Human diarrheal disease caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:333–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman S. A., Murad F. Biochemical mechanisms underlying vascular smooth muscle relaxation: the guanylate cyclase-cyclic GMP system. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1988;12 (Suppl 5):S115–S118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman S. A., Murad F. Cyclic GMP synthesis and function. Pharmacol Rev. 1987 Sep;39(3):163–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman S. A., O'Hanley P., Falkow S., Schoolnik G., Murad F. A simple, sensitive, and specific assay for the heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jan;149(1):83–89. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.1.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]