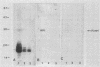
Abstract
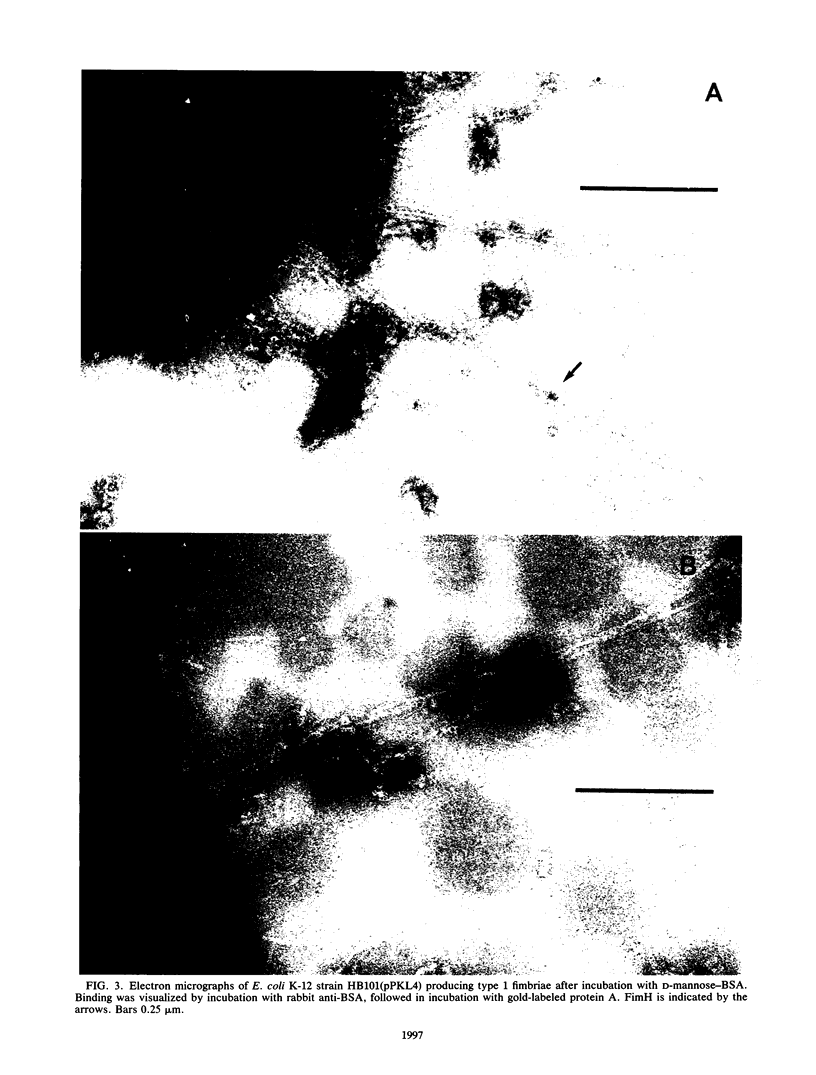
Type 1 fimbriae of Escherichia coli are surface organelles which mediate binding to D-mannose-containing structures. By direct binding of FimH to D-mannose attached to a carrier protein, we demonstrated that this protein was uniquely responsible for the receptor specificity. Furthermore, we show by receptor immunoelectron microscopy that the FimH protein is located laterally in the structure of the type 1 fimbriae.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham S. N., Goguen J. D., Beachey E. H. Hyperadhesive mutant of type 1-fimbriated Escherichia coli associated with formation of FimH organelles (fimbriosomes). Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1023–1029. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1023-1029.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abraham S. N., Goguen J. D., Sun D., Klemm P., Beachey E. H. Identification of two ancillary subunits of Escherichia coli type 1 fimbriae by using antibodies against synthetic oligopeptides of fim gene products. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5530–5536. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5530-5536.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abraham S. N., Sun D., Dale J. B., Beachey E. H. Conservation of the D-mannose-adhesion protein among type 1 fimbriated members of the family Enterobacteriaceae. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):682–684. doi: 10.1038/336682a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinton C. C., Jr The structure, function, synthesis and genetic control of bacterial pili and a molecular model for DNA and RNA transport in gram negative bacteria. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jun;27(8):1003–1054. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1965.tb02342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firon N., Ofek I., Sharon N. Interaction of mannose-containing oligosaccharides with the fimbrial lectin of Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Apr 29;105(4):1426–1432. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90947-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita K., Yamamoto T., Yokota T., Kitagawa R. In vitro adherence of type 1-fimbriated uropathogenic Escherichia coli to human ureteral mucosa. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2574–2579. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2574-2579.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershoni J. M. Protein blotting: a manual. Methods Biochem Anal. 1988;33:1–58. doi: 10.1002/9780470110546.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagberg L., Jodal U., Korhonen T. K., Lidin-Janson G., Lindberg U., Svanborg Edén C. Adhesion, hemagglutination, and virulence of Escherichia coli causing urinary tract infections. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):564–570. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.564-570.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson M. S., Hempel J., Brinton C. C., Jr Purification of the Escherichia coli type 1 pilin and minor pilus proteins and partial characterization of the adhesin protein. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3350–3358. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3350-3358.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemm P., Christiansen G. The fimD gene required for cell surface localization of Escherichia coli type 1 fimbriae. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Jan;220(2):334–338. doi: 10.1007/BF00260505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemm P., Christiansen G. Three fim genes required for the regulation of length and mediation of adhesion of Escherichia coli type 1 fimbriae. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jul;208(3):439–445. doi: 10.1007/BF00328136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemm P., Jørgensen B. J., van Die I., de Ree H., Bergmans H. The fim genes responsible for synthesis of type 1 fimbriae in Escherichia coli, cloning and genetic organization. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;199(3):410–414. doi: 10.1007/BF00330751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemm P. The fimA gene encoding the type-1 fimbrial subunit of Escherichia coli. Nucleotide sequence and primary structure of the protein. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Sep 3;143(2):395–399. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08386.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemm P. Two regulatory fim genes, fimB and fimE, control the phase variation of type 1 fimbriae in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1389–1393. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04372.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogfelt K. A., Klemm P. Investigation of minor components of Escherichia coli type 1 fimbriae: protein chemical and immunological aspects. Microb Pathog. 1988 Mar;4(3):231–238. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90073-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyhse-Andersen J. Electroblotting of multiple gels: a simple apparatus without buffer tank for rapid transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide to nitrocellulose. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1984 Dec;10(3-4):203–209. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(84)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer L., Orndorff P. E. Identification and characterization of genes determining receptor binding and pilus length of Escherichia coli type 1 pili. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):640–645. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.640-645.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neeser J. R., Koellreutter B., Wuersch P. Oligomannoside-type glycopeptides inhibiting adhesion of Escherichia coli strains mediated by type 1 pili: preparation of potent inhibitors from plant glycoproteins. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):428–436. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.428-436.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Mirelman D., Sharon N. Adherence of Escherichia coli to human mucosal cells mediated by mannose receptors. Nature. 1977 Feb 17;265(5595):623–625. doi: 10.1038/265623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old D. C. Inhibition of the interaction between fimbrial haemagglutinins and erythrocytes by D-mannose and other carbohydrates. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Jun;71(1):149–157. doi: 10.1099/00221287-71-1-149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F., Birch-Andersen A. Comparison of Escherichia coli fimbrial antigen F7 with type 1 fimbriae. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):657–666. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.657-666.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallesen L., Madsen O., Klemm P. Regulation of the phase switch controlling expression of type 1 fimbriae in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Jul;3(7):925–931. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00242.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salit I. E., Gotschlich E. C. Hemagglutination by purified type I Escherichia coli pili. J Exp Med. 1977 Nov 1;146(5):1169–1181. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.5.1169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]