Abstract
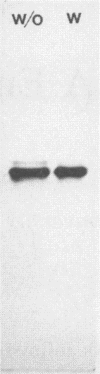
The small satellite bands of enterotoxin frequently seen in polyacrylamide gels following purification of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin were found to be due to endogenous protease activity and were not present if phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF; 1 mM) and EDTA (10 mM) were used in the purification protocol. The use of PMSF was avoided by passing gel filtration-purified enterotoxin material through DEAE-Sephacel. This modified protocol resulted in an 11.4-fold purification of enterotoxin and a 26.8% yield. Contrary to previous reports (B. R. Dasgupta and M. W. Pariza, Infect. Immun. 38: 592-597, 1982), if PMSF and EDTA were included during purification, we were unable to detect the novel enterotoxin ET-1 produced by strain NCTC 10240. C. perfringens proteases cleaved homogeneous enterotoxin into two additional fragments, suggesting that ET-1 was a product of endogenous protease action during purification.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dasgupta B. R., Pariza M. W. Purification of two Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin-like proteins and their effects on membrane permeability in primary cultures of adult rat hepatocytes. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):592–597. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.592-597.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan C. L., Strong D. H. Ileal loop fluid accumulation and production of diarrhea in rabbits by cell-free products of Clostridium perfringens. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):86–94. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.86-94.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enders G. L., Jr, Duncan C. L. Preparative polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis purification of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1977 Aug;17(2):425–429. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.2.425-429.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granum P. E., Whitaker J. R. Improved method for purification of enterotoxin from Clostridium perfringens type A. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jun;39(6):1120–1122. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.6.1120-1122.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granum P. E., Whitaker J. R., Skjelkvåle R. Trypsin activation of enterotoxin from Clostridium perfringens type A: fragmentation and some physicochemical properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 May 29;668(3):325–332. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(81)90165-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschild A. H., Hilsheimer R. Purification and characteristics of the enterotoxin of Clostridium perfringens type A. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Nov;17(11):1425–1433. doi: 10.1139/m71-227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löffler A., Labbé R. Characterization of a parasporal inclusion body from sporulating, enterotoxin-positive Clostridium perfringens type A. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):542–548. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.542-548.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park K. B., Labbé R. G. Artifacts following gold staining of Western-blotted membranes. Anal Biochem. 1989 Jul;180(1):55–58. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90086-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds D., Tranter H. S., Hambleton P. Scaled-up production and purification of Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin. J Appl Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;60(6):517–525. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1986.tb01091.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks L. E., Thompson P. A. Clear, defined medium for the sporulation of Clostridium perfringens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Feb;35(2):405–410. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.2.405-410.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi G., Uemura T., Riemann H. P. Simplified method for purification of Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Nov;26(5):762–767. doi: 10.1128/am.26.5.762-767.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark R. L., Duncan C. L. Purification and biochemical properties of Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):662–673. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.662-673.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]