Abstract
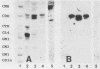
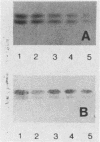
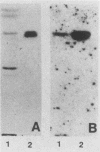
The role of glycosphingolipids as adhesion receptors for yeasts was examined. Cryptococcus neoformans, Candida albicans, and Saccharomyces cerevisiae, as well as Histoplasma capsulatum and Sporotrichum schenckii (in their yeast phases), bound specifically to lactosylceramide (Gal beta 1-4Glc beta 1-1Cer), as measured by overlaying glycosphingolipid chromatograms with 125I-labeled organisms. An unsubstituted galactosyl residue was required for binding, because the yeasts did not bind to glucosylceramide (Glc beta 1-1Cer) derived from lactosylceramide by treatment with beta-galactosidase or to other neutral or acidic glycosphingolipids tested that contained internal lactosyl residues. Interestingly, the yeasts preferentially bound to the upper band of the lactosylceramide doublet in human lung and bovine erythrocytes, suggesting that the ceramide structure also affects binding. Active metabolism of the yeasts was required for binding to lactosylceramide, as binding was maximal in buffer containing glucose and was almost completely abolished in nutrient-deficient medium. C. neoformans also bound to human glioma brain cells grown in monolayers, and this binding was inhibited by liposomes containing lactosylceramide but not by liposomes containing glucosylceramide. Lactosylceramide is a major glycosphingolipid in these cells and the only one to which the yeasts bound. As lactosylceramide is widely distributed in epithelial tissues, this glycosphingolipid may be the receptor for yeast colonization and disseminated disease in humans.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Collins-Lech C., Kalbfleisch J. H., Franson T. R., Sohnle P. G. Inhibition by sugars of Candida albicans adherence to human buccal mucosal cells and corneocytes in vitro. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):831–834. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.831-834.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bernardis F., Palliola E., Lorenzini R., Antonucci G. Evaluation of the experimental pathogenicity of some Cryptococcus species in normal and cyclophosphamide-immunodepressed mice. Microbiol Immunol. 1987;31(5):449–460. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1987.tb03107.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson G. C., Karlsson K. A., Larson G., Strömberg N., Thurin J. Carbohydrate-specific adhesion of bacteria to thin-layer chromatograms: a rationalized approach to the study of host cell glycolipid receptors. Anal Biochem. 1985 Apr;146(1):158–163. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90410-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krivan H. C., Olson L. D., Barile M. F., Ginsburg V., Roberts D. D. Adhesion of Mycoplasma pneumoniae to sulfated glycolipids and inhibition by dextran sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9283–9288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krivan H. C., Roberts D. D., Ginsburg V. Many pulmonary pathogenic bacteria bind specifically to the carbohydrate sequence GalNAc beta 1-4Gal found in some glycolipids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6157–6161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyogashima M., Ginsburg V., Krivan H. C. Escherichia coli K99 binds to N-glycolylsialoparagloboside and N-glycolyl-GM3 found in piglet small intestine. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Apr;270(1):391–397. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90042-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., King R. D. Characterization of Candida albicans adherence to human vaginal epithelial cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1024–1030. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1024-1030.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnani J. L., Brockhaus M., Smith D. F., Ginsburg V. Detection of glycolipid ligands by direct binding of carbohydrate-binding proteins to thin-layer chromatograms. Methods Enzymol. 1982;83:235–241. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)83016-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Svennerholm L., Paulson J. C. Specific gangliosides function as host cell receptors for Sendai virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5406–5410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salkowski C. A., Bartizal K. F., Balish M. J., Balish E. Colonization and pathogenesis of Cryptococcus neoformans in gnotobiotic mice. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2000–2005. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2000-2005.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethi N., Mandell W. Saccharomyces fungemia in a patient with AIDS. N Y State J Med. 1988 May;88(5):278–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stromberg N., Deal C., Nyberg G., Normark S., So M., Karlsson K. A. Identification of carbohydrate structures that are possible receptors for Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4902–4906. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strömberg N., Ryd M., Lindberg A. A., Karlsson K. A. Studies on the binding of bacteria to glycolipids. Two species of Propionibacterium apparently recognize separate epitopes on lactose of lactosylceramide. FEBS Lett. 1988 May 9;232(1):193–198. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80415-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symington F. W., Bernstein I. D., Hakomori S. Monoclonal antibody specific for lactosylceramide. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):6008–6012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomanen E., Towbin H., Rosenfelder G., Braun D., Larson G., Hansson G. C., Hill R. Receptor analogs and monoclonal antibodies that inhibit adherence of Bordetella pertussis to human ciliated respiratory epithelial cells. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):267–277. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura K., Yuzawa M., Taketomi T. Characterization of major glycolipids in bovine erythrocyte membrane. J Biochem. 1978 Feb;83(2):463–471. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vance D. E., Sweeley C. C. Quantitative determination of the neutral glycosyl ceramides in human blood. J Lipid Res. 1967 Nov;8(6):621–630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yednock T. A., Rosen S. D. Lymphocyte homing. Adv Immunol. 1989;44:313–378. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60645-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C., Lee A. M., Roseman S. The sugar-specific adhesion/deadhesion apparatus of the marine bacterium Vibrio furnissii is a sensorium that continuously monitors nutrient levels in the environment. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Nov 30;149(1):86–92. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91608-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]