Abstract
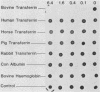
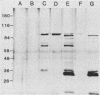
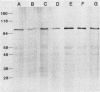
Seven type 1 field isolates of Pasteurella haemolytica were screened for their ability to use different transferrins as a source of iron for growth. All seven strains were capable of using bovine but not human, porcine, avian, or equine transferrin. A screening assay failed to detect siderophore production in any of the strains tested. Iron-deficient cells from these strains expressed a binding activity, specific for bovine transferrin, that was regulated by the level of iron in the medium. Inhibition of expression by translation and transcription inhibitors suggested that iron regulation was occurring at the gene level. Affinity isolation of receptor proteins from all seven strains with biotinylated bovine transferrin identified a 100-kilodalton iron-regulated outer membrane protein as the bovine transferrin receptor. Iron-regulated outer membrane proteins of 71 and 77 kilodaltons were isolated along with the 100-kilodalton protein when less stringent washing procedures were employed in the affinity isolation procedure.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Sultan I. I., Aitken I. D. Promotion of Pasteurella haemolytica infection in mice by iron. Res Vet Sci. 1984 May;36(3):385–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson M. L., Thomson R. G., Valli V. E. The bovine alveolar macrophage. II. In vitro studies with Pasteurella haemolytica. Can J Comp Med. 1978 Jul;42(3):368–369. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullen J. J., Rogers H. J., Griffiths E. Role of iron in bacterial infection. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;80:1–35. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66956-9_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chengappa M. M., Carter G. R., Chang T. S. Hemoglobin enhancement of experimental infection of mice with Pasteurella haemolytica. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Aug;44(8):1545–1546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Confer A. W., Panciera R. J., Fulton R. W., Gentry M. J., Rummage J. A. Effect of vaccination with live or killed Pasteurella haemolytica on resistance to experimental bovine pneumonic pasteurellosis. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Feb;46(2):342–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Confer A. W., Panciera R. J., Mosier D. A. Serum antibodies to Pasteurella haemolytica lipopolysaccharide: relationship to experimental bovine pneumonic pasteurellosis. Am J Vet Res. 1986 May;47(5):1134–1138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosa J. H. The relationship of plasmid-mediated iron transport and bacterial virulence. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984;38:69–89. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.38.100184.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deneer H. G., Potter A. A. Iron-repressible outer-membrane proteins of Pasteurella haemolytica. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Feb;135(Pt 2):435–443. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-2-435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durham J. A., Confer A. W., Mosier D. A., Lessley B. A. Comparison of the antigens associated with saline solution, potassium thiocyanate, and sodium salicylate extracts of Pasteurella haemolytica serotype 1. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Sep;47(9):1946–1951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank G. H. Pasteurella haemolytica and respiratory disease in cattle. Proc Annu Meet U S Anim Health Assoc. 1979;(83):153–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend S. C., Wilkie B. N., Thomson R. G., Barnum D. A. Bovine pneumonic pasteurellosis: experimental induction in vaccinated and nonvaccinated calves. Can J Comp Med. 1977 Jan;41(1):77–83. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry M. J., Confer A. W., Weinberg E. D., Homer J. T. Cytotoxin (leukotoxin) production by Pasteurella haemolytica: requirement for an iron-containing compound. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Sep;47(9):1919–1923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrington D. A., Sparling P. F. Haemophilus influenzae can use human transferrin as a sole source for required iron. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):248–251. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.248-251.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebba P. E., McIntosh M. A., Neilands J. B. Kinetics of biosynthesis of iron-regulated membrane proteins in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):880–888. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.880-888.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessley B. A., Confer A. W., Mosier D. A., Gentry M. J., Durham J. A., Rummage J. A. Saline-extracted antigens of Pasteurella haemolytica: separation by chromatofocusing, preliminary characterization, and evaluation of immunogenicity. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1985 Nov;10(2-3):279–296. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(85)90053-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maheswaran S. K., Berggren K. A., Simonson R. R., Ward G. E., Muscoplat C. C. Kinetics of interaction and fate of Pasteurella hemolytica in bovine alveolar macrophages. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):254–262. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.254-262.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. W., Meek A. H., Davis D. G., Thomson R. G., Johnson J. A., Lopez A., Stephens L., Curtis R. A., Prescott J. F., Rosendal S. Factors associated with mortality in feedlot cattle: the Bruce County Beef Cattle Project. Can J Comp Med. 1980 Jan;44(1):1–10. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mickelsen P. A., Sparling P. F. Ability of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, and commensal Neisseria species to obtain iron from transferrin and iron compounds. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):555–564. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.555-564.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilands J. B. Microbial envelope proteins related to iron. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:285–309. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilands J. B. Microbial iron compounds. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:715–731. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehmtulla A. J., Thomson R. G. A review of the lesions in shipping fever of cattle. Can Vet J. 1981 Jan;22(1):1–8. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schryvers A. B., Gonzalez G. C. Comparison of the abilities of different protein sources of iron to enhance Neisseria meningitidis infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2425–2429. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2425-2429.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schryvers A. B. Identification of the transferrin- and lactoferrin-binding proteins in Haemophilus influenzae. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Jun;29(2):121–130. doi: 10.1099/00222615-29-2-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schryvers A. B., Lee B. C. Comparative analysis of the transferrin and lactoferrin binding proteins in the family Neisseriaceae. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Mar;35(3):409–415. doi: 10.1139/m89-063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schryvers A. B., Morris L. J. Identification and characterization of the human lactoferrin-binding protein from Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1144–1149. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1144-1149.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schryvers A. B., Morris L. J. Identification and characterization of the transferrin receptor from Neisseria meningitidis. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Mar;2(2):281–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00029.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwyn B., Neilands J. B. Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal Biochem. 1987 Jan;160(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90612-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shewen P. E., Wilkie B. N. Antibody titers to Pasteurella haemolytica A1 in Ontario beef cattle. Can J Comp Med. 1982 Oct;46(4):354–356. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squire P. G., Smiley D. W., Croskell R. B. Identification and extraction of Pasteurella haemolytica membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):667–673. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.667-673.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron and infection. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):45–66. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.45-66.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron withholding: a defense against infection and neoplasia. Physiol Rev. 1984 Jan;64(1):65–102. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie B. N., Markham R. J., Shewen P. E. Response of calves to lung challenge exposure with Pasteurella haemolytica after parenteral or pulmonary immunization. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Nov;41(11):1773–1778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates W. D. A review of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis, shipping fever pneumonia and viral-bacterial synergism in respiratory disease of cattle. Can J Comp Med. 1982 Jul;46(3):225–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]