Abstract
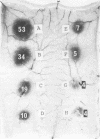
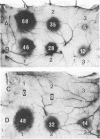
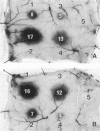
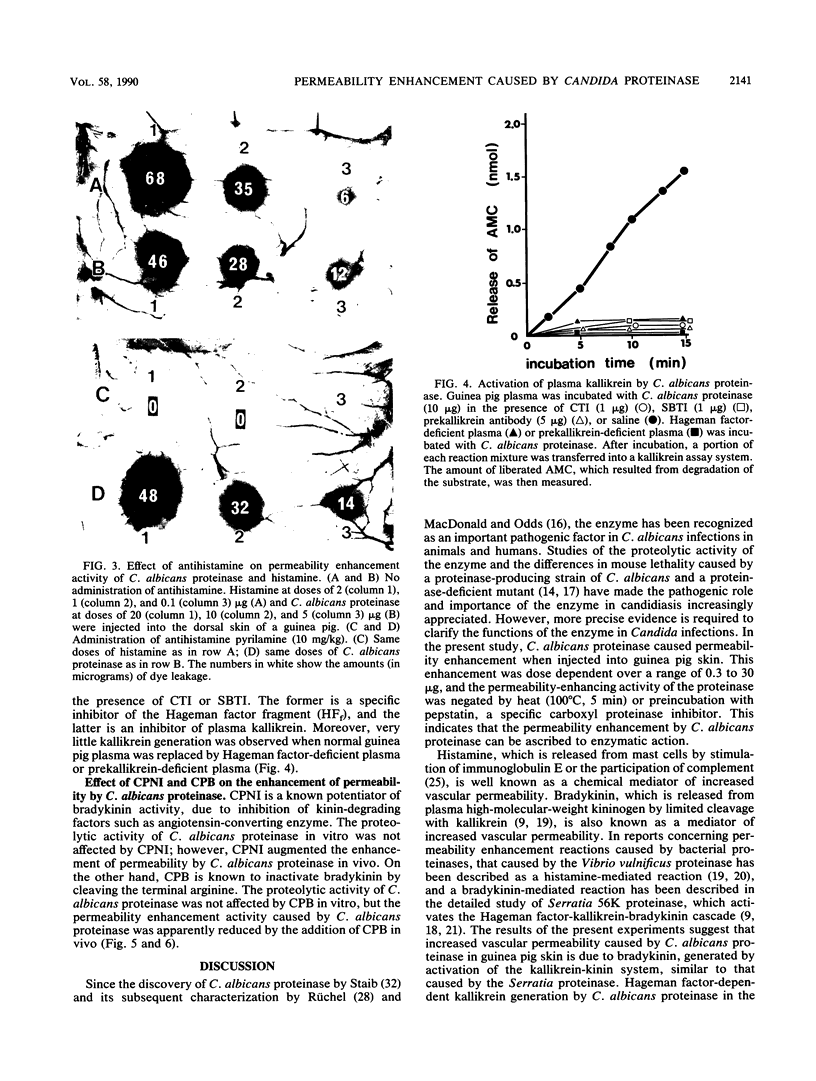
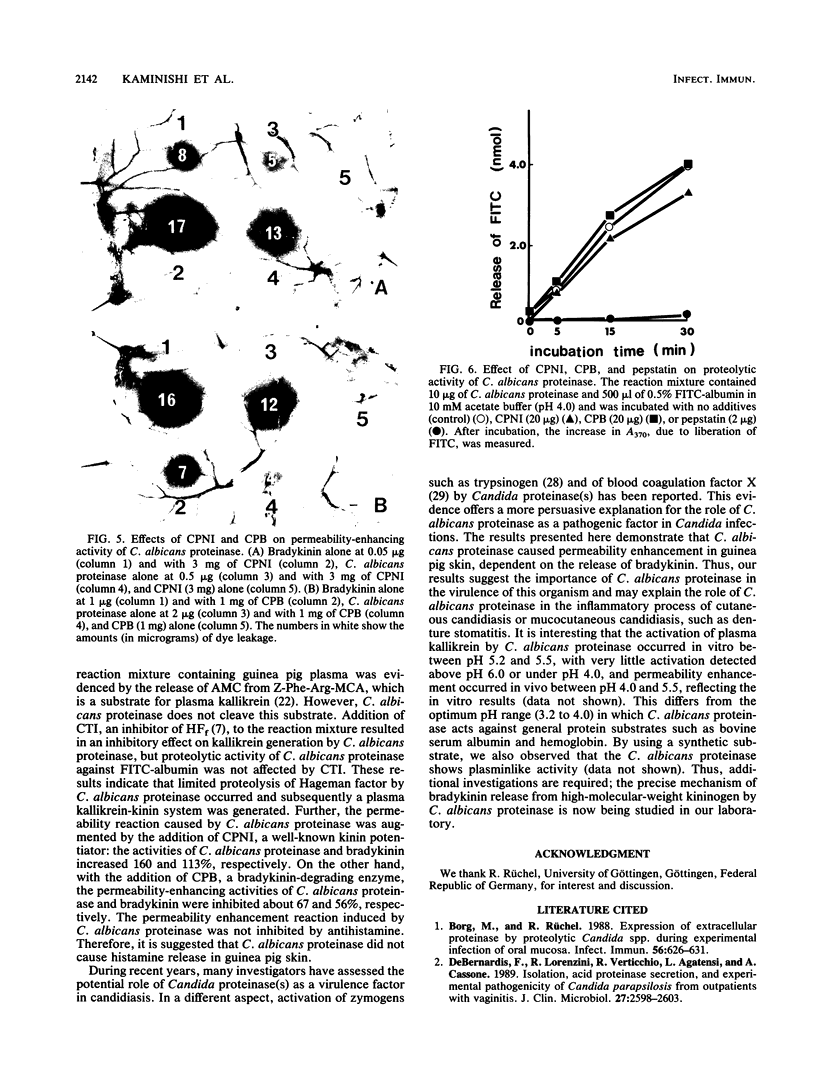
An extracellular carboxyl proteinase produced by the yeast Candida albicans enhanced vascular permeability when injected into the dorsal skin of guinea pigs. The character and mechanism of the permeability-enhancing reaction were studied in vivo and in vitro. Permeability was not enhanced when the C. albicans proteinase was heat treated (100 degrees C, 5 min) or when it was treated with pepstatin, a specific carboxyl proteinase inhibitor. The permeability reaction induced by the C. albicans proteinase was not affected by pretreatment with antihistamine but was greatly augmented by simultaneous injection of a kinin potentiator, carboxypeptidase N inhibitor. However, the simultaneous injection of a kinin-degrading enzyme, carboxypeptidase B, interfered with the reaction. Furthermore, in vitro conversion of plasma prekallikrein to kallikrein by the C. albicans proteinase was observed, and the reaction was inhibited by corn trypsin inhibitor, an inhibitor of activated Hageman factor, and soybean trypsin inhibitor, a well-known inhibitor of plasma kallikrein. These results indicate that C. albicans proteinase enhances vascular permeability through activation of the plasma kallikrein-kinin system, which generates bradykinin.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borg M., Rüchel R. Expression of extracellular acid proteinase by proteolytic Candida spp. during experimental infection of oral mucosa. Infect Immun. 1988 Mar;56(3):626–631. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.3.626-631.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bernardis F., Lorenzini R., Verticchio R., Agatensi L., Cassone A. Isolation, acid proteinase secretion, and experimental pathogenicity of Candida parapsilosis from outpatients with vaginitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Nov;27(11):2598–2603. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.11.2598-2603.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. E., Jr, Lehrer R. I., Stiehm E. R., Fischer T. J., Young L. S. Severe candidal infections: clinical perspective, immune defense mechanisms, and current concepts of therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Jul;89(1):91–106. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-1-91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germaine G. R., Tellefson L. M., Johnson G. L. Proteolytic activity of Candida albicans: action on human salivary proteins. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):861–866. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.861-866.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghannoum M., Abu Elteen K. Correlative relationship between proteinase production, adherence and pathogenicity of various strains of Candida albicans. J Med Vet Mycol. 1986 Oct;24(5):407–413. doi: 10.1080/02681218680000621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Yoshiura K., Negi M., Ogawa H. Keratinolytic proteinase produced by Candida albicans. Sabouraudia. 1984;22(3):175–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hojima Y., Pierce J. V., Pisano J. J. Hageman factor fragment inhibitor in corn seeds: purification and characterization. Thromb Res. 1980 Oct 15;20(2):149–162. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90381-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamata R., Yamamoto T., Matsumoto K., Maeda H. A serratial protease causes vascular permeability reaction by activation of the Hageman factor-dependent pathway in guinea pigs. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):747–753. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.747-753.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminishi H., Hagihara Y., Hayashi S., Cho T. Isolation and characteristics of collagenolytic enzyme produced by Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):312–316. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.312-316.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminishi H., Hagihara Y., Tanaka M., Cho T. Degradation of bovine achilles tendon collagen by Candida albicans proteinase. J Med Vet Mycol. 1988;26(5):315–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. S., Harris C. A., Small C. B., Moll B., Lesser M., Friedland G. H. Oral candidiasis in high-risk patients as the initial manifestation of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1984 Aug 9;311(6):354–358. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198408093110602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi I., Kondoh Y., Shimizu K., Tanaka K. A role of secreted proteinase of Candida albicans for the invasion of chick chorio-allantoic membrane. Microbiol Immunol. 1989;33(9):709–719. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1989.tb00958.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., Lehman D., Good C., Magee P. T. Genetic evidence for role of extracellular proteinase in virulence of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):571–575. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.571-575.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald F., Odds F. C. Inducible proteinase of Candida albicans in diagnostic serology and in the pathogenesis of systemic candidosis. J Med Microbiol. 1980 Aug;13(3):423–435. doi: 10.1099/00222615-13-3-423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald F., Odds F. C. Virulence for mice of a proteinase-secreting strain of Candida albicans and a proteinase-deficient mutant. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Feb;129(2):431–438. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-2-431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Yamamoto T., Kamata R., Maeda H. Pathogenesis of serratial infection: activation of the Hageman factor-prekallikrein cascade by serratial protease. J Biochem. 1984 Sep;96(3):739–749. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi N., Miyoshi S., Sugiyama K., Suzuki Y., Furuta H., Shinoda S. Activation of the plasma kallikrein-kinin system by Vibrio vulnificus protease. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1936–1939. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1936-1939.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molla A., Yamamoto T., Akaike T., Miyoshi S., Maeda H. Activation of hageman factor and prekallikrein and generation of kinin by various microbial proteinases. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10589–10594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagase H., Barrett A. J. Human plasma kallikrein. A rapid purification method with high yield. Biochem J. 1981 Jan 1;193(1):187–192. doi: 10.1042/bj1930187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C. Candida albicans proteinase as a virulence factor in the pathogenesis of Candida infections. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1985 Dec;260(4):539–542. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(85)80069-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray T. L., Payne C. D. Scanning electron microscopy of epidermal adherence and cavitation in murine candidiasis: a role for Candida acid proteinase. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1942–1949. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1942-1949.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remold H., Fasold H., Staib F. Purification and characterization of a proteolytic enzyme from Candida albicans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Oct 8;167(2):399–406. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90219-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüchel R. A variety of Candida proteinases and their possible targets of proteolytic attack in the host. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1984 Jul;257(2):266–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüchel R. On the renin-like activity of Candida proteinases and activation of blood coagulation in vitro. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1983 Sep;255(2-3):368–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüchel R. On the role of proteinases from Candida albicans in the pathogenesis of acronecrosis. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1983 Nov;255(4):524–536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüchel R. Properties of a purified proteinase from the yeast Candida albicans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 May 14;659(1):99–113. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(81)90274-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staib F. Proteolysis and pathogenicity of Candida albicans strains. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1969 May 28;37(4):345–348. doi: 10.1007/BF02129881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udaka K., Takeuchi Y., Movat H. Z. Simple method for quantitation of enhanced vascular permeability. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Apr;133(4):1384–1387. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]