Abstract
We performed a series of studies to examine the sequential development of nephritis during murine malaria infections and to define the role of DNA-binding antibodies in the associated pathology. Serum levels of these antibodies were assessed throughout acute and chronic malaria infections. Increased levels of double-stranded DNA- and single-stranded DNA-binding antibodies were initially detected in mice infected with Plasmodium vinckei or Plasmodium yoelii nigeriensis during the middle stages of infection, and these levels were maintained until death. Infection with the more chronic organism Plasmodium berghei clone RC also resulted in increased single-stranded DNA-binding antibody titers, which fluctuated as the infection progressed. All three species caused kidney damage and dysfunction, as assessed by changes in morphology, blood urea nitrogen, and excreted albumin; this damage correlated with the extent of parasitemia and was observed before the levels of DNA-binding antibodies were detectably elevated in the serum. However, the results of immunohistochemical studies demonstrated that DNA-binding monoclonal antibodies bound ex vivo to glomeruli within kidneys prepared from mice at late stages of infection, after the initial damage had been incurred. Our findings suggest how DNA-binding antibodies could contribute to the kidney pathology associated with both malaria and certain autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus.
Full text
PDF

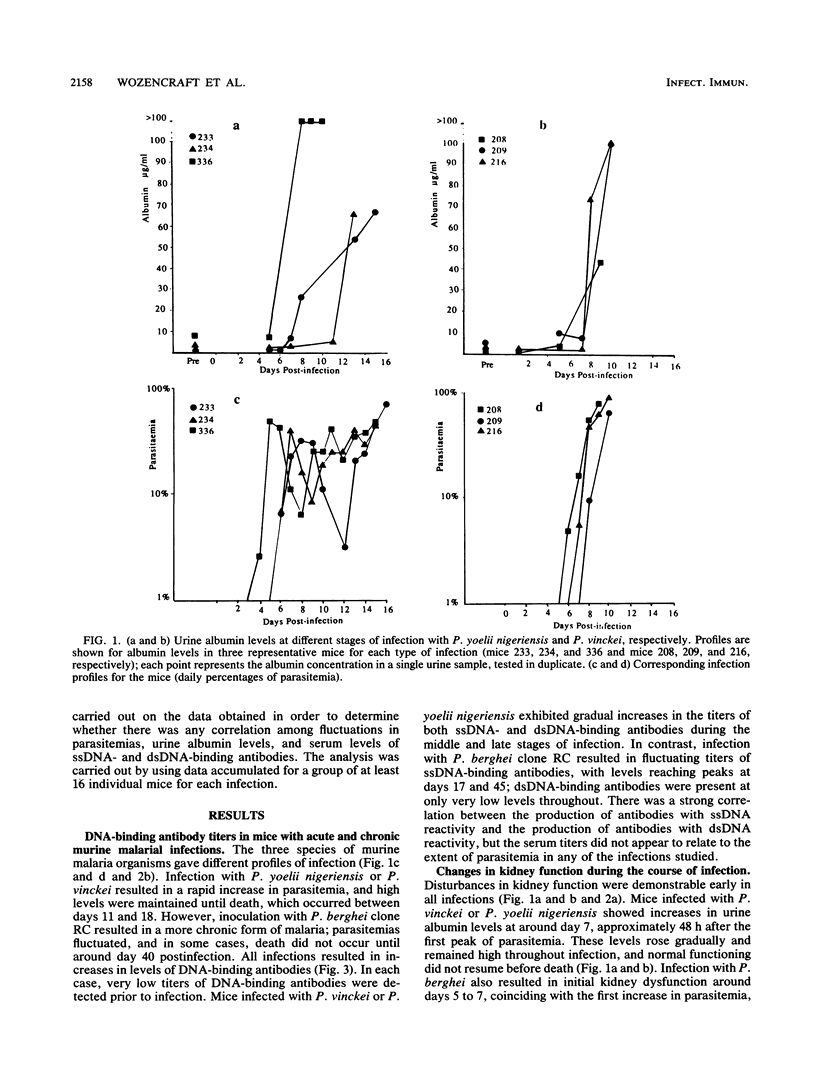
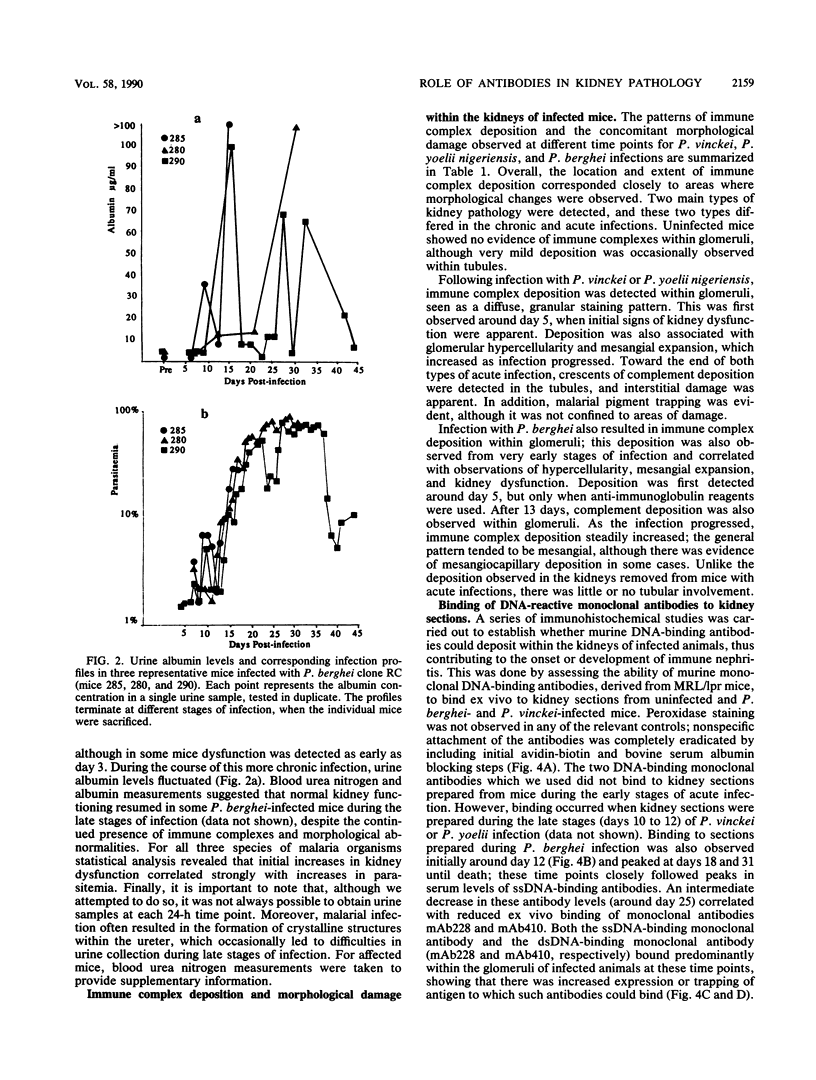
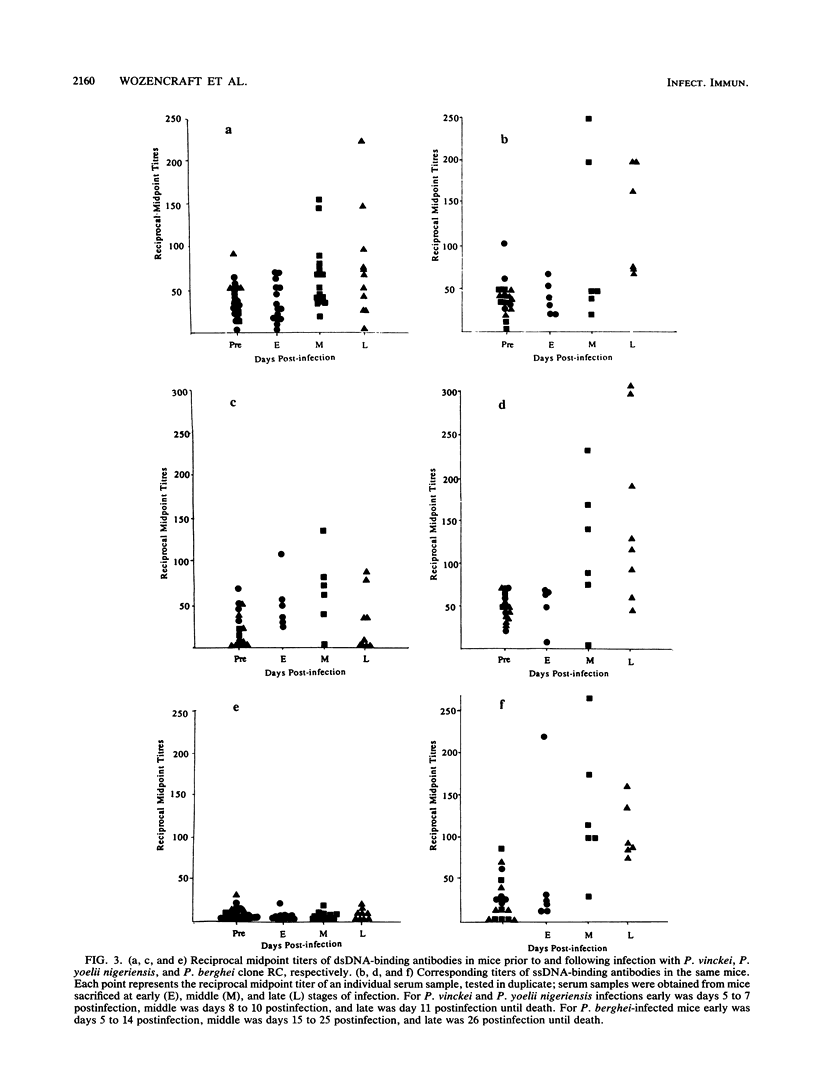

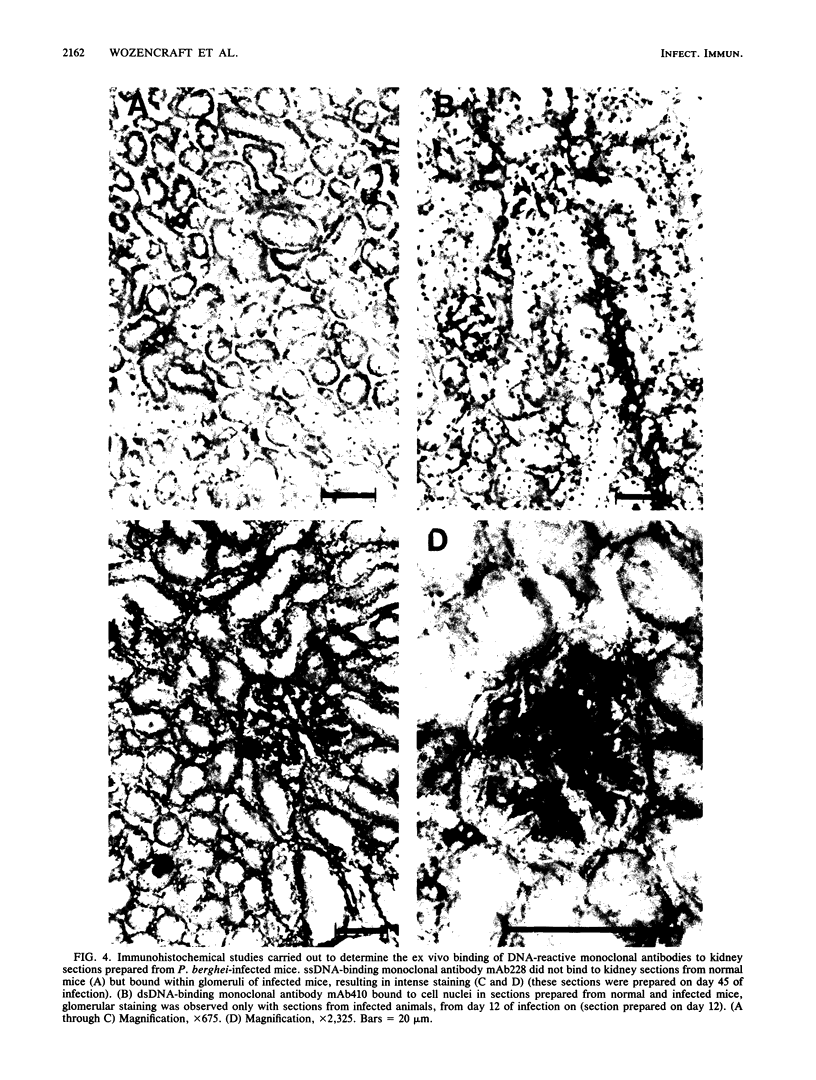


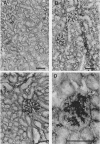
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adu D., Williams D. G., Quakyi I. A., Voller A., Anim-Addo Y., Bruce-Tagoe A. A., Johnson G. D., Holborow E. J. Anti-ssDNA and antinuclear antibodies in human malaria. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Aug;49(2):310–316. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aikawa M., Jacobs G., Whiteley H. E., Igarashi I., Ristic M. Glomerulopathy in squirrel monkeys with acute Plasmodium falciparum infection. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1988 Jan;38(1):7–14. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1988.38.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben Chetrit E., Dunsky E. H., Wollner S., Eilat D. In vivo clearance and tissue uptake of an anti-DNA monoclonal antibody and its complexes with DNA. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Apr;60(1):159–168. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonfa E., Llovet R., Scheinberg M., de Souza J. M., Elkon K. B. Comparison between autoantibodies in malaria and leprosy with lupus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Dec;70(3):529–537. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkman K., Termaat R. M., de Jong J., van den Brink H. G., Berden J. H., Smeenk R. J. Cross-reactive binding patterns of monoclonal antibodies to DNA are often caused by DNA/anti-DNA immune complexes. Res Immunol. 1989 Jun-Aug;140(5-6):595–612. doi: 10.1016/0923-2494(89)90122-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casali P., Notkins A. L. CD5+ B lymphocytes, polyreactive antibodies and the human B-cell repertoire. Immunol Today. 1989 Nov;10(11):364–368. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90268-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel Ribeiro C. T., de Roquefeuil S., Druilhe P., Monjour L., Homberg J. C., Gentilini M. Abnormal anti-single stranded (ss) DNA activity in sera from Plasmodium falciparum infected individuals. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1984;78(6):742–746. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(84)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond B., Scharff M. D. Somatic mutation of the T15 heavy chain gives rise to an antibody with autoantibody specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5841–5844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAWCETT J. K., SCOTT J. E. A rapid and precise method for the determination of urea. J Clin Pathol. 1960 Mar;13:156–159. doi: 10.1136/jcp.13.2.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood B. M., Vick R. M. Evidence for a malaria mitogen in human malaria. Nature. 1975 Oct 16;257(5527):592–594. doi: 10.1038/257592a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houba V. Immunologic aspects of renal lesions associated with malaria. Kidney Int. 1979 Jul;16(1):3–8. doi: 10.1038/ki.1979.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houba V. Immunopathology of nephropathies associated with malaria. Bull World Health Organ. 1975;52(2):199–207. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg D. A., Collins C. Detection of cross-reactive anti-DNA antibody idiotypes on renal tissue-bound immunoglobulins from lupus patients. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):287–294. doi: 10.1172/JCI111959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izui S., Kobayakawa T., Zryd M. J., Louis J., Lambert P. H. Mechanism for induction of anti-DNA antibodies by bacterial lipopolysaccharides in mice; II. Correlation between anti-DNA induction and polyclonal antibody formation by various polyclonal B lymphocyte activators. J Immunol. 1977 Dec;119(6):2157–2162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaburaki J., Stollar B. D. Identification of human anti-DNA, anti-RNP, anti-SM, and anti-SS-A serum antibodies bearing the cross-reactive 16/6 idiotype. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 15;139(2):385–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazyumba G., Berney M., Brighouse G., Cruchaud A., Lambert P. H. Expression of the B cell repertoire and autoantibodies in human African trypanosomiasis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Jul;65(1):10–18. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake R. A., Morgan A., Henderson B., Staines N. A. A key role for fibronectin in the sequential binding of native dsDNA and monoclonal anti-DNA antibodies to components of the extracellular matrix: its possible significance in glomerulonephritis. Immunology. 1985 Feb;54(2):389–395. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake R. A., Staines N. A. A monoclonal DNA-binding autoantibody causes a deterioration in renal function in MRL mice with lupus disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Jul;73(1):103–110. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor I. A. The significance of parasitic infections in terms of clinical disease: a personal view. Parasitology. 1987;94 (Suppl):S159–S178. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000085875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A., Buchanan R. R., Lew A. M., Olsen I., Staines N. A. Five groups of antigenic determinants on DNA identified by monoclonal antibodies from (NZB X NZW)F1 and MRL/Mp-lpr/lpr mice. Immunology. 1985 May;55(1):75–83. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pankewycz O. G., Migliorini P., Madaio M. P. Polyreactive autoantibodies are nephritogenic in murine lupus nephritis. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3287–3294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phanuphak P., Tirawatnpong S., Hanvanich M., Panmuong W., Moollaor P., Vejjajiva S., Sitprija V., Intaraprasert R., Phanthumkosol D. Autoantibodies in falciparum malaria: a sequential study in 183 Thai patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Sep;53(3):627–633. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauch J., Tannenbaum H., Stollar B. D., Schwartz R. S. Monoclonal anti-cardiolipin antibodies bind to DNA. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Jun;14(6):529–534. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlinson W. D., Basten A., Hargrave J. C. Clinical significance of changes in serum proteins, immunoglobulins, and autoantibodies in leprosy. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1987 Jun;55(2):277–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. S., Stollar B. D. Origins of anti-DNA autoantibodies. J Clin Invest. 1985 Feb;75(2):321–327. doi: 10.1172/JCI111704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeenk R. J., Van Rooijen A., Swaak T. J. Dissociation studies of DNA/anti-DNA complexes in relation to anti-DNA avidity. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Apr 22;109(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90438-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M. Autoantibodies to nuclear antigens (ANA): their immunobiology and medicine. Adv Immunol. 1982;33:167–240. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60836-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Reimer G., Sullivan K. Intracellular autoantigens: diagnostic fingerprints but aetiological dilemmas. Ciba Found Symp. 1987;129:25–42. doi: 10.1002/9780470513484.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M. A., Frampton G., Isenberg D. A., Shoenfeld Y., Akinsola A., Ramzy M., Lilleywhite J., Williams D. G. A common anti-DNA antibody idiotype and anti-phospholipid antibodies in sera from patients with schistosomiasis and filariasis with and without nephritis. J Autoimmun. 1989 Dec;2(6):803–811. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(89)90006-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedderburn N., Davies D. R., Mitchell G. H., Desgranges C., de Thé G. Glomerulonephritis in common marmosets infected with Plasmodium brasilianum and Epstein-Barr virus. J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):789–794. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.4.789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida H., Fossati L., Yoshida M., Abdelmoula M., Herrera S., Merino J., Lambert P. H., Izui S. Igh-C allotype-linked control of anti-DNA production and clonotype expression in mice infected with Plasmodium yoelii. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 15;141(6):2125–2131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zouali M., Druilhe P., Eyquem A. IgG-subclass expression of anti-DNA and anti-ribonucleoprotein autoantibodies in human malaria. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Nov;66(2):273–278. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]