Abstract
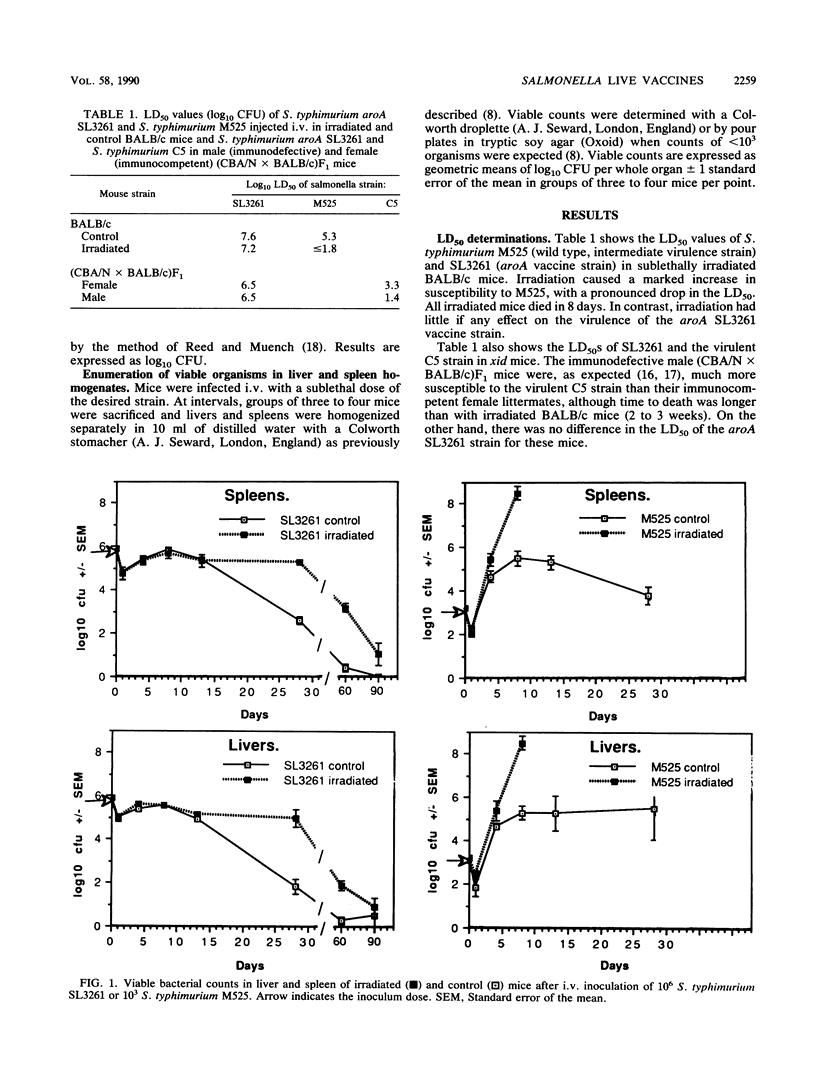
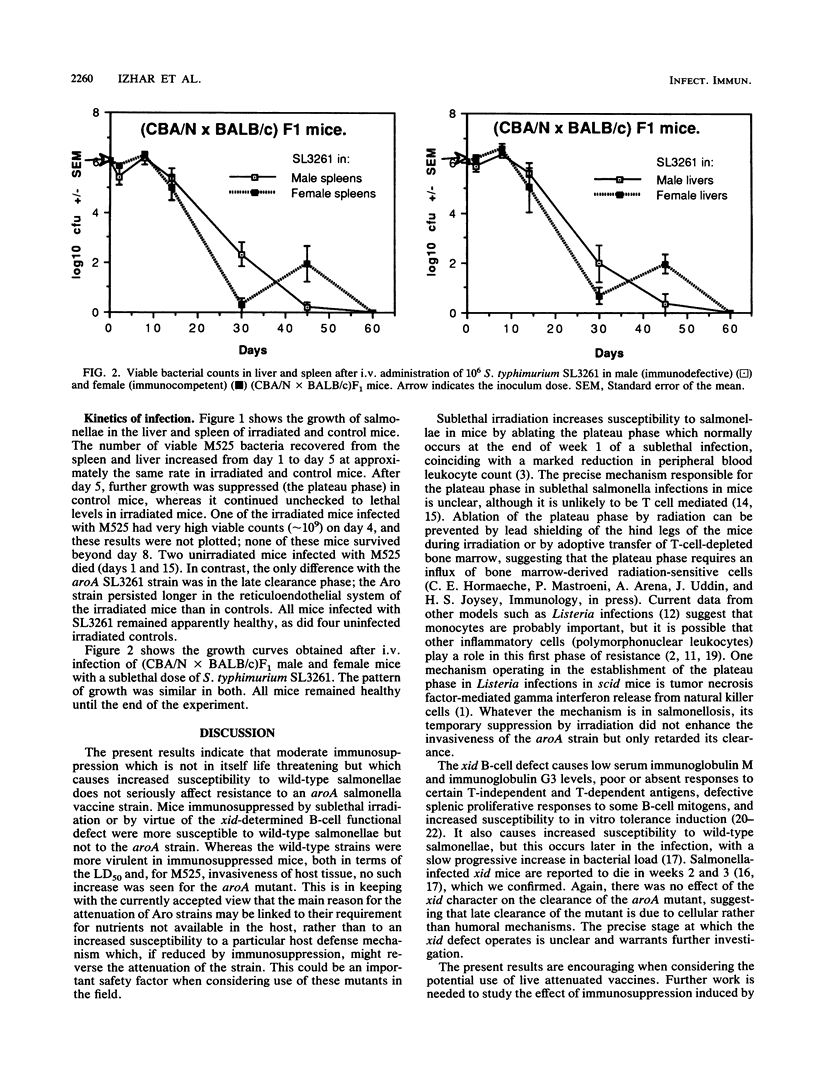
Salmonellae carrying appropriate mutations in genes of the aromatic biosynthesis pathway are effective as live vaccines in animals, and they are candidate typhoid vaccines for human use. They are also very effective as carriers of recombinant antigens from other pathogens to the immune system, eliciting circulatory, secretory, and cell-mediated immunity to foreign antigens. Their attenuation is believed to be due to their requirement for the metabolites p-aminobenzoic acid and 2,3-dihydroxybenzoate, which are not available in mammalian tissues. Immunosuppression (e.g., acquired immunodeficiency syndrome) is a major contraindication to the use of live vaccines. If the avirulence of Aro mutants is largely due to their auxotrophy, they should not be markedly more invasive in immunosuppressed animals. We report that wild-type Salmonella typhimurium M525 of intermediate virulence was much more invasive in sublethally irradiated BALB/c mice than in normal BALB/c mice, whereas sublethal irradiation had little if any effect on the invasiveness of an S. typhimurium aorA vaccine strain apart from a delay in its clearance from the reticuloendothelial system. xid mutant CBA/N mice carry an X-linked B-cell functional defect which results in immunoglobulin G3 agammaglobulinemia, and they are known to be more susceptible to salmonellae in late stages of the infection. We found that whereas male (CBA/N x BALB/c)F1 mice (immunodefective) were more susceptible to wild-type S. typhimurium C5 than female littermates (immunocompetent), there was no difference in the response to the S. typhimurium aroA vaccine strain. The results indicate that moderate immunosuppression does not markedly enhance susceptibility to S. typhimurium aroA live vaccines.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bancroft G. J., Sheehan K. C., Schreiber R. D., Unanue E. R. Tumor necrosis factor is involved in the T cell-independent pathway of macrophage activation in scid mice. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 1;143(1):127–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Mucosal defenses against Salmonella infection in the mouse. J Infect Dis. 1979 May;139(5):503–510. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.5.503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougan G., Hormaeche C. E., Maskell D. J. Live oral Salmonella vaccines: potential use of attenuated strains as carriers of heterologous antigens to the immune system. Parasite Immunol. 1987 Mar;9(2):151–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1987.tb00496.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougan G., Smith L., Heffron F. Live bacterial vaccines and their application as carriers for foreign antigens. Adv Vet Sci Comp Med. 1989;33:271–300. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-039233-9.50012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein T. K., Sultzer B. M. Immunity to Salmonella infection. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1983;162:261–296. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-4481-0_26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiseth S. K., Stocker B. A. Aromatic-dependent Salmonella typhimurium are non-virulent and effective as live vaccines. Nature. 1981 May 21;291(5812):238–239. doi: 10.1038/291238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hormaeche C. E., Fahrenkrog M. C., Pettifor R. A., Brock J. Acquired immunity to Salmonella typhimurium and delayed (footpad) hypersensitivity in BALB/c mice. Immunology. 1981 Jul;43(3):547–554. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hormaeche C. E. Natural resistance to Salmonella typhimurium in different inbred mouse strains. Immunology. 1979 Jun;37(2):311–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hormaeche C. E. The natural resistance of radiation chimeras to S. typhimurium C5. Immunology. 1979 Jun;37(2):329–332. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu H. S. Pathogenesis and immunity in murine salmonellosis. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):390–409. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.390-409.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H. Immunity against intracellular bacteria: biological effector functions and antigen specificity of T lymphocytes. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1988;138:141–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Kaper J. B., Black R. E., Clements M. L. New knowledge on pathogenesis of bacterial enteric infections as applied to vaccine development. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Dec;47(4):510–550. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.4.510-550.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maskell D. J., Hormaeche C. E., Harrington K. A., Joysey H. S., Liew F. Y. The initial suppression of bacterial growth in a salmonella infection is mediated by a localized rather than a systemic response. Microb Pathog. 1987 Apr;2(4):295–305. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90127-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Metcalf E. S. Control of early Salmonella typhimurium growth in innately Salmonella-resistant mice does not require functional T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1349–1351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Scher I., Campbell G. H., MacDermott R. P., Formal S. B. Susceptibility of CBA/N mice to infection with Salmonella typhimurium: influence of the X-linked gene controlling B lymphocyte function. J Immunol. 1979 Aug;123(2):720–724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Scher I., Metcalf E. S. Genetically conferred defect in anti-Salmonella antibody formation renders CBA/N mice innately susceptible to Salmonella typhimurium infection. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1368–1372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts E. C., Demartini J. C., Orme I. M. Passive transfer of acquired resistance to Listeria monocytogenes infection is independent of mononuclear cell granuloma formation. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3215–3218. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3215-3218.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher I., Ahmed A., Strong D. M., Steinberg A. D., Paul W. E. X-linked B-lymphocyte immune defect in CBA/HN mice. I. Studies of the function and composition of spleen cells. J Exp Med. 1975 Apr 1;141(4):788–803. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher I., Steinberg A. D., Berning A. K., Paul W. E. X-linked B-lymphocyte immune defect in CBA/N mice. II. Studies of the mechanisms underlying the immune defect. J Exp Med. 1975 Sep 1;142(3):637–650. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.3.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



