Abstract
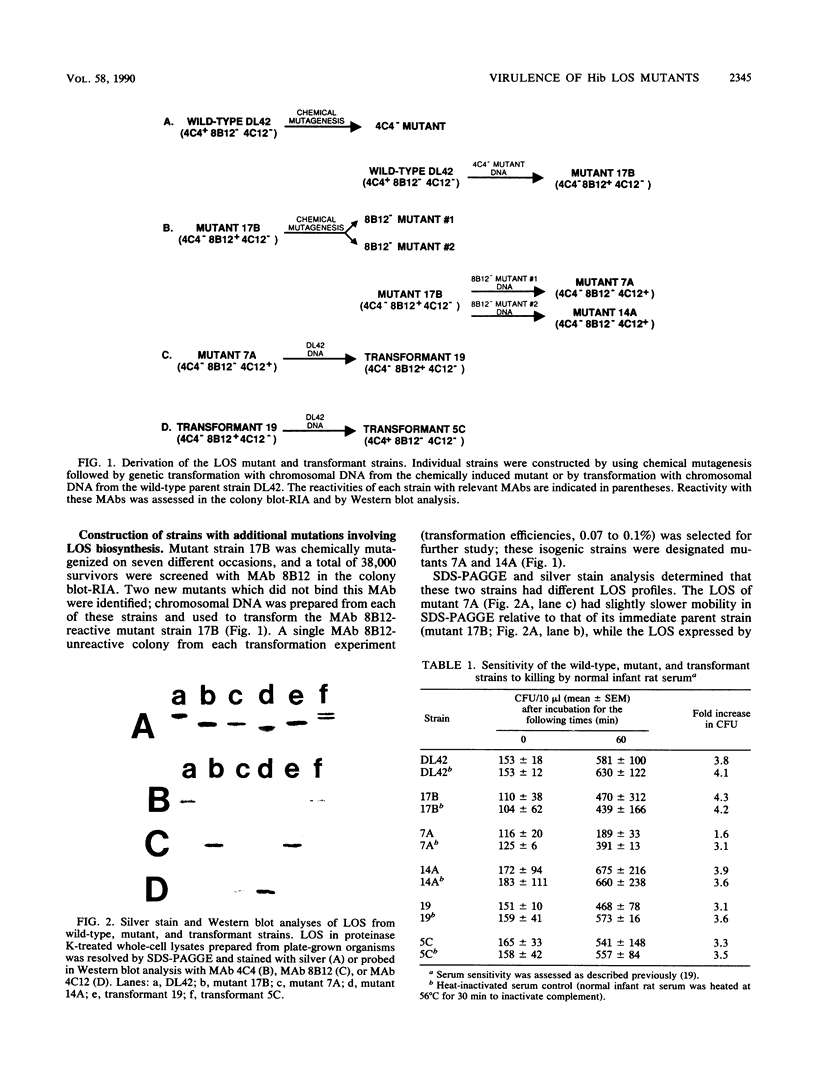
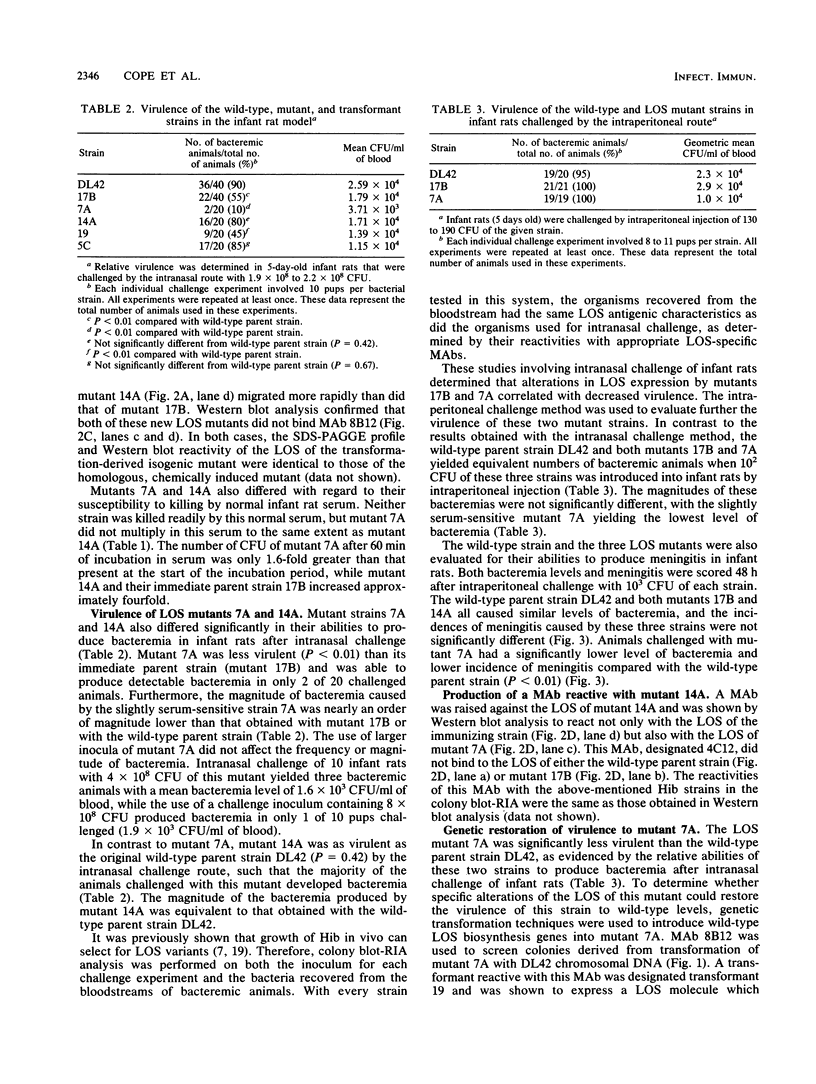
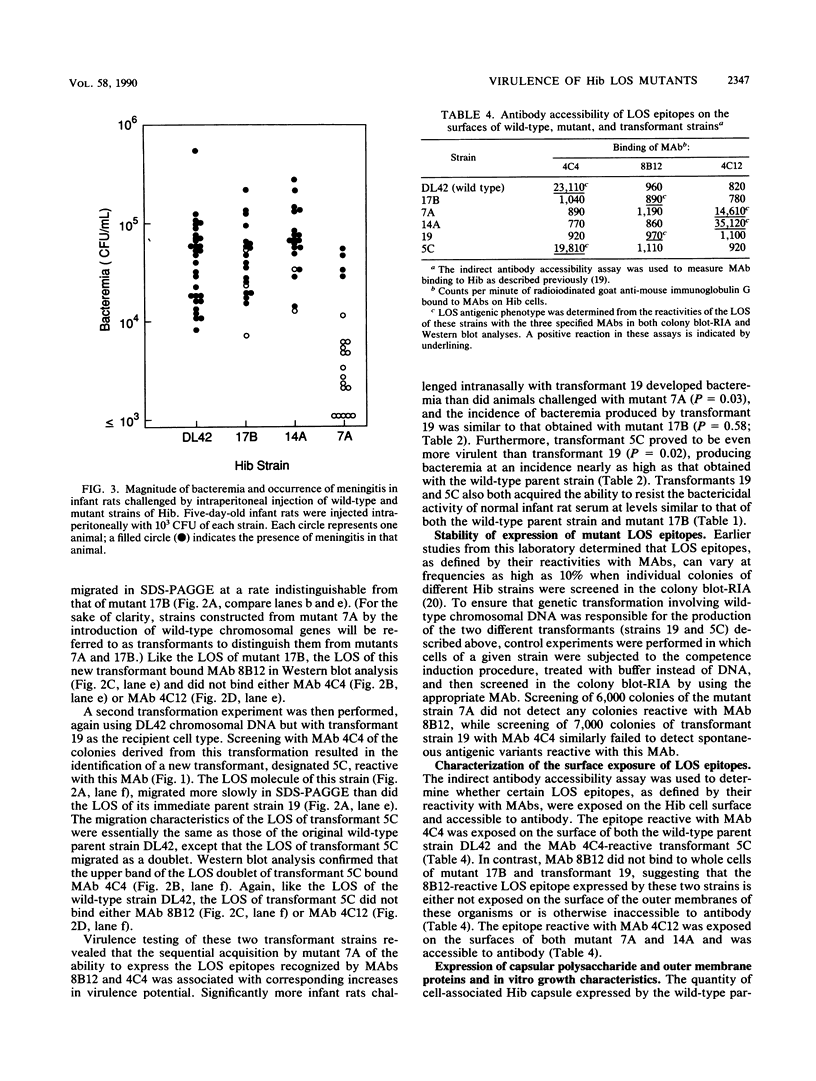
Chemical mutagenesis techniques and genetic transformation methods were used to construct isogenic mutants of Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) defective in the ability to synthesize lipooligosaccharide (LOS). A mutant (17B) which expressed a LOS molecule with an altered oligosaccharide was less virulent than the wild-type parent strain, as determined by measurement of the ability of these strains to produce bacteremia in infant rats after intranasal challenge. Further mutagenesis of this mutant strain yielded two new mutants with different LOS phenotypes. Mutant 7A was slightly sensitive to the bactericidal activity present in normal infant rat serum and was even less virulent than its immediate parent strain (17B) in the intranasal challenge model. However, both mutants 17B and 7A could produce bacteremia and meningitis when introduced into infant rats by the intraperitoneal route. The other LOS mutant (14A) derived from mutant 17B exhibited a level of virulence equivalent to that of the original wild-type strain. Genetic transformation of wild-type chromosomal DNA into the essentially avirulent mutant 7A and selection of transformants on the basis of their LOS antigenic characteristics resulted in the sequential restoration of full virulence to this mutant. These findings suggest that LOS is involved on at least two different levels in the ability of Hib to produce invasive disease in the infant rat model. Changes in LOS phenotype can independently affect the ability of Hib to produce bacteremia after intranasal challenge and the sensitivity of Hib to killing by normal infant rat serum. These results reinforce the significance of Hib LOS in the expression of virulence by this pathogen.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson P., Flesher A., Shaw S., Harding A. L., Smith D. H. Phenotypic and genetic variation in the susceptibility of Haemophilus influenzae type b to antibodies to somatic antigens. J Clin Invest. 1980 Apr;65(4):885–891. doi: 10.1172/JCI109741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochi S. L., Broome C. V. Vaccine prevention of Haemophilus influenzae type b disease: past, present and future. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1986 Jan-Feb;5(1):12–19. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198601000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denny F. W. Effect of a toxin produced by Haemophilus influenzae on ciliated respiratory epithelium. J Infect Dis. 1974 Feb;129(2):93–100. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.2.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudas K. C., Apicella M. A. Selection and immunochemical analysis of lipooligosaccharide mutants of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):499–504. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.499-504.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farley M. M., Stephens D. S., Mulks M. H., Cooper M. D., Bricker J. V., Mirra S. S., Wright A. Pathogenesis of IgA1 protease-producing and -nonproducing Haemophilus influenzae in human nasopharyngeal organ cultures. J Infect Dis. 1986 Nov;154(5):752–759. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.5.752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flesher A. R., Insel R. A. Characterization of lipopolysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae. J Infect Dis. 1978 Dec;138(6):719–730. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.6.719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilsdorf J. R., Ferrieri P. Susceptibility of phenotypic variants of Haemophilus influenzae type b to serum bactericidal activity: relation to surface lipopolysaccharide. J Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;153(2):223–231. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.2.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerola N., Ingraham J. L., Cerdá-Olmedo E. Induction of closely linked multiple mutations by nitrosoguanidine. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 24;230(12):122–125. doi: 10.1038/newbio230122a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulig P. A., McCracken G. H., Jr, Frisch C. F., Johnston K. H., Hansen E. J. Antibody response of infants to cell surface-exposed outer membrane proteins of Haemophilus influenzae type b after systemic Haemophilus disease. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):82–88. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.82-88.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulig P. A., Patrick C. C., Hermanstorfer L., McCracken G. H., Jr, Hansen E. J. Conservation of epitopes in the oligosaccharide portion of the lipooligosaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):513–520. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.513-520.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. J., Frisch C. F., McDade R. L., Jr, Johnston K. H. Identification of immunogenic outer membrane proteins of Haemophilus influenzae type b in the infant rat model system. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1084–1092. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1084-1092.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helander I. M., Lindner B., Brade H., Altmann K., Lindberg A. A., Rietschel E. T., Zähringer U. Chemical structure of the lipopolysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae strain I-69 Rd-/b+. Description of a novel deep-rough chemotype. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Nov 15;177(3):483–492. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14398.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herriott R. M., Meyer E. M., Vogt M. Defined nongrowth media for stage II development of competence in Haemophilus influenzae. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):517–524. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.517-524.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inzana T. J. Electrophoretic heterogeneity and interstrain variation of the lipopolysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):492–499. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. P., Clark J. B., Osborn M. F. Scanning electron microscopy of the interaction between Haemophilus influenzae and organ cultures of rat trachea. J Med Microbiol. 1983 Nov;16(4):477–482. doi: 10.1099/00222615-16-4-477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. P., Inzana T. J. Loss of ciliary activity in organ cultures of rat trachea treated with lipo-oligosaccharide from Haemophilus influenzae. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Nov;22(3):265–268. doi: 10.1099/00222615-22-3-265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan S. L., Hawkins E. P., Inzana T. J., Patrick C. C., Mason E. O., Jr Contribution of Haemophilus influenzae type b lipopolysaccharide to pathogenesis of infection. Microb Pathog. 1988 Jul;5(1):55–62. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90081-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Gulig P. A., McCracken G. H., Jr, Loftus T. A., Hansen E. J. A minor high-molecular-weight outer membrane protein of Haemophilus influenzae type b is a protective antigen. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):253–259. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.253-259.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Hansen E. J. Antigenic and phenotypic variations of Haemophilus influenzae type b lipopolysaccharide and their relationship to virulence. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):69–79. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.69-79.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Patrick C. C., Miller E. E., Cope L. D., McCracken G. H., Jr, Hansen E. J. Haemophilus influenzae type b lipooligosaccharide: stability of expression and association with virulence. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):1979–1986. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.1979-1986.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDade R. L., Jr, Johnston K. H. Characterization of serologically dominant outer membrane proteins of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1980 Mar;141(3):1183–1191. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.3.1183-1191.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxon E. R., Glode M. P., Sutton A., Robbins J. B. The infant rat as a model of bacterial meningitis. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136 (Suppl):S186–S190. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement.s186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxon E. R., Ostrow P. T. Haemophilus influenzae meningitis in infant rats: role of bacteremia in pathogenesis of age-dependent inflammatory responses in cerebrospinal fluid. J Infect Dis. 1977 Feb;135(2):303–307. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.2.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxon E. R., Smith A. L., Averill D. R., Smith D. H. Haemophilus influenzae meningitis in infant rats after intranasal inoculation. J Infect Dis. 1974 Feb;129(2):154–162. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.2.154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxon E. R., Vaughn K. A. The type b capsular polysaccharide as a virulence determinant of Haemophilus influenzae: studies using clinical isolates and laboratory transformants. J Infect Dis. 1981 Apr;143(4):517–524. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.4.517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa M. M., Ramilo O., Syrogiannopoulos G. A., Olsen K. D., McCracken G. H., Jr, Hansen E. J. Induction of meningeal inflammation by outer membrane vesicles of Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Infect Dis. 1989 May;159(5):917–922. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.5.917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrow P. T., Moxon E. R., Vernon N., Kapko R. Pathogenesis of bacterial meningitis. Studies on the route of meningeal invasion following Hemophilus influenzae inoculation of infant rats. Lab Invest. 1979 Jun;40(6):678–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick C. C., Kimura A., Jackson M. A., Hermanstorfer L., Hood A., McCracken G. H., Jr, Hansen E. J. Antigenic characterization of the oligosaccharide portion of the lipooligosaccharide of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):2902–2911. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.2902-2911.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick C. C., Pelzel S. E., Miller E. E., Haanes-Fritz E., Radolf J. D., Gulig P. A., McCracken G. H., Jr, Hansen E. J. Antigenic evidence for simultaneous expression of two different lipooligosaccharides by some strains of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):1971–1978. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.1971-1978.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson S. M., Frisch C. F., Gulig P. A., Kettman J. R., Johnston K. H., Hansen E. J. Monoclonal antibodies directed against a cell surface-exposed outer membrane protein of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):80–88. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.80-88.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. L., Smith D. H., Averill D. R., Jr, Marino J., Moxon E. R. Production of Haemophilus influenzae b meningitis in infant rats by intraperitoneal inoculation. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):278–290. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.278-290.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein D. C., Petricoin E. F., Griffiss J. M., Schneider H. Use of transformation to construct Neisseria gonorrhoeae strains with altered lipooligosaccharides. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):762–765. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.762-765.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton A., Schneerson R., Kendall-Morris S., Robbins J. B. Differential complement resistance mediates virulence of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):95–104. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.95-104.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syrogiannopoulos G. A., Hansen E. J., Erwin A. L., Munford R. S., Rutledge J., Reisch J. S., McCracken G. H., Jr Haemophilus influenzae type b lipooligosaccharide induces meningeal inflammation. J Infect Dis. 1988 Feb;157(2):237–244. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.2.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser J. N., Lindberg A. A., Manning E. J., Hansen E. J., Moxon E. R. Identification of a chromosomal locus for expression of lipopolysaccharide epitopes in Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):3045–3052. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.3045-3052.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller P. F., Smith A. L., Anderson P., Smith D. H. The role of encapsulation and host age in the clearance of Haemophilus influenzae bacteremia. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jan;135(1):34–41. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.1.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wispelwey B., Hansen E. J., Scheld W. M. Haemophilus influenzae outer membrane vesicle-induced blood-brain barrier permeability during experimental meningitis. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2559–2562. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2559-2562.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wispelwey B., Lesse A. J., Hansen E. J., Scheld W. M. Haemophilus influenzae lipopolysaccharide-induced blood brain barrier permeability during experimental meningitis in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1988 Oct;82(4):1339–1346. doi: 10.1172/JCI113736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogev R., Hansen E. J. Dissociation of virulence and protection from infection by mutant analysis in Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1944–1947. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1944-1947.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamze S. E., Moxon E. R. Composition of the lipopolysaccharide from different capsular serotype strains of Haemophilus influenzae. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Jun;133(6):1443–1451. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-6-1443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwahlen A., Rubin L. G., Connelly C. J., Inzana T. J., Moxon E. R. Alteration of the cell wall of Haemophilus influenzae type b by transformation with cloned DNA: association with attenuated virulence. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):485–492. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwahlen A., Rubin L. G., Moxon E. R. Contribution of lipopolysaccharide to pathogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae: comparative virulence of genetically-related strains in rats. Microb Pathog. 1986 Oct;1(5):465–473. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwahlen A., Winkelstein J. A., Moxon E. R. Surface determinants of Haemophilus influenzae pathogenicity: comparative virulence of capsular transformants in normal and complement-depleted rats. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):385–394. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Alphen L., Riemens T., Poolman J., Hopman C., Zanen H. C. Homogeneity of cell envelope protein subtypes, lipopolysaccharide serotypes, and biotypes among Haemophilus influenzae type b from patients with meningitis in The Netherlands. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jul;148(1):75–81. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



