Abstract
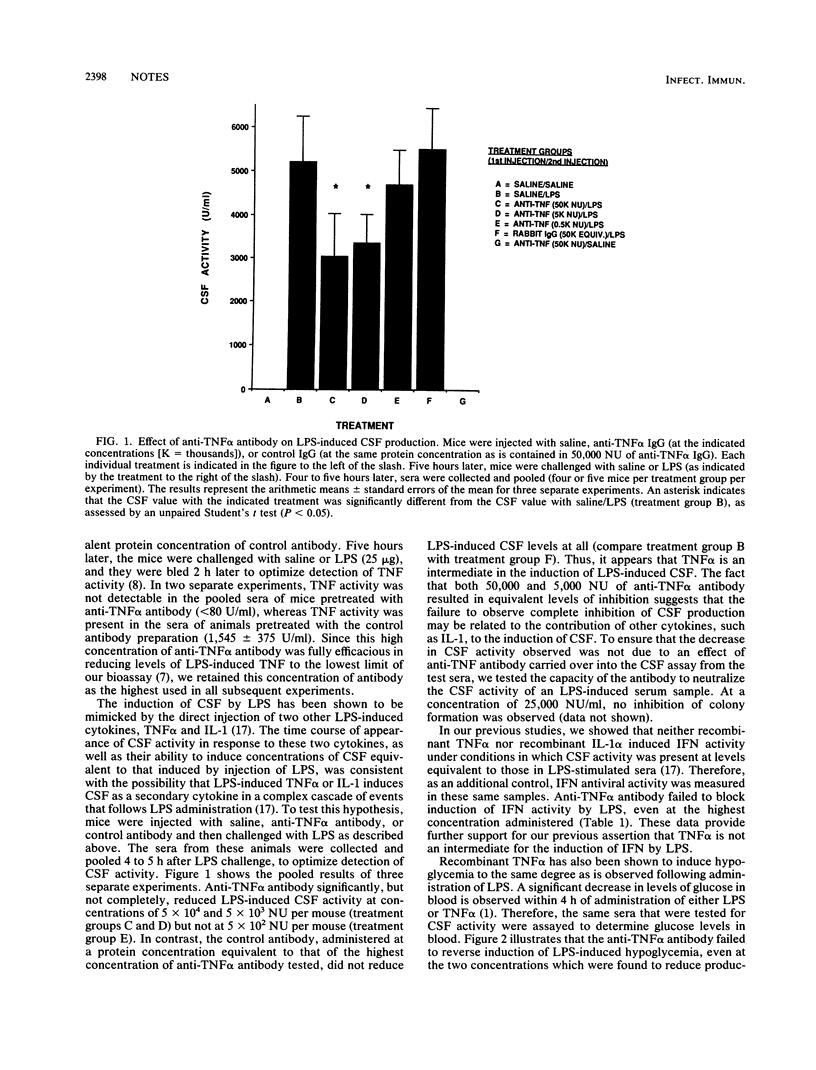
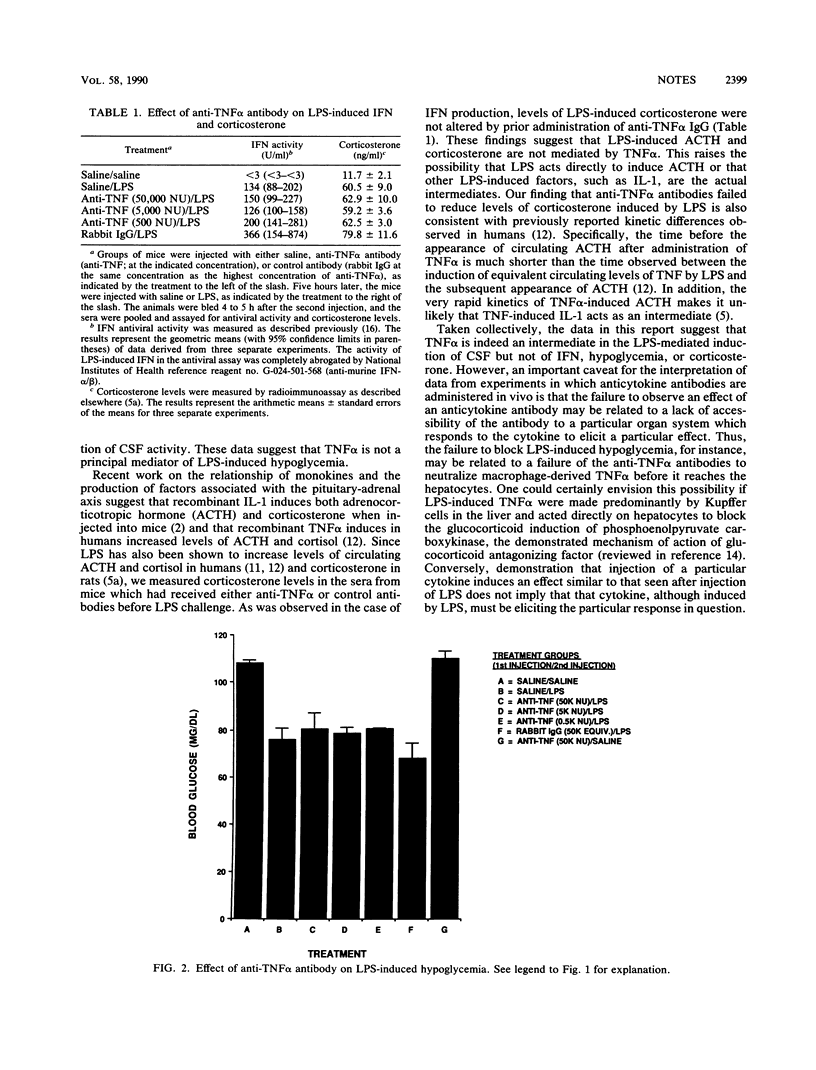
Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha) has been implicated as a major mediator of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced phenomena. Administration to mice of a polyclonal, monospecific antibody prepared against recombinant murine TNF alpha abolished detection of LPS-induced TNF alpha activity and significantly reduced levels of LPS-induced colony-stimulating factor but failed to reduce the production of LPS-induced interferon, corticosterone, or LPS-induced hypoglycemia.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauss F., Dröge W., Männel D. N. Tumor necrosis factor mediates endotoxic effects in mice. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1622–1625. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1622-1625.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besedovsky H., del Rey A., Sorkin E., Dinarello C. A. Immunoregulatory feedback between interleukin-1 and glucocorticoid hormones. Science. 1986 Aug 8;233(4764):652–654. doi: 10.1126/science.3014662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. The biology of cachectin/TNF--a primary mediator of the host response. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:625–655. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. C. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):869–871. doi: 10.1126/science.3895437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Cannon J. G., Wolff S. M., Bernheim H. A., Beutler B., Cerami A., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, O'Connor J. V. Tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is an endogenous pyrogen and induces production of interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1433–1450. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuerstein G., Hallenbeck J. M., Vanatta B., Rabinovici R., Perera P. Y., Vogel S. N. Effect of gram-negative endotoxin on levels of serum corticosterone, TNF alpha, circulating blood cells, and the survival of rats. Circ Shock. 1990 Mar;30(3):265–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A. Production of tumor necrosis factor during murine listeriosis. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):4225–4231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan M. M., Vogel S. N. Production of tumor necrosis factor by rIFN-gamma-primed C3H/HeJ (Lpsd) macrophages requires the presence of lipid A-associated proteins. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 15;141(12):4196–4202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiener P. A., Marek F., Rodgers G., Lin P. F., Warr G., Desiderio J. Induction of tumor necrosis factor, IFN-gamma, and acute lethality in mice by toxic and non-toxic forms of lipid A. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):870–874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madonna G. S., Vogel S. N. Early endotoxin tolerance is associated with alterations in bone marrow-derived macrophage precursor pools. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):3763–3771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntire F. C., Sievert H. W., Barlow G. H., Finley R. A., Lee A. Y. Chemical, physical, biological properties of a lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli K-235. Biochemistry. 1967 Aug;6(8):2363–2372. doi: 10.1021/bi00860a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michie H. R., Manogue K. R., Spriggs D. R., Revhaug A., O'Dwyer S., Dinarello C. A., Cerami A., Wolff S. M., Wilmore D. W. Detection of circulating tumor necrosis factor after endotoxin administration. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jun 9;318(23):1481–1486. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806093182301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michie H. R., Spriggs D. R., Manogue K. R., Sherman M. L., Revhaug A., O'Dwyer S. T., Arthur K., Dinarello C. A., Cerami A., Wolff S. M. Tumor necrosis factor and endotoxin induce similar metabolic responses in human beings. Surgery. 1988 Aug;104(2):280–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J., Havell E. A. The antitumor function of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) II. Analysis of the role of endogenous TNF in endotoxin-induced hemorrhagic necrosis and regression of an established sarcoma. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):1086–1099. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.1086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan K. C., Ruddle N. H., Schreiber R. D. Generation and characterization of hamster monoclonal antibodies that neutralize murine tumor necrosis factors. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 1;142(11):3884–3893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel S. N., Douches S. D., Kaufman E. N., Neta R. Induction of colony stimulating factor in vivo by recombinant interleukin 1 alpha and recombinant tumor necrosis factor alpha 1. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2143–2148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel S. N., Kaufman E. N., Tate M. D., Neta R. Recombinant interleukin-1 alpha and recombinant tumor necrosis factor alpha synergize in vivo to induce early endotoxin tolerance and associated hematopoietic changes. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2650–2657. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2650-2657.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel S. N., Moore R. N., Sipe J. D., Rosenstreich D. L. BCG-induced enhancement of endotoxin sensitivity in C3H/HeJ mice. I. In vivo studies. J Immunol. 1980 Apr;124(4):2004–2009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


