Abstract
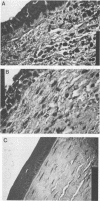
The virulence plasmid (pYV) of Yersinia enterocolitica is necessary for production of conjunctivitis in guinea pigs and for mouse lethality. To identify the genes responsible for production of conjunctivitis in guinea pigs, we subcloned the BamHI and SalI restriction fragments of the virulence plasmid of Y. enterocolitica A2635 (serotype O:8) into derivatives of the broad-host-range plasmid pRK290 and introduced the constructions into plasmid-negative Y. enterocolitica strains. A mild, transient conjunctivitis was evident 24 h after inoculation with strains containing a 2.8-kilobase (kb) BamHI fragment of pYV. These strains were cytotoxic to HEp-2 cells but did not cause death in iron-loaded adult mice. When the 2.8- and adjacent 0.5-kb BamHI fragments were deleted from the virulence plasmid of a fully virulent Y. enterocolitica isolate, the resultant strain did not cause conjunctivitis in guinea pigs and was not cytotoxic to HEp-2 cells. However, the strain with the deletion appeared to be more virulent for mice, with more rapid dissemination after orogastric inoculation, compared with that of the parent strain. When the deletion was complemented by introduction of a plasmid containing the 2.8-kb BamHI fragment, the strain again caused conjunctivitis but had decreased virulence for mice.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aulisio C. C., Hill W. E., Stanfield J. T., Sellers R. L., Jr Evaluation of virulence factor testing and characteristics of pathogenicity in Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):330–335. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.330-335.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakour R., Balligand G., Laroche Y., Cornelis G., Wauters G. A simple adult-mouse test for tissue invasiveness in Yersinia enterocolitica strains of low experimental virulence. J Med Microbiol. 1985 Apr;19(2):237–246. doi: 10.1099/00222615-19-2-237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balligand G., Laroche Y., Cornelis G. Genetic analysis of virulence plasmid from a serogroup 9 Yersinia enterocolitica strain: role of outer membrane protein P1 in resistance to human serum and autoagglutination. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):782–786. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.782-786.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhaduri S., Conway L. K., Lachica R. V. Assay of crystal violet binding for rapid identification of virulent plasmid-bearing clones of Yersinia enterocolitica. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jun;25(6):1039–1042. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.6.1039-1042.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black R. E., Jackson R. J., Tsai T., Medvesky M., Shayegani M., Feeley J. C., MacLeod K. I., Wakelee A. M. Epidemic Yersinia enterocolitica infection due to contaminated chocolate milk. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jan 12;298(2):76–79. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197801122980204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottone E. J. Current trends of Yersinia enterocolitica isolates in the New York City area. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jan;17(1):63–67. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.1.63-67.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottone E. J. Yersinia enterocolitica: a panoramic view of a charismatic microorganism. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1977;5(2):211–241. doi: 10.3109/10408417709102312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölin I., Forsberg A., Norlander L., Skurnik M., Wolf-Watz H. Identification and mapping of the temperature-inducible, plasmid-encoded proteins of Yersinia spp. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):343–348. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.343-348.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölin I., Norlander L., Wolf-Watz H. Temperature-inducible outer membrane protein of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Yersinia enterocolitica is associated with the virulence plasmid. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):506–512. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.506-512.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang M. T., Schink J., Shimaoka J., Doyle M. P. Comparison of three tests for virulent Yersinia enterocolitica. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):589–591. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.589-591.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis G., Laroche Y., Balligand G., Sory M. P., Wauters G. Yersinia enterocolitica, a primary model for bacterial invasiveness. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):64–87. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Schmidhauser T., Yakobson E., Lu P., Liang X. W., Finlay D. R., Guiney D., Helinski D. R. Plasmids related to the broad host range vector, pRK290, useful for gene cloning and for monitoring gene expression. Plasmid. 1985 Mar;13(2):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Stanfield S., Corbin D., Helinski D. R. Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7347–7351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figurski D. H., Helinski D. R. Replication of an origin-containing derivative of plasmid RK2 dependent on a plasmid function provided in trans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1648–1652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Lazere J. R., Casey T. Plasmid associated with pathogenicity and calcium dependency of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):682–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.682-685.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goguen J. D., Walker W. S., Hatch T. P., Yother J. Plasmid-determined cytotoxicity in Yersinia pestis and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):788–794. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.788-794.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goguen J. D., Yother J., Straley S. C. Genetic analysis of the low calcium response in Yersinia pestis mu d1(Ap lac) insertion mutants. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):842–848. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.842-848.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGUCHI K., SMITH J. L. Studies on the nutrition and physiology of Pasteurella pestis. VI. A differential plating medium for the estimation of the mutation rate to avirulence. J Bacteriol. 1961 Apr;81:605–608. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.4.605-608.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay B. A., Wachsmuth K., Gemski P., Feeley J. C., Quan T. J., Brenner D. J. Virulence and phenotypic characterization of Yersinia enterocolitica isolated from humans in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jan;17(1):128–138. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.1.128-138.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluftinger J. L., Lutz F., Hancock R. E. Pseudomonas aeruginosa cytotoxin: periplasmic localization and inhibition of macrophages. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):882–886. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.882-886.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachica R. V., Zink D. L. Plasmid-associated cell surface charge and hydrophobicity of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):540–543. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.540-543.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird W. J., Cavanaugh D. C. Correlation of autoagglutination and virulence of yersiniae. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Apr;11(4):430–432. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.4.430-432.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., McGrath P. P., Carter P. H., Eide E. L. The ability of some Yersinia enterocolitica strains to invade HeLa cells. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Dec;23(12):1714–1722. doi: 10.1139/m77-247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H. Testing for the recovery of Yersinia enterocolitica in foods and their ability to invade HeLa cells. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1979;5:228–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez R. J. Plasmid-mediated and temperature-regulated surface properties of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):921–930. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.921-930.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T., Sansonetti P. J. Identification of a chromosomal gene controlling temperature-regulated expression of Shigella virulence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2820–2824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miliotis M. D., Galen J. E., Kaper J. B., Morris J. G., Jr Development and testing of a synthetic oligonucleotide probe for the detection of pathogenic Yersinia strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jul;27(7):1667–1670. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.7.1667-1670.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Falkow S. Evidence for two genetic loci in Yersinia enterocolitica that can promote invasion of epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1242–1248. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1242-1248.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Farmer J. J., 3rd, Hill W. E., Falkow S. The ail locus is found uniquely in Yersinia enterocolitica serotypes commonly associated with disease. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):121–131. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.121-131.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäki M., Vesikari T., Rantala I., Sundqvist C., Grönroos P. Pathogenicity of 42-44 Mdal plasmid positive and negative Yersinia pseudotuberculosis I and Yersinia enterocolitica 0:8 and 0:9 studied in the guinea pig eye model (Serény test). Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1983 Aug;91(4):241–244. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1983.tb00040.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibuchi M., Kaper J. B. Nucleotide sequence of the thermostable direct hemolysin gene of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):558–564. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.558-564.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai C. H., DeStephano L. Serum resistance associated with virulence in Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):605–611. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.605-611.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai C. H., Mors V. Production of enterotoxin by Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):908–911. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.908-911.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Blank H. F., Kingsbury D. T., Falkow S. Genetic analysis of essential plasmid determinants of pathogenicity in Yersinia pestis. J Infect Dis. 1983 Aug;148(2):297–304. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.2.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Martinez R. J. Role of a plasmid in the pathogenicity of Yersinia species. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;118:29–51. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70586-1_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Characterization of plasmids and plasmid-associated determinants of Yersinia enterocolitica pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):775–782. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.775-782.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Wolf-Watz H., Bolin I., Beeder A. B., Falkow S. Characterization of common virulence plasmids in Yersinia species and their role in the expression of outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):108–114. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.108-114.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prpic J. K., Robins-Browne R. M., Davey R. B. Differentiation between virulent and avirulent Yersinia enterocolitica isolates by using Congo red agar. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):486–490. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.486-490.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prpic J. K., Robins-Browne R. M., Davey R. B. In vitro assessment of virulence in Yersinia enterocolitica and related species. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jul;22(1):105–110. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.1.105-110.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitmeyer J. C., Peterson J. W., Wilson K. J. Salmonella cytotoxin: a component of the bacterial outer membrane. Microb Pathog. 1986 Oct;1(5):503–510. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins-Browne R. M., Miliotis M. D., Cianciosi S., Miller V. L., Falkow S., Morris J. G., Jr Evaluation of DNA colony hybridization and other techniques for detection of virulence in Yersinia species. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Apr;27(4):644–650. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.4.644-650.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins-Browne R. M., Prpic J. K. Effects of iron and desferrioxamine on infections with Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):774–779. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.774-779.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins-Browne R. M., Tzipori S., Gonis G., Hayes J., Withers M., Prpic J. K. The pathogenesis of Yersinia enterocolitica infection in gnotobiotic piglets. J Med Microbiol. 1985 Jun;19(3):297–308. doi: 10.1099/00222615-19-3-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosqvist R., Skurnik M., Wolf-Watz H. Increased virulence of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis by two independent mutations. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):522–524. doi: 10.1038/334522a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosqvist R., Wolf-Watz H. Virulence plasmid-associated HeLa cell induced cytotoxicity of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Microb Pathog. 1986 Jun;1(3):229–240. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90047-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SERENY B. Experimental shigella keratoconjunctivitis; a preliminary report. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1955;2(3):293–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiemann D. A., Devenish J. A. Relationship of HeLa cell infectivity to biochemical, serological, and virulence characteristics of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):497–506. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.497-506.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiemann D. A., Devenish J. A. Virulence of Yersinia enterocolitica determined by lethality in Mongolian gerbils and by the Serény test. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):500–506. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.500-506.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesikari T., Nurmi T., Mäki M., Skurnik M., Sundqvist C., Granfors K., Grönroos P. Plasmids in Yersinia enterocolitica serotypes O:3 and O:9: correlation with epithelial cell adherence in vitro. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):870–876. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.870-876.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesikari T., Sundqvist C., Mäki M. Adherence and toxicity of Yersinia enterocolitica 0:3 and 0:9 containing virulence-associated plasmids for various cultured cells. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1983 Apr;91(2):121–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1983.tb00020.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]