Abstract
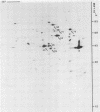
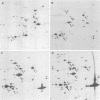
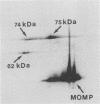
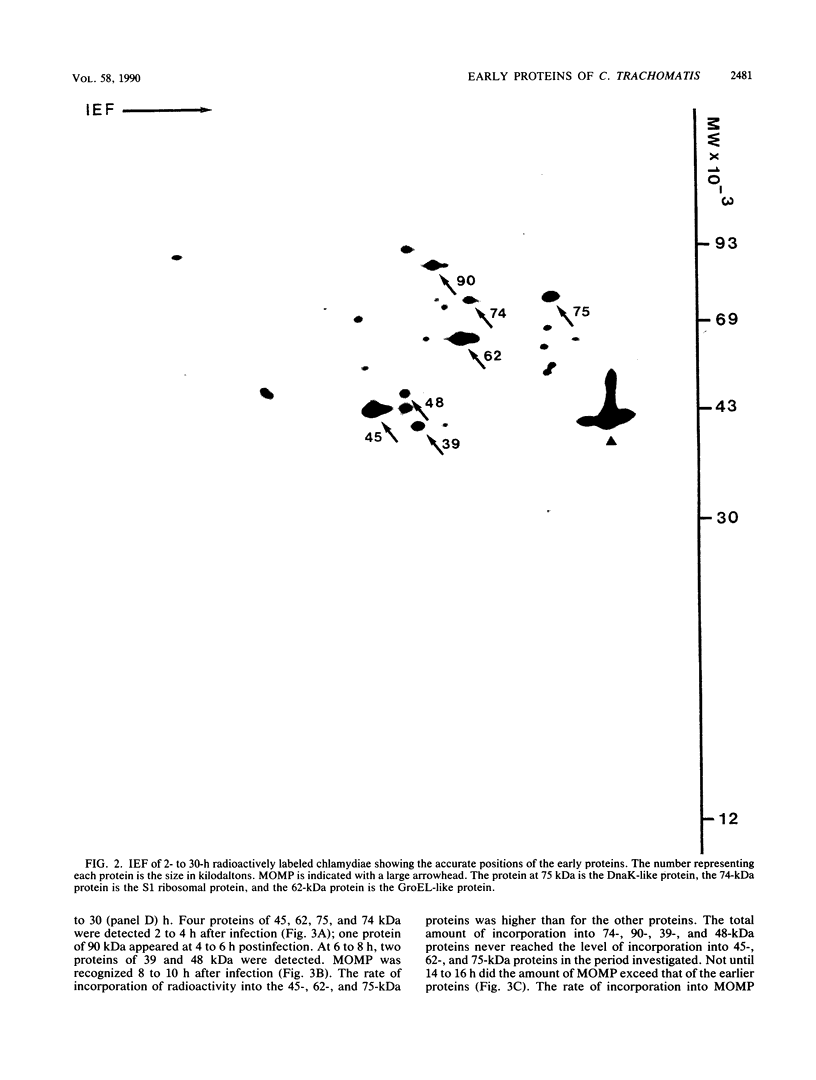
The synthesis of early proteins from Chlamydia trachomatis serovar L2 was analyzed by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. By pulse-label experiments, the synthesis of seven proteins was observed at 2 to 8 h postinfection before the major outer membrane protein was detected at 8 to 10 h after infection. The early proteins were synthesized throughout the 30-h period investigated, but the synthesis of three proteins of 75, 62, and 45 kilodaltons decreased from 26 to 30 h postinfection. Pulse-chase analysis showed that the signals from the same three proteins declined 26 to 30 h after infection. Three of the early proteins were identified as the S1 ribosomal protein, the GroEL-like protein, and DnaK-like protein, respectively.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birkelund S., Lundemose A. G., Christiansen G. Characterization of native and recombinant 75-kilodalton immunogens from Chlamydia trachomatis serovar L2. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2683–2690. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2683-2690.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkelund S., Lundemose A. G., Christiansen G. Chemical cross-linking of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1988 Mar;56(3):654–659. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.3.654-659.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng M. Y., Hartl F. U., Martin J., Pollock R. A., Kalousek F., Neupert W., Hallberg E. M., Hallberg R. L., Horwich A. L. Mitochondrial heat-shock protein hsp60 is essential for assembly of proteins imported into yeast mitochondria. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):620–625. doi: 10.1038/337620a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirico W. J., Waters M. G., Blobel G. 70K heat shock related proteins stimulate protein translocation into microsomes. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):805–810. doi: 10.1038/332805a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christman M. F., Morgan R. W., Jacobson F. S., Ames B. N. Positive control of a regulon for defenses against oxidative stress and some heat-shock proteins in Salmonella typhimurium. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):753–762. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Poffenroth L., Wilt J. C., Kordová N. Ultrastructural studies of the nucleoids of the pleomorphic forms of Chlamydia psittaci 6BC: a comparison with bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Jan;22(1):16–28. doi: 10.1139/m76-003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danilition S. L., Maclean I. W., Peeling R., Winston S., Brunham R. C. The 75-kilodalton protein of Chlamydia trachomatis: a member of the heat shock protein 70 family? Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):189–196. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.189-196.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshaies R. J., Koch B. D., Werner-Washburne M., Craig E. A., Schekman R. A subfamily of stress proteins facilitates translocation of secretory and mitochondrial precursor polypeptides. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):800–805. doi: 10.1038/332800a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goloubinoff P., Gatenby A. A., Lorimer G. H. GroE heat-shock proteins promote assembly of foreign prokaryotic ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase oligomers in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1989 Jan 5;337(6202):44–47. doi: 10.1038/337044a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackstadt T. Identification and properties of chlamydial polypeptides that bind eucaryotic cell surface components. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jan;165(1):13–20. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.1.13-20.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackstadt T., Todd W. J., Caldwell H. D. Disulfide-mediated interactions of the chlamydial major outer membrane protein: role in the differentiation of chlamydiae? J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):25–31. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.25-31.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P., Allan I., Pearce J. H. Structural and polypeptide differences between envelopes of infective and reproductive life cycle forms of Chlamydia spp. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):13–20. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.13-20.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P., Miceli M., Sublett J. E. Synthesis of disulfide-bonded outer membrane proteins during the developmental cycle of Chlamydia psittaci and Chlamydia trachomatis. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):379–385. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.379-385.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Sakaki Y. Dideoxy sequencing method using denatured plasmid templates. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmingsen S. M., Woolford C., van der Vies S. M., Tilly K., Dennis D. T., Georgopoulos C. P., Hendrix R. W., Ellis R. J. Homologous plant and bacterial proteins chaperone oligomeric protein assembly. Nature. 1988 May 26;333(6171):330–334. doi: 10.1038/333330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S. The heat-shock response. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1151–1191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manire G. P., Tamura A. Preparation and chemical composition of the cell walls of mature infectious dense forms of meningopneumonitis organisms. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1178–1183. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1178-1183.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan R. W., Christman M. F., Jacobson F. S., Storz G., Ames B. N. Hydrogen peroxide-inducible proteins in Salmonella typhimurium overlap with heat shock and other stress proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8059–8063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison R. P., Belland R. J., Lyng K., Caldwell H. D. Chlamydial disease pathogenesis. The 57-kD chlamydial hypersensitivity antigen is a stress response protein. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1271–1283. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison R. P., Lyng K., Caldwell H. D. Chlamydial disease pathogenesis. Ocular hypersensitivity elicited by a genus-specific 57-kD protein. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):663–675. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newhall W. J., 5th Biosynthesis and disulfide cross-linking of outer membrane components during the growth cycle of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):162–168. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.162-168.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newhall W. J., Jones R. B. Disulfide-linked oligomers of the major outer membrane protein of chlamydiae. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):998–1001. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.998-1001.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. Heat-shock proteins. Coming in from the cold. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):776–777. doi: 10.1038/332776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaunt M. R., Hatch T. P. Protein synthesis early in the developmental cycle of Chlamydia psittaci. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3021–3025. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3021-3025.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reading D. S., Hallberg R. L., Myers A. M. Characterization of the yeast HSP60 gene coding for a mitochondrial assembly factor. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):655–659. doi: 10.1038/337655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reznikoff W. S., Siegele D. A., Cowing D. W., Gross C. A. The regulation of transcription initiation in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:355–387. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.002035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ripa K. T., Mårdh P. A. Cultivation of Chlamydia trachomatis in cycloheximide-treated mccoy cells. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Oct;6(4):328–331. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.4.328-331.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardinia L. M., Engel J. N., Ganem D. Chlamydial gene encoding a 70-kilodalton antigen in Escherichia coli: analysis of expression signals and identification of the gene product. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):335–341. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.335-341.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardinia L. M., Segal E., Ganem D. Developmental regulation of the cysteine-rich outer-membrane proteins of murine Chlamydia trachomatis. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Apr;134(4):997–1004. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-4-997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter J., Caldwell H. D. Chlamydiae. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:285–309. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter J. The intracellular life of Chlamydia. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1988;138:109–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter E. M. Synthesis of nucleic acid and protein in L cells infected with the agent of meningopneumonitis. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):2069–2080. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.2069-2080.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley K. K. Solubilization and immune-detection of beta-galactosidase hybrid proteins carrying foreign antigenic determinants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):4077–4092. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.4077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian A. R. Structure and functions of ribosomal protein S1. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1983;28:101–142. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60085-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura A., Matsumoto A., Higashi N. Purification and chemical composition of reticulate bodies of the meningopneumonitis organisms. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jun;93(6):2003–2008. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.6.2003-2008.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagar E. A., Stephens R. S. Developmental-form-specific DNA-binding proteins in Chlamydia spp. Infect Immun. 1988 Jul;56(7):1678–1684. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.7.1678-1684.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D., Lathigra R., Hendrix R., Sweetser D., Young R. A. Stress proteins are immune targets in leprosy and tuberculosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4267–4270. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]