Abstract
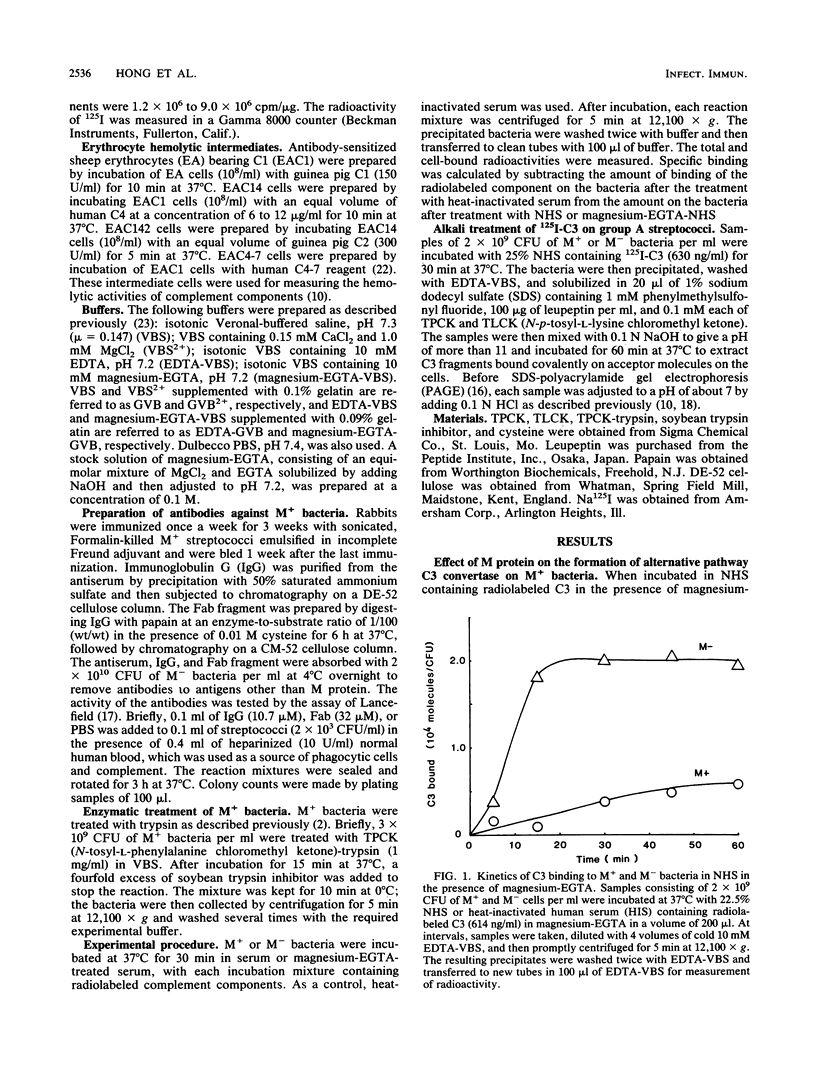
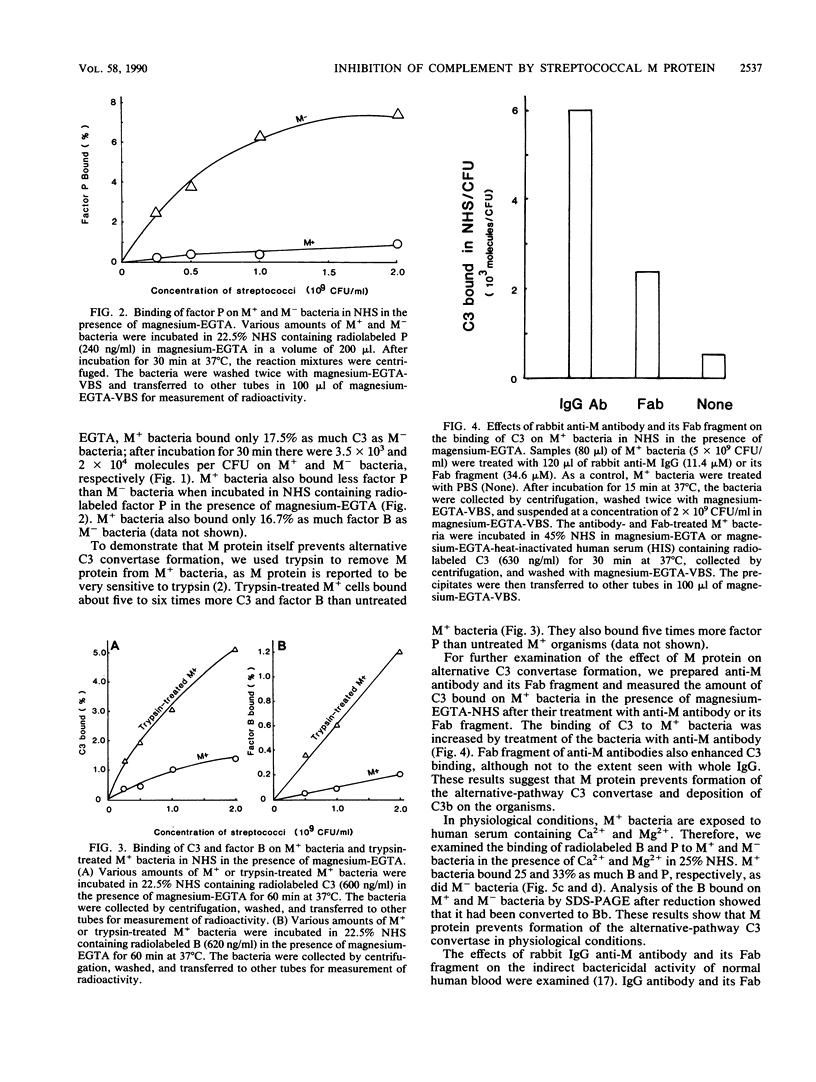
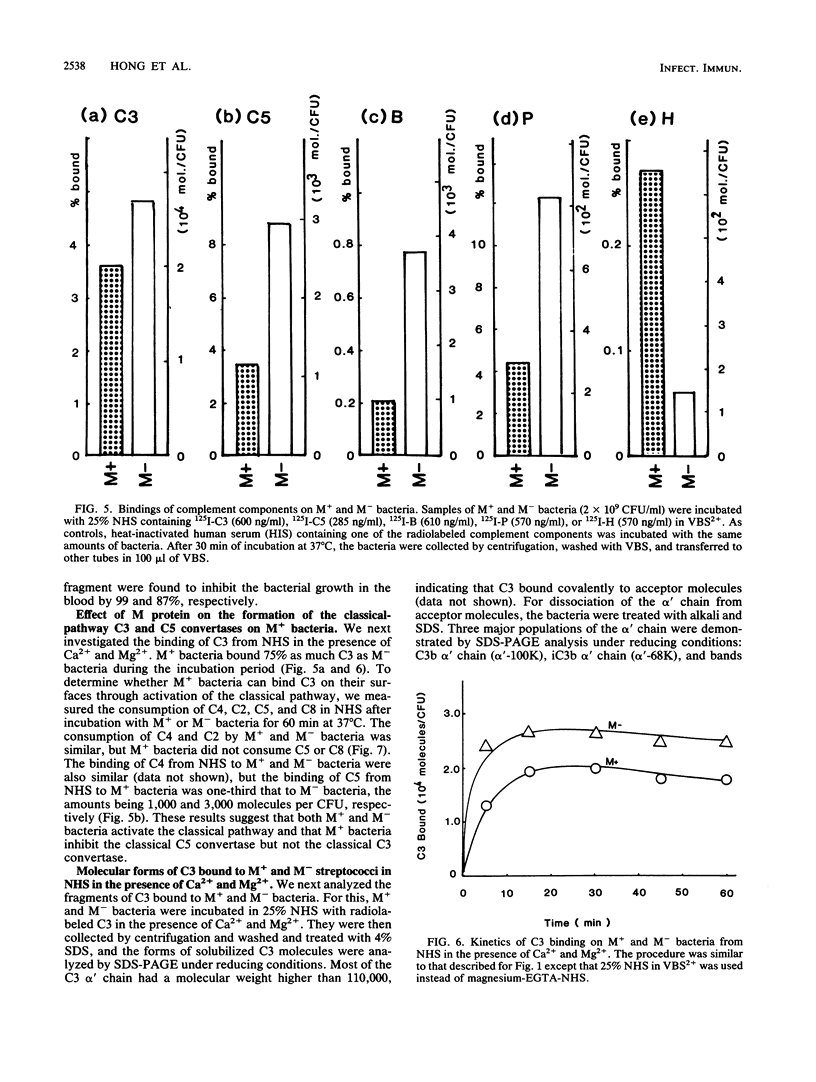
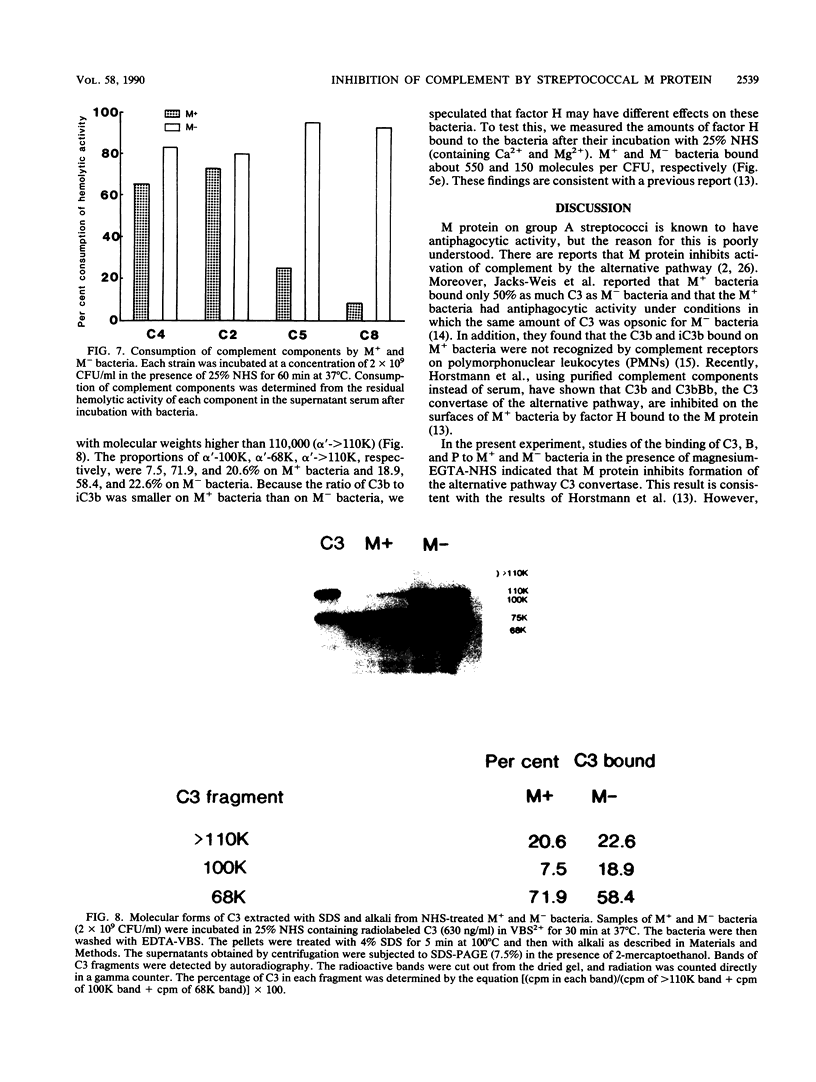
When Streptococcus pyogenes group A type 3 strain C203 (M+) and its M-protein-lacking derivative, strain C203S (M-), were treated with normal human serum in the presence of magnesium-EGTA [ethylene glycol-bis(beta-aminoethyl ether)-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid], virulent M+ bacteria bound only 10 to 30% as much C3 and factors B and P as did avirulent M- bacteria. After treatment of M+ bacteria with trypsin, which inactivates M protein, their binding of these substances was similar to that of M- bacteria. Pretreatment of M+ bacteria with the Fab fragment of rabbit immunoglobulin G anti-M antibody also increased their binding of C3 in the absence of Ca2+. Therefore, M protein inhibits the alternative C3 convertase. In contrast, in the presence of Ca2+ and Mg2+, M+ bacteria bound 75% as much C3 as M- bacteria. This binding was mostly mediated by classical pathway activation, because M+ bacteria bound much smaller amounts of factors B and P than did M- bacteria but consumed amounts of C4 and C2 comparable to those consumed by M- bacteria. On the other hand, the amount of C5 bound to M+ bacteria was much less than that bound to M- bacteria, and the consumption of C5 and C8 by M+ bacteria was also much less than that by M- bacteria. Therefore, M protein does not inhibit the classical C3 convertase but does inhibit the classical C5 convertase. When M+ and M- streptococci were incubated with normal human serum containing radiolabeled C3 in the presence of Ca2+ and Mg2+, more than 85% of the C3 bound to either type of streptococcus was extractable by sodium dodecyl sulfate and alkali treatment. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis of the C3 extracted from both strains showed that it was mostly C3b and iC3b. The proportions of C3b and iC3b, respectively, were 7.5 and 71.9% on M+ bacteria and 18.9 and 58.4% on M- bacteria. These results support and extend previous findings that the antiphagocytic activity of streptococcal M protein may be due to complement inhibition mediated by the binding of factor H.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnaout M. A., Hakim R. M., Todd R. F., 3rd, Dana N., Colten H. R. Increased expression of an adhesion-promoting surface glycoprotein in the granulocytopenia of hemodialysis. N Engl J Med. 1985 Feb 21;312(8):457–462. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198502213120801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisno A. L. Alternate complement pathway activation by group A streptococci: role of M-protein. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1172–1176. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1172-1176.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boenisch T., Alper C. A. Isolation and properties of a glycine-rich beta-glycoprotein of human serum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Dec 22;221(3):529–535. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90224-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolotin C., Morris S., Tack B., Prahl J. Purification and structural analysis of the fourth component of human complement. Biochemistry. 1977 May 3;16(9):2008–2015. doi: 10.1021/bi00628a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. C., Cleary P. P. Cloning and expression of the streptococcal C5a peptidase gene in Escherichia coli: linkage to the type 12 M protein gene. Infect Immun. 1989 Jun;57(6):1740–1745. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.6.1740-1745.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez H. N., Henson P. M., Otani A., Hugli T. E. Chemotactic response to human C3a and C5a anaphylatoxins. I. Evaluation of C3a and C5a leukotaxis in vitro and under stimulated in vivo conditions. J Immunol. 1978 Jan;120(1):109–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A. Requirements for the opsonic activity of human IgG directed to type 6 group A streptococci: net basic charge and intact Fc region. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):896–902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong K., Kinoshita T., Dohi Y., Inoue K. Effect of trypsinization on the activity of human factor H. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):647–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong K., Kinoshita T., Inoue K. Simple methods for preparing EAC1,4b,2a,3b and EAC4b,3b with human or guinea pig complement components using an anticomplementary agent, K-76 monocarboxylic acid. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):109–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong K., Kinoshita T., Miyazaki W., Izawa T., Inoue K. An anticomplementary agent, K-76 monocarboxylic acid: its site and mechanism of inhibition of the complement activation cascade. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2418–2423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horstmann R. D., Sievertsen H. J., Knobloch J., Fischetti V. A. Antiphagocytic activity of streptococcal M protein: selective binding of complement control protein factor H. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1657–1661. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks-Weis J., Kim Y., Cleary P. P. Restricted deposition of C3 on M+ group A streptococci: correlation with resistance to phagocytosis. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1897–1902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C. Differentiation of group A streptococci with a common R antigen into three serological types, with special reference to the bactericidal test. J Exp Med. 1957 Oct 1;106(4):525–544. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.4.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. K., Fearon D. T., Levine R. P. Action of the C3b-inactivator on the cell-bound C3b. J Immunol. 1979 Mar;122(3):759–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J., Hakim R. M., Fearon D. T. Increased expression of the C3b receptor by neutrophils and complement activation during haemodialysis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Apr;56(1):205–214. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesavre P. H., Hugli T. E., Esser A. F., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The alternative pathway C3/C5 convertase: chemical basis of factor B activation. J Immunol. 1979 Aug;123(2):529–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loos M., Clas F., Fischer W. Interaction of purified lipoteichoic acid with the classical complement pathway. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):595–599. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.595-599.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manni J. A., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The eighth component of human complement (C8): isolation, characterization, and hemolytic efficiency. J Exp Med. 1969 Nov 1;130(5):1145–1160. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.5.1145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medicus R. G., Esser A. F., Fernandez H. N., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Native and activated properdin: interconvertibility and identity of amino- and carboxy-terminal sequences. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):602–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore F. D., Jr, Davis C., Rodrick M., Mannick J. A., Fearon D. T. Neutrophil activation in thermal injury as assessed by increased expression of complement receptors. N Engl J Med. 1986 Apr 10;314(15):948–953. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198604103141503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Schmeling D., Cleary P. P., Wilkinson B. J., Kim Y., Quie P. G. Inhibition of alternative complement pathway opsonization by group A streptococcal M protein. J Infect Dis. 1979 May;139(5):575–585. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.5.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tack B. D., Prahl J. W. Third component of human complement: purification from plasma and physicochemical characterization. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 5;15(20):4513–4521. doi: 10.1021/bi00665a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis J. J., Law S. K., Levine R. P., Cleary P. P. Resistance to phagocytosis by group A streptococci: failure of deposited complement opsonins to interact with cellular receptors. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):500–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wexler D. E., Chenoweth D. E., Cleary P. P. Mechanism of action of the group A streptococcal C5a inactivator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8144–8148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoden A., Moriyama T., Inoue K., Inai S. The role of the C9b domain in the binding of C9 molecules to EAC1-8 defined by monoclonal antibodies to C9. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;140(7):2317–2321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]