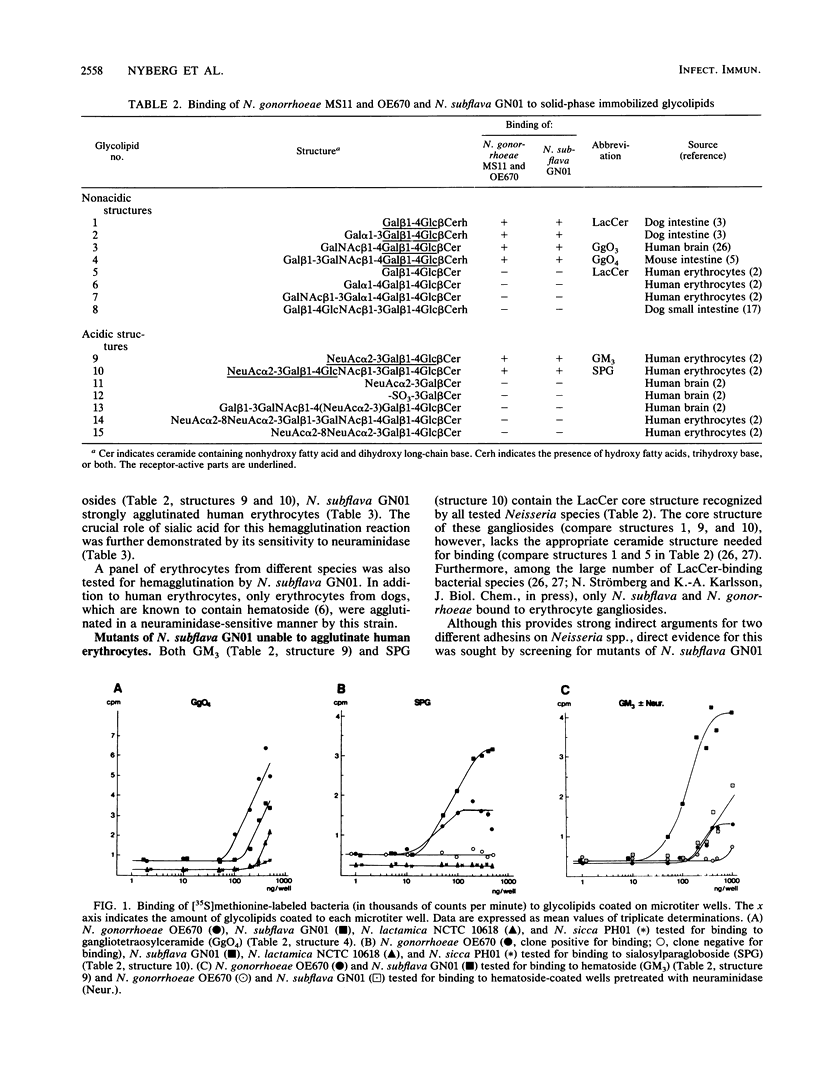
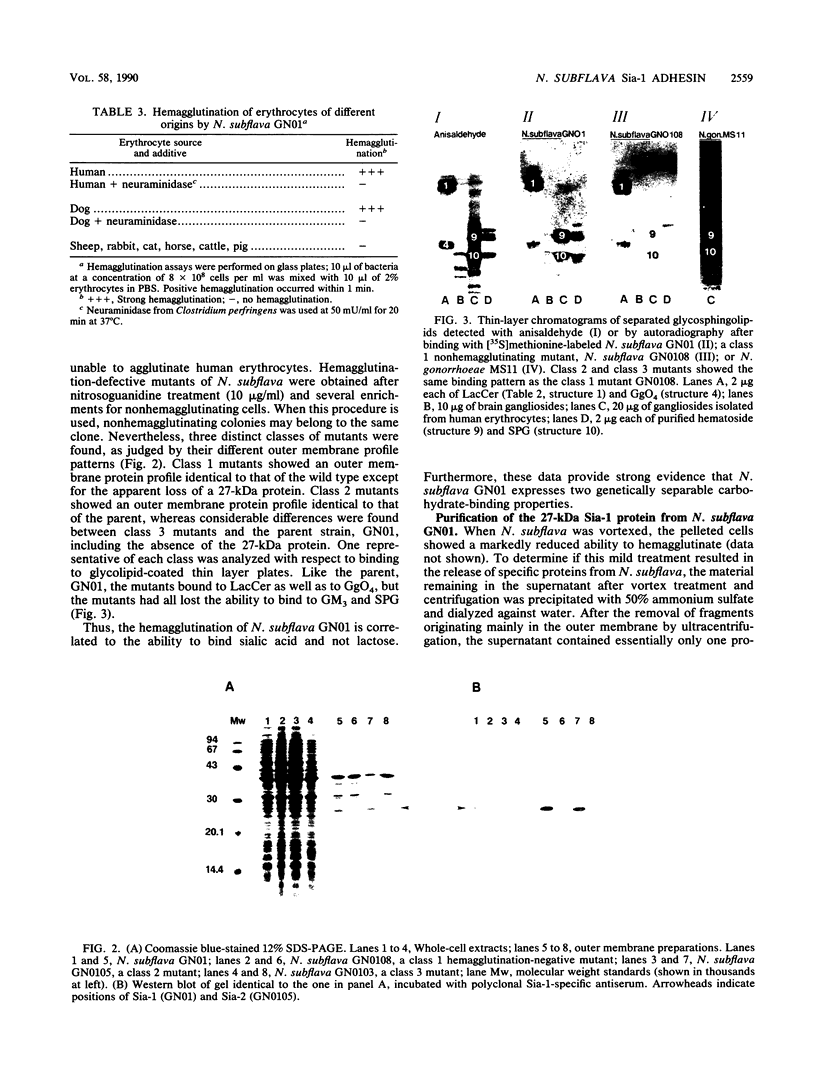
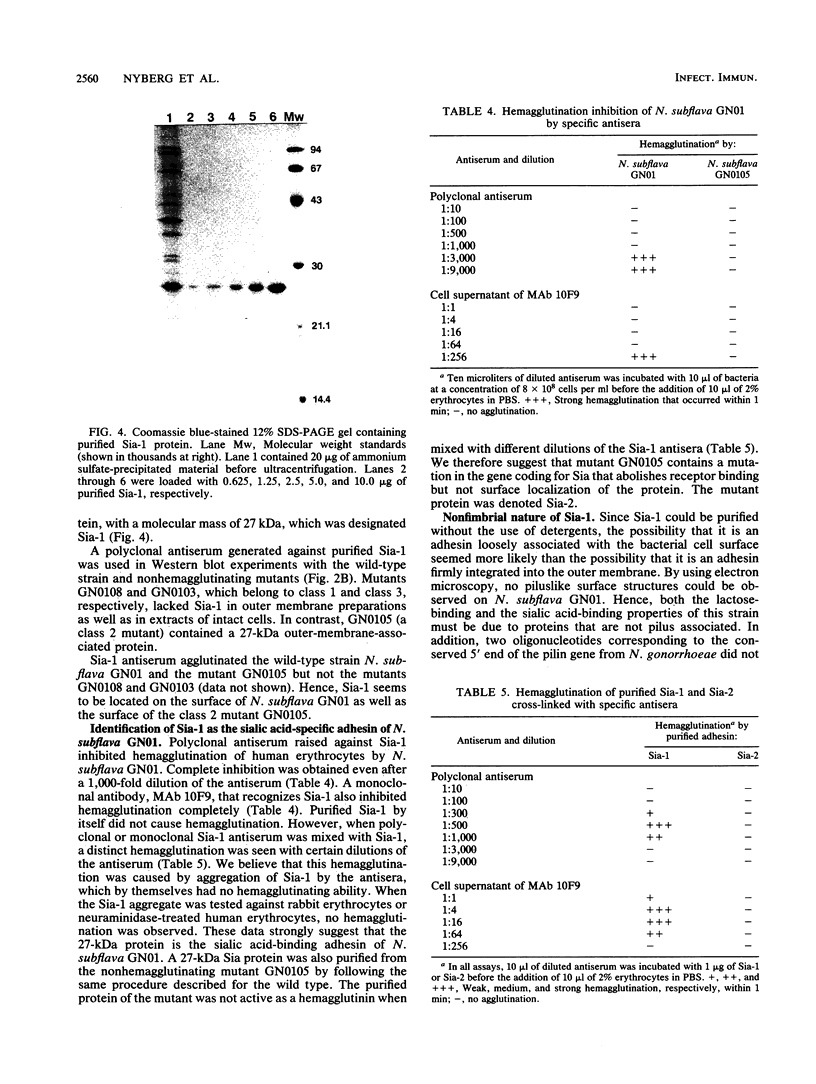
Abstract
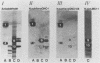
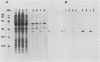
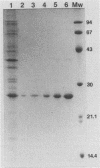
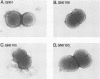
Neisseria gonorrhoeae was recently shown to bind to a subset of lactose-containing glycolipids (N. Strömberg, C. Deal, G. Nyberg, S. Normark, M. So, and K.-A. Karlsson, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85:4902-4906, 1988). A number of commensal Neisseria strains were also shown to be lactose binders. In addition, Neisseria subflava bound to immobilized gangliosides, such as hematoside and sialosyl paragloboside, carrying the NeuAc alpha 2-3Gal beta 1-4Glc sequence. To a lesser extent, N. gonorrhoeae also bound to this receptor in vitro. In N. subflava GN01, this binding property mediated agglutination of human erythrocytes in a neuraminidase-sensitive fashion. Nitrosoguanidine-induced nonhemagglutinative mutants of N. subflava GN01 had lost the ability to bind hematoside and sialosylparagloboside but remained able to bind lactosylceramide and gangliotetraosylceramide. These mutants fell into three classes with respect to their outer membrane protein profiles in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Class 1 mutants were identical to the parent strain save for the loss of a 27-kilodalton (kDa) protein. Class 2 mutants showed an outer membrane protein profile identical to that of the wild type, whereas mutants belonging to class 3 showed a number of changes, including the apparent absence of the 27-kDa protein. The 27-kDa protein from N. subflava GN01 was purified from the supernatant. A polyclonal antiserum to the purified Sia-1 protein as well as a Sia-1-specific monoclonal antibody inhibited hemagglutination by strain GN01. The purified Sia-1 protein in the presence of diluted anti-Sia-1 antiserum mediated a neuraminidase-sensitive hemagglutination. The purified Sia protein from a class 2 mutant was not able to hemagglutinate when cross-linked with antibodies, suggesting that it is a mutant form of Sia-1 affected in the receptor-binding site. Immunoelectron microscopy with a Sia-1-specific monoclonal antibody revealed that the adhesin was nonfimbrial in nature, with aggregates of the adhesin extended out from the cells in a patchy fashion.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Moulds J. J., Graham D. Y. N-acetylneuraminyllactose-binding fibrillar hemagglutinin of Campylobacter pylori: a putative colonization factor antigen. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2896–2906. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2896-2906.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson G. C., Karlsson K. A., Larson G., McKibbin J. M., Strömberg N., Thurin J. Isoglobotriaosylceramide and the Forssman glycolipid of dog small intestine occupy separate tissue compartments and differ in ceramide composition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jan 7;750(1):214–216. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90224-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson G. C., Karlsson K. A., Larson G., Strömberg N., Thurin J. Carbohydrate-specific adhesion of bacteria to thin-layer chromatograms: a rationalized approach to the study of host cell glycolipid receptors. Anal Biochem. 1985 Apr;146(1):158–163. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90410-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson G. C., Karlsson K. A., Leffler H., Strömberg N. Gangliotetraosylceramide is a major glycolipid of epithelial cells of mouse small intestine. FEBS Lett. 1982 Mar 22;139(2):291–294. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80873-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto Y., Yamakawa T., Tanabe Y. Further studies on the red cell glycolipids of various breeds of dogs. A possible assumption about the origin of Japanese dogs. J Biochem. 1984 Dec;96(6):1777–1782. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. G., Perry M. B., McDonald I. J. Studies of the cellular and free lipopolysaccharides form Neisseria canis and N. subflava. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Feb;22(2):189–196. doi: 10.1139/m76-026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston K. H., Holmes K. K., Gotschlich E. C. The serological classification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. I. Isolation of the outer membrane complex responsible for serotypic specificity. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):741–758. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson K. A. Preparation of total nonacid glycolipids for overlay analysis of receptors for bacteria and viruses and for other studies. Methods Enzymol. 1987;138:212–220. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)38018-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson K. A., Strömberg N. Overlay and solid-phase analysis of glycolipid receptors for bacteria and viruses. Methods Enzymol. 1987;138:220–232. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)38019-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labigne-Roussel A. F., Lark D., Schoolnik G., Falkow S. Cloning and expression of an afimbrial adhesin (AFA-I) responsible for P blood group-independent, mannose-resistant hemagglutination from a pyelonephritic Escherichia coli strain. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):251–259. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.251-259.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg F. P., Lund B., Normark S. Genes of pyelonephritogenic E. coli required for digalactoside-specific agglutination of human cells. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1167–1173. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01946.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomes L. M., Uemura K., Childs R. A., Paulson J. C., Rogers G. N., Scudder P. R., Michalski J. C., Hounsell E. F., Taylor-Robinson D., Feizi T. Erythrocyte receptors for Mycoplasma pneumoniae are sialylated oligosaccharides of Ii antigen type. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):560–563. doi: 10.1038/307560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKibbin J. M., Spencer W. A., Smith E. L., Mansson J. E., Karlsson K. A., Samuelsson B. E., Li Y. T., Li S. C. Lewis blood group fucolipids and their isomers from human and canine intestine. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):755–760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moch T., Hoschützky H., Hacker J., Kröncke K. D., Jann K. Isolation and characterization of the alpha-sialyl-beta-2,3-galactosyl-specific adhesin from fimbriated Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3462–3466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momoi T., Ando S., Magai Y. High resolution preparative column chromatographic system for gangliosides using DEAE-Sephadex and a new porus silica, Iatrobeads. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 27;441(3):488–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkkinen J., Finne J., Achtman M., Väisänen V., Korhonen T. K. Escherichia coli strains binding neuraminyl alpha 2-3 galactosides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 16;111(2):456–461. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90328-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paruchuri D. K., Seifert H. S., Ajioka R. S., Karlsson K. A., So M. Identification and characterization of a Neisseria gonorrhoeae gene encoding a glycolipid-binding adhesin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):333–337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal E., Billyard E., So M., Storzbach S., Meyer T. F. Role of chromosomal rearrangement in N. gonorrhoeae pilus phase variation. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):293–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90143-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit H., Gaastra W., Kamerling J. P., Vliegenthart J. F., de Graaf F. K. Isolation and structural characterization of the equine erythrocyte receptor for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K99 fimbrial adhesin. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):578–584. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.578-584.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stromberg N., Deal C., Nyberg G., Normark S., So M., Karlsson K. A. Identification of carbohydrate structures that are possible receptors for Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4902–4906. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strömberg N., Ryd M., Lindberg A. A., Karlsson K. A. Studies on the binding of bacteria to glycolipids. Two species of Propionibacterium apparently recognize separate epitopes on lactose of lactosylceramide. FEBS Lett. 1988 May 9;232(1):193–198. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80415-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugasawara R. J., Cannon J. G., Black W. J., Nachamkin I., Sweet R. L., Brooks G. F. Inhibition of Neisseria gonorrhoeae attachment to HeLa cells with monoclonal antibody directed against a protein II. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):980–985. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.980-985.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Bergström S., Barrera O., Robbins K., Corwin D. Pilus- gonococcal variants. Evidence for multiple forms of piliation control. J Exp Med. 1985 Aug 1;162(2):729–744. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.2.729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Mayer L. W., Tam M. R. Antigenicity of Neisseria gonorrhoeae outer membrane protein(s) III detected by immunoprecipitation and Western blot transfer with a monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):668–672. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.668-672.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]