Abstract
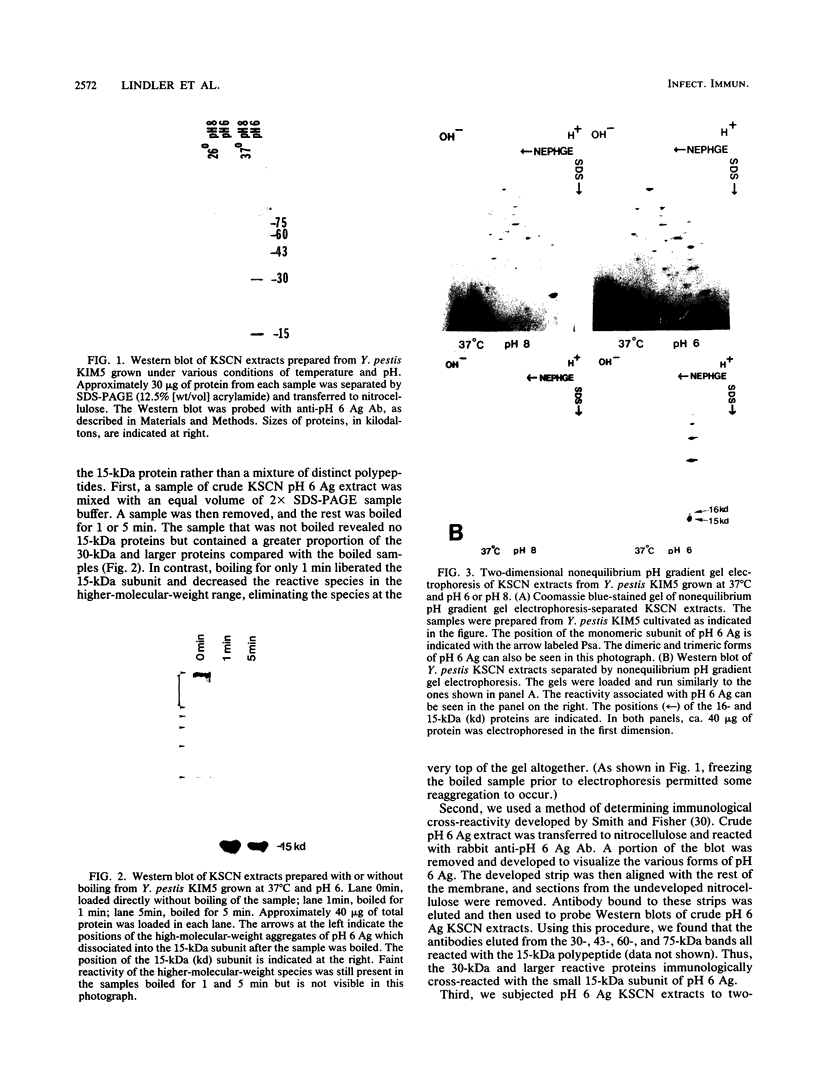
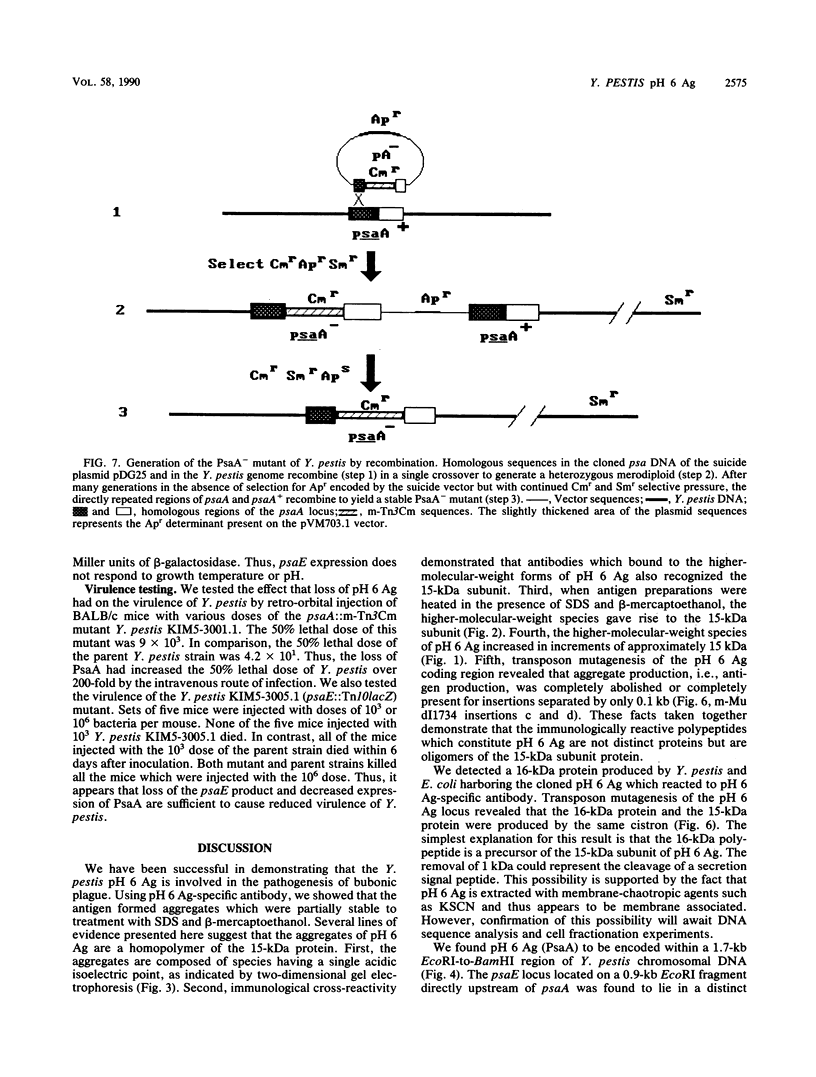
We studied a protein antigen, designated pH 6 Ag, that has the same regulation of expression as the previously described Yersinia pestis pH 6 Ag. Monospecific antiserum to this antigen recognized several proteins, ranging from 15 to over 75 kilodaltons (kDa), which were strongly expressed when Y. pestis was cultivated at 37 degrees C and pH 6 but were expressed weakly, if at all, at 37 degrees C and pH 8 and at 26 degrees C. The antigen appeared to be composed of aggregates of a 15-kDa subunit. Escherichia coli minicell analysis and Western blotting (immunoblotting) of minicell extracts containing the cloned pH 6 Ag locus revealed that a 1.7-kilobase-pair (kb) region of Y. pestis chromosomal DNA produced 16- and 15-kDa immunoreactive proteins. We used transposon mutagenesis of the pH 6 Ag-coding region to demonstrate that the 16- and 15-kDa polypeptides were produced by the same cistron. The pH 6 Ag structural gene, psaA, was located within a 0.5-kb region of DNA. A Tn10lacZ transposon insertion 1.2 kb upstream of the psaA locus but outside the psaA transcriptional unit caused decreased expression of pH 6 Ag in both E. coli and Y. pestis and defined the psaE locus necessary for maximum pH 6 Ag expression. This locus itself was not regulated by temperature or pH. However, psaA remained responsive to both of these environmental signals in a Y. pestis psaE mutant. Mutation of either psaE or psaA resulted in at least a 100-fold reduction in the intravenous 50% lethal dose of Y. pestis in mice. Accordingly, pH 6 Ag is involved in the pathogenesis of bubonic plague.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BICHOWSKY-SLOMNICKI L., BEN-EFRAIM S. BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITIES IN EXTRACTS OF PASTEURELLA PESTIS AND THEIR RELATION TO THE "PH 6 ANTIGEN". J Bacteriol. 1963 Jul;86:101–111. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.1.101-111.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Efraim S., Aronson M., Bichowsky-Slomnicki L. NEW ANTIGENIC COMPONENT OF PASTEURELLA PESTIS FORMED UNDER SPECIFIED CONDITIONS OF pH AND TEMPERATURE. J Bacteriol. 1961 May;81(5):704–714. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.5.704-714.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Backman K. Plasmids of Escherichia coli as cloning vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:245–267. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAVANAUGH D. C., RANDALL R. The role of multiplication of Pasteurella pestis in mononuclear phagocytes in the pathogenesis of flea-borne plague. J Immunol. 1959 Oct;83:348–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castilho B. A., Olfson P., Casadaban M. J. Plasmid insertion mutagenesis and lac gene fusion with mini-mu bacteriophage transposons. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):488–495. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.488-495.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charnetzky W. T., Shuford W. W. Survival and growth of Yersinia pestis within macrophages and an effect of the loss of the 47-megadalton plasmid on growth in macrophages. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):234–241. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.234-241.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. Escherichia coli plasmids packageable in vitro in lambda bacteriophage particles. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:309–326. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goguen J. D., Walker W. S., Hatch T. P., Yother J. Plasmid-determined cytotoxicity in Yersinia pestis and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):788–794. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.788-794.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Voorhis D. L., Falkow S. Identification of invasin: a protein that allows enteric bacteria to penetrate cultured mammalian cells. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):769–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90335-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy N., Beutin L., Achtman M., Skurray R., Rahmsdorf U., Herrlich P. Conjugation proteins encoded by the F sex factor. Nature. 1977 Dec 15;270(5638):580–585. doi: 10.1038/270580a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung K. Y., Straley S. C. The yopM gene of Yersinia pestis encodes a released protein having homology with the human platelet surface protein GPIb alpha. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4623–4632. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4623-4632.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. L., Erfle M., Wykes E. J. The pIC plasmid and phage vectors with versatile cloning sites for recombinant selection by insertional inactivation. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):481–485. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Mekalanos J. J. A novel suicide vector and its use in construction of insertion mutations: osmoregulation of outer membrane proteins and virulence determinants in Vibrio cholerae requires toxR. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2575–2583. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2575-2583.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack C., Straley S. C., Klempner M. S. Probing the phagolysosomal environment of human macrophages with a Ca2+-responsive operon fusion in Yersinia pestis. 1986 Aug 28-Sep 3Nature. 322(6082):834–836. doi: 10.1038/322834a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert H. S., Chen E. Y., So M., Heffron F. Shuttle mutagenesis: a method of transposon mutagenesis for Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):735–739. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. E., Fisher P. A. Identification, developmental regulation, and response to heat shock of two antigenically related forms of a major nuclear envelope protein in Drosophila embryos: application of an improved method for affinity purification of antibodies using polypeptides immobilized on nitrocellulose blots. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):20–28. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Bowmer W. S. Virulence genes regulated at the transcriptional level by Ca2+ in Yersinia pestis include structural genes for outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):445–454. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.445-454.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Cibull M. L. Differential clearance and host-pathogen interactions of YopE- and YopK- YopL- Yersinia pestis in BALB/c mice. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1200–1210. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1200-1210.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Harmon P. A. Growth in mouse peritoneal macrophages of Yersinia pestis lacking established virulence determinants. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):649–654. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.649-654.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Harmon P. A. Yersinia pestis grows within phagolysosomes in mouse peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):655–659. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.655-659.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Une T., Nakajima R., Brubaker R. R. Roles of V antigen in promoting virulence in Yersiniae. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1987;9:179–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way J. C., Davis M. A., Morisato D., Roberts D. E., Kleckner N. New Tn10 derivatives for transposon mutagenesis and for construction of lacZ operon fusions by transposition. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):369–379. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]